A skyscraper is a continuously habitable high-rise building having multiple floors and a height that is considerably greater than its width, generally containing amenities such as offices, hotels, and residential units. The term “skyscraper” is typically used for structures that are at least 150 meters (492 feet) tall, but there is no universally accepted definition.
Skyscrapers are often constructed in densely populated urban areas where land is scarce and expensive. They are designed to accommodate a large number of people and businesses in a relatively small footprint, making them a more efficient use of space than sprawling single-story buildings. Additionally, skyscrapers can be iconic landmarks and symbols of a city’s power and prestige.
There are many famous skyscrapers around the world, including the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the Shanghai Tower in China, and the Empire State Building in New York City. These buildings are marvels of engineering and architectural design, and they continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in construction.
1. Height
Height is a defining characteristic of a skyscraper, often exceeding 150 meters. This vertical dimension plays a crucial role in several aspects:
- Structural stability: Taller buildings require robust structural systems to withstand wind forces and seismic activity. Engineers employ advanced techniques to ensure the stability of these towering structures.
- Space optimization: Height allows for efficient land use in densely populated urban areas. Skyscrapers can accommodate a large number of people and functions within a relatively small footprint.
- Iconic landmarks: The height of skyscrapers often makes them iconic landmarks, symbolizing a city’s economic power and architectural prowess. The Empire State Building, for example, has been an iconic symbol of New York City since its completion in 1931.
- Engineering advancements: The construction of skyscrapers pushes the boundaries of engineering. Architects and engineers must consider factors such as wind resistance, seismic activity, and material strength to ensure the safety and integrity of these structures.
In conclusion, the height of a skyscraper is not merely a numerical value but a critical aspect that influences its design, engineering, and impact on the urban landscape. Skyscrapers continue to redefine skylines and challenge the limits of architectural innovation, shaping the way we live and work in vertical spaces.
2. Structure
The structure of a skyscraper is a crucial aspect that determines its stability, functionality, and overall performance. Skyscrapers are marvels of engineering, and their structures are designed to withstand various forces and ensure the safety and comfort of their occupants.
- Foundation: The foundation of a skyscraper is its base, which transfers the weight of the building to the ground. Skyscrapers often have deep foundations that extend below the surface, providing a solid and stable base for the entire structure.
- Core: The core of a skyscraper is its central load-bearing structure, which provides stability and support to the entire building. The core typically consists of reinforced concrete or steel and houses elevators, stairwells, and other essential services.
- Exterior walls: The exterior walls of a skyscraper play a crucial role in protecting the building from the elements and providing thermal insulation. They are typically made of reinforced concrete, steel, or glass, and may incorporate various architectural features to enhance the building’s aesthetics.
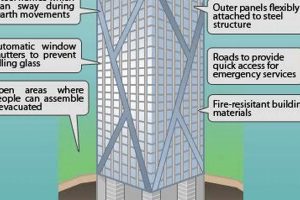
- Wind bracing: Skyscrapers are subjected to strong wind forces, especially at higher altitudes. Wind bracing systems are employed to strengthen the structure and resist lateral forces. These systems may include diagonal bracing, shear walls, or outrigger systems.
The structure of a skyscraper is not merely a collection of components but a carefully engineered system that works together to ensure the safety and functionality of the building. Skyscrapers push the boundaries of engineering and architectural design, and their structures are a testament to human ingenuity and innovation.
3. Design
Design plays a pivotal role in the conception and realization of skyscrapers, shaping their form, function, and impact on the urban landscape.
- Aesthetics and Form: Skyscraper design often incorporates striking and innovative architectural styles, contributing to the visual character of a city’s skyline. Architects explore various shapes, facades, and materials to create visually appealing and iconic structures.
- Functionality and Space Planning: Design optimizes space utilization within skyscrapers, accommodating a multitude of functions such as offices, residential units, retail spaces, and public amenities. Efficient floor plans and space allocation ensure the smooth flow of people and activities.
- Sustainability and Energy Efficiency: Sustainable design principles are increasingly incorporated into skyscrapers, reducing their environmental impact. Architects employ strategies such as natural lighting, energy-efficient systems, and green roofs to minimize energy consumption and promote environmental responsibility.
- Structural Considerations: Design must consider the structural integrity of skyscrapers, ensuring they can withstand various forces such as wind, seismic activity, and gravity. Engineers and architects collaborate to create structures that are both visually striking and structurally sound.
In conclusion, design is an integral aspect of skyscrapers, influencing their aesthetics, functionality, sustainability, and structural integrity. Through innovative design approaches, skyscrapers continue to push the boundaries of architectural expression and engineering ingenuity, shaping the skylines and urban environments of the future.
4. Engineering
Engineering plays a vital role in the design, construction, and maintenance of skyscrapers, these towering structures that shape skylines and redefine urban landscapes.
- Structural Design: Engineers employ advanced structural engineering techniques to ensure the stability and integrity of skyscrapers, considering factors such as wind forces, seismic activity, and gravity. They design load-bearing systems, foundations, and exterior walls that can withstand these forces and m
aintain the structural integrity of the building. - Materials and Innovation: Engineering innovation is crucial in the development of new materials and construction methods for skyscrapers. Engineers explore high-strength materials like reinforced concrete, steel alloys, and composite materials to achieve greater heights and structural efficiency. These advancements enable the construction of taller and more complex skyscrapers.
- Wind Engineering: Skyscrapers are subjected to strong wind forces, especially at higher altitudes. Engineers employ wind engineering principles to design aerodynamic shapes, incorporate wind bracing systems, and conduct wind tunnel tests to mitigate wind-induced vibrations and ensure the safety of the structure.
- Sustainability and Energy Efficiency: Engineering contributes to sustainable skyscraper design by incorporating energy-efficient systems, optimizing natural lighting, and utilizing renewable energy sources. Engineers work to reduce the environmental impact of skyscrapers and promote sustainable urban development.
In conclusion, engineering is a fundamental discipline that drives the design and construction of skyscrapers. Through innovative engineering solutions, engineers enable the creation of these architectural marvels that push the boundaries of human ingenuity and redefine the urban skyline.
5. Urbanization
Urbanization, the process of population concentration in urban areas, has a profound connection with the development and proliferation of skyscrapers. Skyscrapers, as towering structures designed to accommodate high-density living and working, are a direct response to the challenges and opportunities presented by urbanization.
One of the primary drivers of skyscraper construction is the need for space optimization in densely populated urban areas. As cities grow and land becomes scarce, building upwards becomes a viable solution to accommodate the increasing population and economic activities. Skyscrapers allow for the vertical expansion of urban environments, maximizing land use efficiency and creating more space for essential infrastructure, green spaces, and other amenities.
In addition to space optimization, skyscrapers contribute to the economic vitality of urban centers. They house corporate headquarters, financial institutions, and commercial enterprises, creating employment opportunities and attracting businesses to urban areas. The concentration of these activities in skyscrapers fosters innovation, collaboration, and economic growth within cities.
Furthermore, skyscrapers serve as iconic landmarks and symbols of urban power and prestige. They reflect the architectural prowess and economic strength of cities, shaping their skylines and contributing to their global recognition. From the Empire State Building in New York City to the Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur, skyscrapers have become synonymous with urban identity and ambition.
However, the relationship between urbanization and skyscrapers is not without its challenges. The construction and maintenance of skyscrapers require significant resources and can strain urban infrastructure. Additionally, the concentration of population and activities in high-rise buildings can lead to issues such as traffic congestion, pollution, and strain on public services.
Despite these challenges, skyscrapers continue to play a vital role in urban development, providing solutions to the challenges of urbanization while also contributing to the economic, social, and cultural fabric of cities. As urbanization continues to shape the world’s population distribution, skyscrapers will undoubtedly remain a prominent feature of urban landscapes.
6. Landmark
Skyscrapers, as towering structures that reshape skylines and dominate urban landscapes, often become iconic landmarks, symbolizing the economic power, architectural prowess, and cultural identity of cities.
One of the defining characteristics of a landmark skyscraper is its unique and striking design. Architects push the boundaries of architectural expression to create visually captivating structures that stand out from their surroundings. The Empire State Building in New York City, with its Art Deco style and distinctive silhouette, is a prime example of a skyscraper that has become an iconic landmark.
Beyond their aesthetic appeal, landmark skyscrapers often have historical or cultural significance. They may be associated with major events or embody the spirit of a particular era. The Chrysler Building in New York City, with its intricate Art Deco ornamentation and its role in the race to build the world’s tallest building, is a notable example of a skyscraper that has become a cultural landmark.
The status of a skyscraper as a landmark can have a profound impact on its preservation and appreciation. Landmark designation often provides legal protection, ensuring that these iconic structures are preserved for future generations. The Willis Tower in Chicago, formerly known as the Sears Tower, is an example of a skyscraper that has been recognized as a landmark for its architectural and historical significance.
In conclusion, the connection between skyscrapers and landmarks is a testament to the enduring power of architecture to shape our cities and leave a lasting impression on our collective consciousness. Landmark skyscrapers serve as symbols of urban identity, cultural heritage, and architectural innovation, enriching our urban environments and inspiring generations to come.
7. Symbol
Skyscrapers, as towering structures that dominate skylines and shape urban landscapes, often transcend their functional purpose and become potent symbols, embodying the economic power, cultural identity, and architectural aspirations of cities.
The symbolic significance of skyscrapers stems from their sheer height and grandeur. They are physical manifestations of human ambition and ingenuity, pushing the boundaries of architectural possibility and reshaping the urban environment. The Empire State Building in New York City, standing at 102 stories tall, is a prime example of a skyscraper that has become a symbol of American economic dominance and architectural prowess.
Beyond their physical presence, skyscrapers also carry cultural and historical meanings. The Chrysler Building in New York City, with its Art Deco ornamentation and its role in the race to build the world’s tallest building, has become a symbol of the Roaring Twenties and the architectural exuberance of that era. Similarly, the Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur, with their unique design inspired by Islamic architecture, have become symbols of Malaysia’s economic and cultural identity.
The symbolic power of skyscrapers is not limited to individual buildings. Skylines themselves have become symbols of cities and nations. The Manhattan skyline, with its dense concentration of skyscrapers, is instantly recognizable and synonymous with the economic and cultural power of New York City. The Shanghai skyline, with its futuristic skyscrapers, has become a symbol of China’s rapid economic growth and its ambitions to become a global superpower.
In conclusion, skyscrapers are not merely functional structure
s but also powerful symbols that reflect the aspirations, values, and identities of cities and nations. Their symbolic significance extends beyond their physical presence, shaping our perceptions of urban environments and contributing to the cultural heritage of humanity.
Skyscraper FAQs
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions surrounding skyscrapers, providing concise and informative answers to enhance your understanding of these architectural marvels.
Question 1: What is the defining characteristic of a skyscraper?
Skyscrapers are continuously habitable high-rise buildings with multiple floors, typically exceeding 150 meters (492 feet) in height, primarily designed for residential, commercial, or mixed-use purposes.
Question 2: Why are skyscrapers constructed primarily in urban areas?
Skyscrapers are predominantly built in densely populated urban environments where land is scarce and expensive. They offer an efficient solution to accommodate a large number of people and businesses within a relatively small footprint, maximizing space utilization.
Question 3: How do skyscrapers withstand strong winds and seismic activity?
Skyscrapers employ advanced engineering techniques and structural systems to ensure stability and resilience against lateral forces. These include wind bracing systems, shear walls, and outrigger systems to resist wind loads, and robust foundations and earthquake-resistant designs to withstand seismic activity.
Question 4: Are skyscrapers environmentally sustainable?
Modern skyscrapers increasingly incorporate sustainable design principles to minimize their environmental impact. Strategies such as energy-efficient systems, natural lighting, and rainwater harvesting are employed to reduce energy consumption and promote resource conservation.
Question 5: How do skyscrapers contribute to urban development?
Skyscrapers play a significant role in urban development by optimizing land use, fostering economic growth, and enhancing urban aesthetics. They create vertical communities that house businesses, residents, and amenities, contributing to the vitality and dynamism of cities.
Question 6: What is the significance of skyscrapers as cultural landmarks?
Skyscrapers often transcend their functional purpose and become iconic landmarks, symbolizing the economic power, cultural identity, and architectural prowess of cities. Their unique designs and historical associations make them beloved symbols recognized worldwide.
These FAQs provide a deeper understanding of skyscrapers, their construction, and their impact on urban environments. As architectural marvels that continue to shape skylines and redefine the way we live and work, skyscrapers remain a testament to human ingenuity and the pursuit of vertical frontiers.
Transitioning to the next section, we will delve into the engineering marvels that make skyscrapers possible, exploring the innovative techniques and materials that enable these towering structures to withstand various forces and achieve extraordinary heights.
Skyscraper Design and Engineering Tips
Skyscrapers, as architectural marvels that redefine skylines and push the boundaries of engineering, require meticulous planning and innovative design approaches. Here are some key tips to consider for successful skyscraper design and engineering:
Tip 1: Prioritize Structural Integrity
Ensure structural stability by employing robust materials, advanced engineering techniques, and wind-resistant designs. Consider factors such as wind loads, seismic activity, and gravity to maintain the building’s integrity.
Tip 2: Optimize Space Utilization
Maximize space efficiency through innovative floor plans and space allocation strategies. Utilize vertical space effectively to accommodate various functions such as offices, residential units, and public amenities.
Tip 3: Incorporate Sustainable Features
Implement sustainable design principles to reduce environmental impact. Employ energy-efficient systems, natural lighting, and rainwater harvesting techniques to minimize energy consumption and promote resource conservation.
Tip 4: Consider Wind Engineering
Address wind forces effectively through aerodynamic designs, wind bracing systems, and wind tunnel testing. Mitigate wind-induced vibrations and ensure the building’s stability under strong winds.
Tip 5: Utilize Advanced Materials
Explore innovative materials such as high-strength concrete, steel alloys, and composite materials to achieve greater heights and structural efficiency. These materials enhance load-bearing capacity and allow for more slender and visually striking designs.
Tip 6: Ensure Fire Safety
Implement comprehensive fire safety measures, including fire-resistant materials, compartmentalization, and advanced fire detection and suppression systems. Prioritize occupant safety and minimize potential fire hazards.
Tip 7: Plan for Maintenance and Accessibility
Consider long-term maintenance and accessibility during the design phase. Incorporate features such as easily accessible mechanical systems and efficient cleaning mechanisms to ensure the building’s functionality and safety over its lifespan.
Tip 8: Collaborate with Experts
Foster effective collaboration between architects, engineers, and other specialists throughout the design and construction process. Share knowledge, expertise, and innovative ideas to achieve optimal outcomes.
By adhering to these tips, architects and engineers can design and construct skyscrapers that are not only visually stunning but also structurally sound, sustainable, and resilient. These architectural marvels will continue to shape skylines, redefine urban landscapes, and serve as testaments to human ingenuity and engineering prowess.
Skyscraper
Skyscrapers, as architectural wonders that redefine skylines and push the boundaries of engineering, stand as testaments to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of vertical frontiers. Throughout this exploration, we have delved into the various aspects of skyscrapers, from their towering heights and structural marvels to their impact on urbanization and their symbolic significance.
Skyscrapers are not merely functional structures but also powerful symbols of economic power, cultural identity, and architectural prowess. They shape the character of cities, becoming iconic landmarks that are instantly recognizable around the world. Their designs often incorporate innovative and sustainable features, reflecting our commitment to progress and environmental responsibility.
As we continue to push the limits of architectural possibility, skyscrapers will undoubtedly continue to evolve and amaze. They will serve as reminders of our capacity for innovation and our . Let us embrace these architectural marvels and continue to strive for new heights, both literally and figuratively.