Skyscraper design is the art and science of designing tall buildings. Skyscrapers are buildings that are over 150 meters (492 feet) tall, and they are typically used for commercial purposes, such as offices, hotels, and apartments.
Skyscrapers are important because they allow us to build more buildings on a smaller amount of land. This is especially important in densely populated cities, where land is scarce. Skyscrapers also provide a number of benefits, such as:
- Improved views
- Increased natural light
- Reduced energy consumption
- Enhanced safety
The history of skyscraper design dates back to the 19th century, when the first skyscrapers were built in Chicago. Since then, skyscraper design has evolved dramatically, and today’s skyscrapers are marvels of engineering and architecture.
Some of the most famous skyscrapers in the world include the Empire State Building, the Burj Khalifa, and the Shanghai Tower. These buildings are not only architectural wonders, but they are also important landmarks in their respective cities.
1. Height
In the realm of skyscrapers, height is a defining characteristic that sets them apart from other architectural marvels. Reaching towards the sky, these towering structures push the boundaries of engineering and design, defying gravity’s unrelenting force.
- Structural Ingenuity: Skyscrapers require innovative structural systems to withstand immense gravitational forces. These systems, often composed of reinforced concrete, steel frameworks, or composite materials, ensure stability and resilience against wind, seismic activity, and other environmental challenges.
- Vertical Transportation: The great heights of skyscrapers necessitate efficient vertical transportation systems. Elevators, escalators, and skybridges seamlessly connect different levels, allowing for swift and convenient movement of occupants.
- Breathtaking Views: Height offers unparalleled panoramic views of the surrounding cityscape. Floor-to-ceiling windows and observation decks provide breathtaking vistas, transforming skyscrapers into veritable vantage points.
- Urban Icons: Skyscrapers have become iconic landmarks, shaping the skylines of major cities around the world. Their towering presence symbolizes economic prosperity, architectural prowess, and a city’s aspirations.
Thus, height in skyscraper design is not merely a quantitative measure but a testament to human ingenuity and the pursuit of architectural excellence. These soaring structures not only redefine our skylines but also serve as symbols of urban progress and innovation.
2. Structure
In the realm of skyscraper design, structure plays a paramount role in ensuring the stability and strength of these towering edifices. The skeletal frameworks that form the backbone of skyscrapers are meticulously engineered to withstand the immense forces of gravity, wind, and seismic activity.
These frameworks, typically constructed from reinforced concrete, structural steel, or composite materials, provide a rigid and resilient support system for the entire building. They distribute the weight of the skyscraper evenly, preventing catastrophic failures under extreme loads.
The design of the skeletal framework is crucial, as it determines the overall stability and integrity of the structure. Engineers employ advanced computer modeling and analysis techniques to optimize the framework’s load-bearing capacity and resistance to lateral forces.
The strength of the skeletal framework is also essential for ensuring the safety of occupants during earthquakes or other natural disasters. By providing a robust and flexible support system, the framework helps to minimize structural damage and protect human lives.
Real-life examples of innovative structural designs include the Burj Khalifa, which utilizes a reinforced concrete core and exterior buttresses for stability, and the Shanghai Tower, whose spiraling form and composite structure enhance its resistance to wind loads.
Understanding the connection between structure and skyscraper design is crucial for architects and engineers. It enables them to create safe, stable, and resilient buildings that can withstand the challenges of urban environments.
3. Facade
In skyscraper design, the facade plays a pivotal role in shaping the building’s aesthetics, functionality, and connection with the surrounding urban environment.
Glass and steel have emerged as the dominant materials for skyscraper facades due to their unique properties. Glass offers transparency, allowing natural light to penetrate deep into the building and providing occupants with panoramic views of the cityscape. Steel, known for its strength and durability, provides the necessary structural support for the facade and contributes to the overall stability of the skyscraper.
The design of the facade is crucial in optimizing energy efficiency. Advanced glazing technologies, such as low-emissivity glass and reflective coatings, help regulate heat gain and loss, reducing energy consumption and creating a more comfortable interior environment.
Real-life examples of innovative facade designs include the Burj Khalifa, whose exterior features a complex system of glass panels and aluminum cladding, and the Shanghai Tower, which utilizes a double-skin facade to enhance thermal insulation and reduce wind loads.
Understanding the connection between facade design and skyscraper design is essential for architects and engineers. It enables them to create visually stunning and energy-efficient buildings that harmonize with the urban landscape and provide occupants with a comfortable and inspiring work and living environment.
4. Sustainability
In the realm of skyscraper design, sustainability has emerged as a paramount consideration, driven by the need to reduce the environmental impact of these towering structures and promote a more sustainable built environment.
- Energy Efficiency: Skyscrapers consume a significant amount of energy, primarily for heating, cooling, and lighting. Sustainable designs incorporate energy-efficient technologies, such as double-skin facades, high-performance glazing, and automated building management systems, to minimize energy consumption and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Water Conservation: Water conservation is crucial in skyscraper design, especially in water
-scarce regions. Sustainable buildings implement rainwater harvesting systems, low-flow fixtures, and drought-tolerant landscaping to reduce water usage and promote water conservation. - Material Selection: The choice of building materials significantly impacts a skyscraper’s environmental footprint. Sustainable designs prioritize the use of eco-friendly materials, such as recycled steel, low-VOC paints, and sustainably sourced timber, to reduce the embodied carbon and promote sustainable construction practices.
- Waste Management: Skyscrapers generate a substantial amount of waste during construction and operation. Sustainable designs incorporate waste management strategies, such as waste sorting, recycling programs, and composting systems, to minimize landfill waste and promote a circular economy.
By integrating sustainable principles into skyscraper design, architects and engineers can create buildings that are not only visually stunning but also environmentally responsible, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient urban environment.
5. Function
The function of a skyscraper plays a crucial role in shaping its design. Skyscrapers can serve a variety of purposes, including offices, residential units, hotels, retail spaces, and mixed-use developments. Each function has unique requirements that influence the building’s design, from its height and floor plan to its facade and amenities.
For example, office skyscrapers prioritize efficient space utilization and natural light, often featuring large floor plates and floor-to-ceiling windows. Residential skyscrapers, on the other hand, require thoughtful unit layouts, communal spaces, and amenities such as fitness centers and rooftop terraces. Mixed-use skyscrapers combine different functions within a single structure, presenting design challenges in balancing the needs of each use and creating a cohesive and functional overall design.
Understanding the connection between function and skyscraper design is essential for architects and engineers. It enables them to create buildings that not only meet the specific needs of their occupants but also contribute positively to the urban environment. By considering the function of a skyscraper from the outset, designers can create tailored solutions that enhance the building’s functionality, aesthetics, and overall impact on the city.
6. Form
In the realm of skyscraper design, form transcends mere aesthetics; it becomes an artistic expression that shapes skylines and defines the character of cities. Skyscrapers are not simply functional structures but also canvases for architectural creativity, where architects push the boundaries of design to create iconic landmarks that captivate the imagination.
The form of a skyscraper is intricately connected to its overall design. It is influenced by factors such as the building’s function, structural requirements, and the architect’s artistic vision. For instance, the Burj Khalifa, the world’s tallest building, derives its distinctive form from its Y-shaped floor plan, which provides optimal structural stability and stunning views from its upper floors. Another striking example is the Shanghai Tower, whose spiraling form not only adds a dynamic element to the skyline but also enhances the building’s wind resistance.
Understanding the connection between form and skyscraper design is crucial for architects and engineers. It empowers them to create buildings that are not only structurally sound but also visually appealing and iconic. By carefully considering the form of a skyscraper, designers can create landmarks that become symbols of a city’s identity and cultural heritage. Moreover, innovative forms can lead to advancements in architectural engineering, pushing the limits of what is possible in high-rise construction.
7. Innovation
In the realm of skyscraper design, innovation plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of high-rise architecture. By pushing architectural boundaries and incorporating cutting-edge technologies, architects and engineers create skyscrapers that are not only visually stunning but also structurally sound, energy-efficient, and sustainable.
- Advanced Materials and Construction Techniques: Skyscrapers are constantly evolving thanks to advancements in materials and construction techniques. High-strength concrete, composite materials, and innovative facade systems allow architects to design taller and more complex structures that were previously impossible.
- Sustainable Design Strategies: Innovation is also driving the adoption of sustainable design strategies in skyscrapers. Green roofs, rainwater harvesting systems, and energy-efficient lighting are just a few examples of how technology is being used to reduce the environmental impact of these massive structures.
- Integrated Building Systems: Cutting-edge technologies are also being incorporated into the building systems of skyscrapers. Smart elevators, automated climate control systems, and advanced security measures enhance the comfort, convenience, and safety of occupants.
- Digital Design and Fabrication: Digital design and fabrication techniques are transforming the way skyscrapers are designed and built. Parametric modeling, 3D printing, and virtual reality are used to create complex geometries, optimize structural performance, and reduce construction time and costs.
The connection between innovation and skyscraper design is undeniable. By embracing new technologies and pushing architectural boundaries, architects and engineers are creating skyscrapers that are not only iconic landmarks but also testaments to human ingenuity and technological prowess.
8. Context
In the realm of skyscraper design, context plays a crucial role in shaping the building’s relationship with its surroundings and its impact on the urban environment. It involves understanding the existing architectural landscape, cultural heritage, and social fabric to create skyscrapers that are not only visually compatible but also contribute positively to the community.
Skyscrapers, by their very nature, have a significant visual presence that can either complement or clash with their surroundings. Contextual design ensures that skyscrapers harmonize with the existing urban fabric, respecting the scale, rhythm, and style of neighboring buildings. This can be achieved through the use of similar materials, colors, and architectural details, creating a cohesive and visually appealing streetscape. For instance, the Bank of America Tower in New York City draws inspiration from the Art Deco style prevalent in its surrounding area, blending seamlessly into the urban context.
Beyond visual compatibility, contextual design considers the social and cultural impact of skyscrapers. By incorporating elements that resonate with the local community, architects can create buildings that are not only landmarks but also symbols of civic pride. For exam
ple, the Shanghai Tower incorporates traditional Chinese architectural motifs, reflecting the city’s cultural heritage and strengthening its sense of identity.
Understanding the connection between context and skyscraper design is essential for architects and urban planners. It enables them to create buildings that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also socially and environmentally responsible. By considering the context from the outset, designers can create skyscrapers that enhance the urban environment, contribute to the city’s identity, and create a sense of place for its inhabitants.
Skyscraper Design FAQs
This section addresses frequently asked questions about skyscraper design, providing concise and informative answers to common concerns and misconceptions.
Question 1: What are the key considerations in designing a skyscraper?
Answer: Skyscraper design involves a complex interplay of factors, including height, structural stability, facade design, sustainability, function, form, innovation, and context. Each aspect must be carefully considered to ensure the building’s safety, functionality, and aesthetic appeal.
Question 2: How is sustainability incorporated into skyscraper design?
Answer: Sustainability plays a crucial role in modern skyscraper design. Architects and engineers employ energy-efficient technologies, water conservation measures, eco-friendly materials, and waste management strategies to minimize the building’s environmental impact and promote a sustainable built environment.
Question 3: What innovative technologies are used in skyscraper design?
Answer: Skyscraper design is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in materials, construction techniques, and digital technologies. These innovations include high-strength concrete, composite materials, smart building systems, and digital design and fabrication, enabling architects to push architectural boundaries and create taller, more efficient, and visually stunning structures.
Question 4: How does context influence skyscraper design?
Answer: Contextual design is essential in skyscraper architecture. Architects consider the surrounding urban fabric, cultural heritage, and social needs to create buildings that harmonize with their environment. This involves respecting the scale, style, and character of neighboring structures while also contributing positively to the community’s sense of place and identity.
Question 5: What are the main challenges in designing supertall skyscrapers?
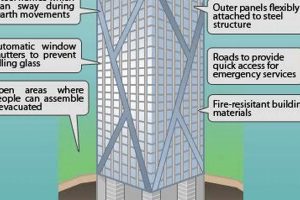
Answer: Supertall skyscrapers, exceeding 300 meters in height, present unique design challenges. Engineers must ensure structural stability against wind forces, optimize elevator systems for efficient vertical transportation, and address complex safety considerations, including fire protection and emergency evacuation.
Question 6: How do architects balance aesthetics with functionality in skyscraper design?
Answer: Balancing aesthetics and functionality is a delicate task in skyscraper design. Architects strive to create visually striking buildings that also meet functional requirements. This involves carefully considering the building’s form, facade design, and interior layout to achieve both architectural excellence and practical usability.
In summary, skyscraper design is a complex and multifaceted discipline that demands a holistic approach. By considering the interplay of various factors and embracing innovation and sustainability, architects and engineers can create skyscrapers that are not only awe-inspiring landmarks but also functional, sustainable, and Contextually responsive additions to the urban environment.
Transition to the next article section: The Future of Skyscraper Design
Skyscraper Design Tips
Creating awe-inspiring and functional skyscrapers requires careful consideration of various design aspects. Here are some essential tips for architects and engineers to achieve successful skyscraper design.
Tip 1: Prioritize Structural Stability and Safety
Skyscrapers must withstand various forces, including wind, earthquakes, and gravity. Employ robust structural systems, such as reinforced concrete or steel frameworks, to ensure stability and safety. Implement advanced engineering techniques to minimize sway and vibrations.
Tip 2: Optimize Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Incorporate sustainable design strategies to reduce environmental impact. Utilize energy-efficient materials, install smart building systems, and implement rainwater harvesting systems. Consider renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to minimize operating costs.
Tip 3: Enhance Vertical Transportation and Accessibility
Plan efficient vertical transportation systems, including elevators, escalators, and skybridges. Consider the capacity, speed, and accessibility requirements for occupants. Ensure seamless connectivity between different levels of the skyscraper.
Tip 4: Design a Visually Appealing and Contextually Responsive Facade
The facade plays a crucial role in the aesthetics and functionality of a skyscraper. Choose materials that complement the surrounding environment and enhance the building’s overall appearance. Consider incorporating green walls or vertical gardens to improve air quality and aesthetics.
Tip 5: Integrate Mixed-Use Functionality
Maximize space utilization and cater to diverse needs by incorporating mixed-use functionality. Combine residential, commercial, retail, and public spaces within a single skyscraper. This approach enhances vibrancy, promotes walkability, and creates a more sustainable urban environment.
Tip 6: Embrace Innovation and Cutting-Edge Technologies
Stay updated with the latest advancements in materials, construction techniques, and digital tools. Embrace innovative technologies to optimize structural performance, enhance energy efficiency, and improve building management. Explore the use of smart sensors, automated systems, and digital fabrication techniques.
Tip 7: Consider Cultural and Social Context
Understand the cultural and social context of the building’s location. Respect the existing urban fabric and incorporate elements that resonate with the local community. Integrate public spaces, art installations, or historical references to enhance the building’s social and cultural significance.
Tip 8: Seek Professional Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Input
Successful skyscraper design requires collaboration among architects, engineers, sustainability experts, and urban planners. Foster interdisciplinary communication to ensure a comprehensive and well-rounded design approach. Seek input from specialists in various fields to address technical, environmental, and social considerations.
By adhering to these tips, architects and engineers can create skyscrapers that are not only visually stunning but also structurally sound, sustainable, and responsive to the needs of both occupants and the urban environment.
Skyscraper Design
Skyscraper design has emerged as a complex and multifaceted discipline, pushing the boundaries of architecture, engineering, and sustainability. By carefully considering factors such as structural stability, energy efficiency, functionality, and aesthetics, architects and engineers create towering structures that redefine urban skylines and contribute to the vitality of cities.
The future of skyscraper design promises even more innovation and sustainable solutio
ns. As technologies continue to advance, we can expect to see skyscrapers that are taller, more energy-efficient, and more responsive to the needs of their occupants and the environment. These architectural marvels will continue to shape the way we live, work, and interact with our urban environments.