A skyscraper is a tall, multi-story building. Skyscrapers are typically used for commercial purposes, such as offices, retail stores, and hotels. The height of a skyscraper is measured by the number of floors it has. The average skyscraper has between 50 and 100 floors, but some skyscrapers can have as many as 150 floors or more. The tallest skyscraper in the world is the Burj Khalifa, which has 163 floors.
Skyscrapers are important because they allow people to live and work in close proximity to each other. This can help to reduce traffic congestion and pollution. Skyscrapers can also be used to create landmarks and to symbolize the economic power of a city or country.
The first skyscrapers were built in the late 19th century. The Home Insurance Building in Chicago, which was completed in 1885, is considered to be the first skyscraper. Since then, skyscrapers have been built all over the world. Today, skyscrapers are a common sight in major cities.
1. Connection to "How many floors does a skyscraper have"
The height of a skyscraper is a crucial aspect that directly correlates to the number of floors it has. Each additional floor adds to the building’s vertical presence, significantly influencing its design and functionality.
- Structural Considerations: The number of floors impacts the structural integrity of a skyscraper. Taller buildings require reinforced support systems, thicker columns, and more advanced engineering techniques to withstand wind loads and seismic activity.
- Space Utilization: The number of floors determines the amount of usable space within a skyscraper. More floors allow for greater occupancy, whether for offices, residential units, or mixed-use purposes.
- Vertical Transportation: High-rise buildings rely heavily on efficient vertical transportation systems, such as elevators and stairwells. The number of floors influences the capacity and design of these systems to ensure smooth and swift movement of occupants.
- Views and Natural Light: Higher floors offer panoramic views and access to natural light. This aspect is particularly valuable for luxury apartments, executive offices, and public observatories, enhancing the overall desirability and value of the building.
In conclusion, the number of floors in a skyscraper is intricately linked to its height. It affects structural integrity, space utilization, vertical transportation, and the quality of life for occupants. Understanding this connection is essential in designing and constructing skyscrapers that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also safe, functional, and sustainable.
2. Function
The number of floors in a skyscraper is closely tied to its intended use, influencing design choices and shaping the building’s overall character and functionality. Understanding this connection is crucial in creating skyscrapers that effectively meet the needs of their occupants and contribute positively to the surrounding environment.
- Residential Use: Skyscrapers designed primarily for residential purposes feature a higher proportion of floors dedicated to living spaces. These buildings often include amenities such as fitness centers, swimming pools, and communal areas to cater to the needs of residents.
- Commercial Use: Commercial skyscrapers are designed to accommodate office spaces, retail stores, and other business ventures. They prioritize efficient floor plans, high-speed elevators, and ample parking facilities to support a large influx of workers and visitors during business hours.
- Mixed-Use: Mixed-use skyscrapers combine residential and commercial functions within a single building. This approach allows for greater flexibility and adaptability, creating vibrant urban environments where people can live, work, and socialize in close proximity.
- Supertall Skyscrapers: Supertall skyscrapers, defined as those exceeding 300 meters in height, often have specialized functions. They may incorporate luxury residences, high-end offices, and observation decks that offer panoramic views of the city.
In conclusion, the number of floors in a skyscraper is a key determinant of its intended use. Careful consideration of this aspect ensures that skyscrapers align with the needs of their occupants and contribute positively to the urban fabric. By balancing aesthetics, functionality, and sustainability, architects and engineers create skyscrapers that are not only iconic landmarks but also vibrant and livable spaces.
3. Occupancy
The number of floors in a skyscraper directly impacts the building’s occupancy and population density. Each additional floor adds usable space, allowing for a greater number of occupants within the building. This relationship is crucial in understanding how skyscrapers function and their impact on the urban environment.
High-rise buildings designed for commercial use, such as office towers, typically have a higher population density compared to residential skyscrapers. During business hours, these buildings accommodate a large influx of workers, creating a concentrated population within a relatively small footprint. Conversely, residential skyscrapers have a lower population density as they are designed to provide living spaces for a smaller number of people.
Mixed-use skyscrapers, which combine residential and commercial functions, offer a balance between population density and diversity. These buildings create vibrant urban environments where people can live, work, and socialize in close proximity. By accommodating a variety of uses within a single structure, mixed-use skyscrapers promote walkability, reduce traffic congestion, and foster a sense of community.
Understanding the relationship between the number of floors and occupancy is essential for architects and urban planners. It allows them to design skyscrapers that meet the needs of their intended occupants while also considering the impact on the surrounding infrastructure and environment. By carefully managing population density, skyscrapers can contribute positively to the urban fabric and create livable and sustainable cities.
4. Structural integrity
The number of floors in a s
kyscraper directly influences its structural integrity. As buildings rise higher, they become more susceptible to lateral forces such as wind and earthquakes. To ensure the safety and stability of these towering structures, architects and engineers must design robust structural systems that can withstand these forces.
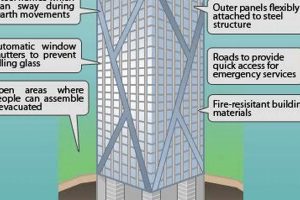
- Wind Resistance: Skyscrapers are designed to resist wind loads through a combination of structural elements, including reinforced concrete cores, steel frames, and exterior cladding. These elements work together to distribute and dissipate wind forces throughout the building, preventing excessive swaying or collapse.
- Seismic Resistance: In earthquake-prone regions, skyscrapers are equipped with specialized structural systems to withstand seismic activity. These systems may include base isolators, which absorb and redirect earthquake energy, and shear walls, which provide lateral stability and prevent the building from twisting or buckling.
- Redundancy: Skyscrapers often incorporate redundant structural elements to enhance their resilience. This means that if one structural element is damaged or fails, other elements can step in to carry the load and maintain the stability of the building.
- Regular Shape: Skyscrapers with regular shapes, such as rectangular or square footprints, are generally more structurally sound than buildings with irregular shapes. Regular shapes distribute forces more evenly throughout the structure, reducing the risk of localized failures.
The relationship between the number of floors and structural integrity is a critical consideration in skyscraper design. By carefully engineering these structures to withstand lateral forces, architects and engineers ensure the safety and longevity of these iconic landmarks.
5. Fire safety
The number of floors in a skyscraper directly influences the fire safety measures that must be implemented to ensure the safety of occupants and the integrity of the building.
- Compartmentalization: Skyscrapers are divided into compartments, which are sections of the building separated by firewalls. This compartmentalization prevents fire from spreading from one part of the building to another, giving occupants more time to evacuate.
- Fire escapes: Skyscrapers are equipped with fire escapes, which are external staircases that provide a means of escape in the event of a fire. Fire escapes are typically located on the exterior of the building and are protected from the fire by fire-resistant materials.
- Sprinkler systems: Skyscrapers are equipped with sprinkler systems, which are networks of pipes that distribute water throughout the building. Sprinkler systems are designed to activate in the event of a fire and can help to contain and extinguish the fire.
- Smoke detectors and alarms: Skyscrapers are equipped with smoke detectors and alarms, which are designed to detect smoke and alert occupants to a fire. Smoke detectors and alarms are typically located throughout the building and are connected to a central fire alarm system.
The implementation of these fire safety measures is crucial in skyscrapers due to the increased risk of fire in high-rise buildings. The presence of numerous floors, coupled with the large number of occupants and the potential for rapid fire spread, necessitates the adoption of robust fire safety measures to protect lives and property.
6. Views
The height of a skyscraper, measured by the number of floors it has, plays a significant role in determining the quality and desirability of the views it offers. Higher floors provide panoramic vistas that encompass expansive cityscapes, natural landscapes, and iconic landmarks, making them highly sought after for both commercial and residential purposes.
- Offices with a View: Many companies prioritize securing office spaces on higher floors to provide their employees with inspiring and motivating work environments. Panoramic views can enhance employee morale, reduce stress, and foster a sense of well-being, leading to increased productivity and creativity.
- Luxury Living in the Sky: High-end residential apartments on the upper floors of skyscrapers offer unparalleled views that command a premium in the real estate market. Residents can enjoy breathtaking vistas of the city lights, sprawling coastlines, or verdant parklands from the comfort of their own living spaces.
- Tourism and Observation Decks: The allure of panoramic views extends beyond offices and apartments. Many skyscrapers feature public observation decks or revolving restaurants that allow visitors to ascend to great heights and experience the city from a unique perspective. These attractions generate revenue and contribute to the overall appeal of the skyscraper.
- Architectural Landmarks: Skyscrapers with striking designs and exceptional views become iconic landmarks that define a city’s skyline. The Empire State Building in New York City and the Burj Khalifa in Dubai are prime examples of how architectural marvels can captivate the imagination and attract visitors from around the world.
In conclusion, the number of floors in a skyscraper directly influences the quality and desirability of the views it offers. Panoramic vistas from higher floors enhance the value of commercial office spaces, create exclusive residential experiences, attract tourists, and contribute to the architectural legacy of a city.
7. Elevators
The number of floors in a skyscraper has a direct impact on the efficiency and design of its elevator systems. As skyscrapers soar higher, the need for reliable and efficient vertical transportation becomes paramount. Elevators play a critical role in ensuring the smooth and swift movement of occupants between floors, influencing the overall functionality and experience of the building.
The number of elevators required in a skyscraper is determined by several factors, including the total number of floors, the occupancy load, and the desired level of service. Taller skyscrapers with a large number of floors necessitate more elevators to handle the increased traffic and maintain acceptable wait times. The capacity and speed of the elevators must also be carefully considered to accommodate the peak demand during business hours or special events.
The design of elevator systems in skyscrapers involves sophisticated engineering and planning. Architects and engineers must consider the optimal placement of elevator shafts, the capacity and speed of the elevators, and the integration with other building systems such as fire safety and emergency evacuation procedures. Advanced technologies, such as destination dispatch algorithms and predictive modeling, are employed to enhance elevator efficiency and reduce wait times.
Efficient elevator systems are not only essential for the convenience and comfort of occupants but also for the overall safety and functionality of the skyscraper. In the event of an emergency, such as a fire or power outage, elevators play a vital role in evacuating occupants quickly and safely. Re
dundant systems and backup power sources are often incorporated to ensure that elevators remain operational during emergencies.
In conclusion, the number of floors in a skyscraper directly influences the design and efficiency of its elevator systems. By carefully planning and implementing these systems, architects and engineers ensure that skyscrapers remain accessible, functional, and safe for their occupants.
8. Sustainability
In the realm of modern skyscrapers, sustainability has emerged as a driving force, shaping the design and construction of these towering structures. The number of floors in a skyscraper directly influences the implementation and effectiveness of sustainable features, as taller buildings require more energy and resources to operate efficiently.
- Energy Efficiency: As skyscrapers rise higher, their energy consumption increases significantly. Sustainable design strategies, such as energy-efficient lighting systems and double-glazed windows, play a crucial role in reducing energy usage. These measures minimize heat loss and optimize natural light, lowering the overall energy footprint of the building.
- Water Conservation: Rainwater harvesting systems collect and store rainwater for non-potable uses, such as irrigation and flushing toilets. By reducing reliance on municipal water supplies, skyscrapers can conserve precious resources and minimize their environmental impact.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Some skyscrapers incorporate renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, to generate electricity. These systems help offset the building’s energy consumption and reduce its carbon emissions.
- Green Roofs and Facades: Green roofs and facades are vegetated areas that enhance air quality, reduce heat island effects, and provide insulation. By incorporating these features, skyscrapers can improve their environmental performance and contribute to the well-being of occupants.
The pursuit of sustainability in skyscraper design not only benefits the environment but also aligns with the increasing demand for green and energy-efficient buildings. By carefully integrating sustainable features, architects and engineers can create skyscrapers that are environmentally responsible, cost-effective, and appealing to eco-conscious tenants and investors.
FAQs on “How Many Floors Does a Skyscraper Have?”
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions surrounding the topic of skyscraper floor count, providing informative answers based on expert knowledge.
Question 1: What is the average number of floors in a skyscraper?
The average number of floors in a skyscraper varies depending on factors such as the building’s purpose, location, and year of construction. However, most skyscrapers typically have between 50 and 100 floors, with some supertall skyscrapers exceeding 150 floors.
Question 2: What is the tallest skyscraper in the world, and how many floors does it have?
As of 2023, the tallest skyscraper in the world is the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, with 163 floors.
Question 3: How do architects and engineers determine the number of floors in a skyscraper?
The number of floors in a skyscraper is determined by a combination of factors, including the building’s intended use, structural integrity requirements, fire safety regulations, and elevator capacity. Architects and engineers carefully balance these considerations to create skyscrapers that are safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing.
Question 4: What are the advantages of having a greater number of floors in a skyscraper?
A greater number of floors can provide several advantages, such as increased office or residential space, panoramic views, and potential revenue generation from observation decks or luxury apartments on higher floors.
Question 5: Are there any disadvantages to having a large number of floors in a skyscraper?
While there are advantages to having a large number of floors, there can also be challenges, including increased structural complexity, higher construction costs, and the need for more robust elevator systems to efficiently transport occupants.
Question 6: How do skyscrapers ensure the safety and accessibility of their upper floors?
Skyscrapers employ various safety and accessibility measures, such as advanced fire safety systems, redundant elevators, and emergency evacuation plans. They also incorporate energy-efficient lighting, water conservation systems, and sustainable design features to reduce their environmental impact.
In conclusion, the number of floors in a skyscraper is a crucial aspect that influences its design, functionality, and overall impact. By addressing common questions and misconceptions, this FAQ section provides a deeper understanding of the factors that shape the verticality of these architectural marvels.
Transition to the next article section: The Evolution of Skyscraper Design
Tips on Understanding Skyscraper Floor Count
Grasping the concept of floor count in skyscrapers requires careful consideration of various factors. Here are some valuable tips to enhance your understanding:
Tip 1: Consider Building Purpose and Location:
Skyscrapers designed for commercial use, such as offices, typically have more floors than residential buildings. Additionally, the location of the skyscraper can influence floor count, with buildings in densely populated urban areas often having more floors to maximize space utilization.
Tip 2: Understand Structural Implications:
The number of floors in a skyscraper is closely tied to its structural integrity. Taller buildings require more robust structural systems to withstand wind loads and seismic activity. This can limit the maximum number of floors that can be safely constructed.
Tip 3: Factor in Fire Safety Regulations:
Fire safety regulations play a crucial role in determining the number of floors in a skyscraper. Building codes specify maximum floor heights and require the implementation of fire safety measures, such as sprinkler systems and fire escapes. These regulations can impact the overall floor count.
Tip 4: Consider Elevator Capacity and Efficiency:
The number of floors in a skyscraper directly influences the design and capacity of its elevator systems. Taller buildings require more elevators and advanced elevator technologies to efficiently transport occupants between floors, especially during peak hours.
Tip 5: Explore Sustainability Features:
Modern skyscrapers often incorporate sustainable design features, such as energy-efficient lighting and rainwater harvesting systems. These features can impact the number of floors by influencing the building’s overall energy consumption and environmental footprint.
Summary:
Understanding the factors that influence the number of floors in a skyscraper requires a comprehensive approach. By considering building purpose, structural implications, fire safety regulations, elevator capacity, and sustainability features, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities involved in designing and constructing these architectural marvels.
Conclusion
The exploration of “how many floors does a skyscraper have” unveils a complex interplay of facto
rs that shape the verticality of these architectural wonders. From structural considerations to sustainability features, each floor adds to a skyscraper’s functionality, aesthetics, and impact on the urban landscape.
Understanding the factors that determine floor count empowers us to appreciate the engineering marvels and design intricacies that make skyscrapers possible. As technology advances and architectural boundaries continue to be pushed, the future of skyscrapers holds exciting possibilities for innovation and sustainable urban development.