A skyscraper is a tall building, typically having more than 40 floors. Skyscrapers are often used for commercial or residential purposes, and they can be found in cities around the world.
The first skyscraper was built in Chicago in 1885. It was a 10-story building called the Home Insurance Building. Since then, skyscrapers have become increasingly taller and more complex. Today, the tallest skyscraper in the world is the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, which has 163 floors.
Skyscrapers offer a number of advantages over other types of buildings. They can accommodate more people and businesses in a smaller space, and they can be more energy-efficient. Skyscrapers can also be iconic landmarks that define a city’s skyline.
However, skyscrapers also have some disadvantages. They can be expensive to build and maintain, and they can be difficult to evacuate in the event of a fire or other emergency. Additionally, skyscrapers can cast long shadows and block sunlight from reaching the street below.
Despite these disadvantages, skyscrapers continue to be built all over the world. They are a symbol of progress and prosperity, and they can help to create more livable and sustainable cities.
1. Height
The height of a skyscraper, measured in stories or meters, is directly related to the number of floors it has. The taller the building, the more floors it will have to accommodate its height. This is because each floor adds to the overall height of the building. For example, a 100-story skyscraper will be much taller than a 50-story skyscraper, simply because it has more floors.
The height of a skyscraper is an important factor to consider when determining its overall size and grandeur. It can also impact the building’s design, construction, and maintenance costs.Taller skyscrapers require more complex engineering and construction techniques to ensure their stability and safety. Additionally, the height of a skyscraper can affect the views from its windows and the amount of natural light that enters the building.
Understanding the connection between the height of a skyscraper and the number of floors it has is important for architects, engineers, and construction workers. It is also important for anyone who is interested in skyscrapers and their design.
2. Floors
To delve into the connection between the number of floors in a skyscraper and the overall concept of “how many floors is a skyscraper”, we can explore several facets:
- Vertical Space Utilization: Skyscrapers, with their numerous floors, offer a solution to accommodate a large number of people and functions within a limited footprint, maximizing vertical space utilization in densely populated urban areas.
- Functional Diversity: The multiple floors in skyscrapers allow for a diverse range of uses within a single structure, including offices, residential units, retail spaces, and recreational facilities, creating a mixed-use environment that caters to various needs.
- Engineering Considerations: The number of floors in a skyscraper directly influences its structural design and engineering requirements. Taller buildings with more floors necessitate robust foundations, reinforced frameworks, and efficient elevator systems to ensure stability and safety.
- Height Regulations and Zoning Laws: Building codes and zoning regulations often impose height restrictions on skyscrapers, influencing the maximum number of floors that can be constructed in a particular area. These regulations aim to maintain urban aesthetics, prevent overcrowding, and ensure the safety of surrounding structures.
In summary, the number of floors in a skyscraper is a crucial factor that impacts its overall height, functionality, structural design, and compliance with urban planning regulations. Understanding this connection is essential to grasping the concept of “how many floors is a skyscraper” and appreciating the complexities involved in constructing and managing these towering structures.
3. Purpose
The purpose of a skyscraper, whether commercial, residential, or mixed-use, plays a significant role in determining the number of floors it has. Different purposes necessitate different floor plans, amenities, and structural designs, all of which influence the overall height and number of floors in a skyscraper.
- Commercial Skyscrapers:
Designed primarily for business and office use, commercial skyscrapers tend to have more floors than residential buildings. This is because they require large, open floor plans to accommodate numerous workstations, meeting rooms, and other office-related facilities. For example, the One World Trade Center in New York City has 110 floors, primarily used for office space.
- Residential Skyscrapers:
Skyscrapers designed for residential purposes typically have fewer floors than commercial buildings. This is because residential units require more space per floor for living areas, bedrooms, and amenities such as kitchens and bathrooms. For instance, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the tallest residential building in the world, has 163 floors, with each floor housing multiple residential units.
- Mixed-Use Skyscrapers:
These skyscrapers combine commercial and residential uses within a single structure. They often have a mix of office floors, residential units, and other amenities such as retail stores, restaurants, or fitness centers. Mixed-use skyscrapers offer a convenient and efficient way to live, work, and access various amenities in one location. For example, the Shanghai Tower in China has 128 floors, including offices, apartments, a hotel, and a shopping mall.
- Additional Considerations:
Besides the primary purpose, other factors such as building codes, zoning regulations, and land availability can also influence the number of floors in a skyscraper. For instance, height restrictions in certain areas may limit the number of floors that can be built, while the availability of land can determine the overall footprint and height of the building.
In summary, the purpose of a skyscraper is closely tied to the number of floors it has. Commercial skyscrapers tend to have more floors for office spaces, while residential buildings have fewer floors for living units. Mixed-use skyscrapers combine both commercial and residential uses, offering a diverse range of functions within a single structure. Understanding the purpose of a skyscraper is crucial for determining its overall height and number of floors.
4. Materials
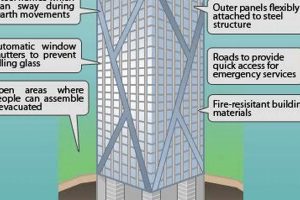
The materials used in skyscraper construction play a crucial role in determining the maximum number of floors a skyscraper can have. Steel, concrete, and glass are the most common materials used in skyscraper construction due to their strength, durability, and ability to withstand the immense weight and forces exerted by high-rise buildings.
Steel is used for the structural framework of skyscrapers because it is strong and lightweight. Concrete is used for the core and floors of skyscrapers because it is strong and fire-resistant. Glass is used for the exterior walls of skyscrapers because it is lightweight and allows natural light to enter the building. The combination of these materials allows skyscrapers to be built to great heights while maintaining structural integrity and safety.
For example, the Burj Khalifa, the tallest building in the world, uses a combination of steel, concrete, and glass in its construction. The building has 163 floors and a height of 828 meters. The steel frame of the Burj Khalifa is made of high-strength steel, which is able to withstand the immense weight of the building. The concrete core of the building provides additional strength and stability. The exterior walls of the building are made of glass, which allows natural light to enter the building and reduces the overall weight of the structure.
Understanding the connection between the materials used in skyscraper construction and the number of floors a skyscraper can have is important for architects, engineers, and construction workers. This understanding allows them to design and construct skyscrapers that are safe, sustainable, and able to withstand the forces of nature.
5. Engineering
Understanding the connection between engineering, specifically the advanced techniques used to withstand wind, seismic forces, and gravity, and the concept of “how many floors is a skyscraper” is crucial for several reasons. Engineering plays a pivotal role in determining the maximum number of floors a skyscraper can have and ensures the safety and stability of these towering structures.
- Structural Design: Engineering advancements have made it possible to design skyscrapers that can withstand immense weight, wind forces, and seismic activity. The use of high-strength materials, innovative structural systems, and advanced computer modeling allows engineers to create buildings that can reach unprecedented heights.
- Wind Resistance: Skyscrapers are subjected to strong wind forces, especially at higher altitudes. Engineers employ various techniques to mitigate these forces, such as utilizing aerodynamic shapes, installing wind baffles, and incorporating tuned mass dampers to reduce sway and vibrations.
- Seismic Stability: In earthquake-prone areas, skyscrapers require special engineering considerations to withstand seismic forces. Engineers use base isolation systems, reinforced concrete cores, and energy-absorbing materials to protect the building from damage and collapse.
- Gravity Loads: The immense weight of a skyscraper exerts significant downward force, which must be effectively distributed and transferred to the ground. Engineers employ robust foundation systems, such as deep pile foundations or spread footings, to ensure the building’s stability and prevent sinking.
In summary, the advanced engineering techniques used to withstand wind, seismic forces, and gravity are fundamental to determining the number of floors a skyscraper can have. By pushing the boundaries of engineering, architects and engineers can create taller and more resilient skyscrapers that redefine the skylines of cities worldwide.
6. Sustainability
The integration of sustainable features into modern skyscrapers has a direct connection to the concept of “how many floors is a skyscraper.” As buildings rise higher, their environmental impact becomes increasingly significant, making sustainability a critical factor in determining the number of floors a skyscraper can have.
- Energy Efficiency:
Skyscrapers consume a substantial amount of energy for lighting, heating, and cooling. Sustainable skyscrapers employ energy-efficient technologies such as LED lighting, double-glazed windows, and efficient HVAC systems to reduce energy consumption. These measures not only lower operating costs but also contribute to a reduced carbon footprint, allowing for more floors to be added without exceeding environmental limits.
- Water Conservation:
Skyscrapers require a significant amount of water for various purposes. Sustainable skyscrapers implement water-saving fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and greywater reuse systems to minimize water consumption. By conserving water, these buildings can reduce their environmental impact and increase the number of floors they can have without straining local water resources.
- Waste Reduction:
Skyscrapers generate a large amount of waste during construction and operation. Sustainable skyscrapers incorporate waste management systems such as recycling programs, composting facilities, and waste-to-energy conversion technologies to reduce their environmental impact. Minimizing waste allows for more floors to be added without overwhelming local waste management systems.
- Material Selection:
The materials used in skyscraper construction can have a significant environmental impact. Sustainable skyscrapers prioritize the use of recycled and sustainable materials, such as low-carbon concrete, recycled steel, and bamboo. By selecting sustainable materials, these buildings reduce their embodied carbon and allow for more floors to be added without compromising environmental integrity.
In conclusion, the integration of sustainable features into modern skyscrapers has a direct impact on the concept of “how many floors is a skyscraper.” By reducing their environmental impact through energy efficiency, water conservation, waste reduction, and sustainable material selection, skyscrapers can increase their height and number of floors while minimizing their ecological footprint.
7. Urban Impact
Skyscrapers, with their towering heights and iconic designs, have a profound impact on the urban environment. Their presence transforms cityscapes, creating landmarks that define skylines and influence urban planning decisions. Understanding the connection between this urban impact and the concept of “how many floors is a skyscraper” provides valuable insights into the relationship between architecture, urban design, and the built environment.
- Vertical Expansion and Land Use: Skyscrapers allow cities to expand vertically, maximizing land use and accommodating growing populations within limited horizontal space. By increasing the number of floors, skyscrapers reduce urban sprawl and preserve valuable land resources.
- Landmark Creation and City Identity: Ico
nic skyscrapers become landmarks that define a city’s skyline and contribute to its unique identity. The height and design of these buildings create a visual impact that shapes the city’s image and attracts both residents and visitors. - Urban Planning and Zoning Regulations: The presence of skyscrapers influences urban planning and zoning regulations. Height restrictions, setbacks, and other regulations aim to maintain urban aesthetics, ensure structural safety, and manage the impact of skyscrapers on surrounding areas.
- Transportation and Infrastructure: The construction of skyscrapers requires careful consideration of transportation and infrastructure needs. Increased building height often necessitates expanded public transit, road networks, and utility services to support the influx of people and businesses.
In conclusion, the urban impact of skyscrapers is closely intertwined with the concept of “how many floors is a skyscraper.” The number of floors in a skyscraper directly affects its height, visibility, and impact on the surrounding environment. By understanding this connection, architects, urban planners, and policymakers can create cities that are not only visually striking but also sustainable and livable.
FAQs about “How Many Floors Is a Skyscraper”
This section addresses frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to the concept of “how many floors is a skyscraper.” It provides concise and informative answers to common concerns and misconceptions, offering a deeper understanding of the topic.
Question 1: What is the minimum number of floors for a building to be considered a skyscraper?
There is no universally accepted definition, but buildings are generally considered skyscrapers when they exceed 40 floors or 150 meters (490 feet) in height. This threshold may vary depending on local regulations and architectural norms.
Question 2: How many floors can a skyscraper have?
The number of floors in a skyscraper is primarily determined by engineering capabilities, building codes, and economic factors. Currently, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai holds the record as the tallest building in the world, with 163 floors.
Question 3: What are the tallest skyscrapers in the world?
As of 2023, the top five tallest skyscrapers in the world are the Burj Khalifa (Dubai, 163 floors), Shanghai Tower (Shanghai, 128 floors), Makkah Royal Clock Tower (Mecca, 120 floors), Ping An Finance Centre (Shenzhen, 116 floors), and Lotte World Tower (Seoul, 123 floors).
Question 4: What are the different types of skyscrapers?
Skyscrapers can be classified based on their primary function, such as commercial skyscrapers (primarily for office use), residential skyscrapers (primarily for living spaces), and mixed-use skyscrapers (combining commercial, residential, and other uses).
Question 5: What factors determine the number of floors in a skyscraper?
Several factors influence the number of floors in a skyscraper, including structural engineering capabilities, building codes, land availability, and economic considerations such as construction costs and potential revenue.
Question 6: How do skyscrapers impact urban environments?
Skyscrapers can have significant impacts on urban environments, including altering skylines, influencing transportation and infrastructure needs, and affecting wind patterns and sunlight distribution at street level.
These FAQs provide a comprehensive overview of common questions related to “how many floors is a skyscraper.” Understanding these aspects deepens our knowledge of skyscrapers and their role in modern architecture and urban development.
Transition to the next article section: Exploring the engineering marvels of skyscrapers and their impact on the built environment
Tips Related to “How Many Floors Is a Skyscraper”
Understanding the concept of “how many floors is a skyscraper” involves considering various aspects of skyscraper design, construction, and impact. Here are a few tips to enhance your knowledge and understanding:
Tip 1: Defining Skyscrapers by Floors
While there is no universal definition, buildings with over 40 floors or exceeding 150 meters (490 feet) in height are generally considered skyscrapers. This threshold may vary based on local regulations and architectural norms.
Tip 2: Engineering Considerations
The number of floors in a skyscraper is heavily influenced by engineering capabilities. Factors like structural design, wind resistance, seismic stability, and gravity loads play a crucial role in determining the maximum height and number of floors a skyscraper can have.
Tip 3: Purpose and Function
The purpose of a skyscraper, whether commercial, residential, or mixed-use, affects the number of floors. Commercial skyscrapers tend to have more floors for office spaces, while residential buildings have fewer floors for living units.
Tip 4: Urban Impact
Skyscrapers have a significant impact on urban environments. They can alter skylines, influence transportation and infrastructure needs, and affect wind patterns and sunlight distribution at street level.
Tip 5: Sustainability Features
Modern skyscrapers incorporate sustainable features to reduce their environmental impact. Energy efficiency, water conservation, waste reduction, and sustainable material selection contribute to increasing the number of floors while minimizing the ecological footprint.
Tip 6: Historical Evolution
The concept of skyscrapers has evolved over time. The first skyscrapers were built in the late 19th century, and their height and design have continued to push architectural boundaries, leading to the iconic structures we see today.
Tip 7: Cultural Significance
Skyscrapers often hold cultural significance and become landmarks that define a city’s identity. Their unique designs and heights can symbolize economic power, technological advancements, and architectural prowess.
Tip 8: Future Trends
As technology and architectural innovations advance, the future of skyscrapers may involve even taller structures, sustainable designs, and integrated smart building systems.
These tips provide valuable insights into the multifaceted concept of “how many floors is a skyscraper.” By considering these aspects, you can gain a deeper understanding of the engineering, design, and impact of these towering structures that shape our urban landscapes.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: Summarizing the key points and highlighting the significance of understanding skyscraper design and impact.
Conclusion
Throughout this exploration of “how many floors is a skyscraper,” we have delved into the multifaceted aspects of these towering structures. From their engineering marvels to their urban impact and sustainable features, skyscrapers represent architectural ingenuity and human ambition.
Understanding the concept of “how many floors is a skyscraper” goes beyond merely counting stories. It encompasses an appreciation for the engineering feats, design considerations, and environmental implications of these vertical cities. Skyscrapers are not just symbols of economic power or technological advancements; they are testaments to human creativity and our ability to shape the built environment.
As we continue to push the boundaries of architectural design, skyscrapers will undoubtedly continue to evolve. The future may hold even taller structures, sustainable innovations, and integrated smart building systems that enhance our urban li
ving experiences.
Whether admiring the iconic skylines they create or contemplating their impact on our cities, understanding “how many floors is a skyscraper” provides a deeper appreciation for these architectural wonders. It is a reminder that the built environment is not merely a backdrop to our lives but an active participant in shaping our societies and inspiring future generations.