Acrophobia, the fear of heights, can manifest in specific phobias such as the fear of skyscrapers, known as megalophobia. Individuals with megalophobia experience intense anxiety or fear when confronted with tall buildings, often accompanied by physical symptoms like dizziness, trembling, and shortness of breath.
Understanding megalophobia is important for mental health professionals to provide effective treatment plans. It can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, affecting their ability to work, socialize, and engage in activities that involve tall buildings or high altitudes. Recognizing the nature and causes of this fear can lead to appropriate interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, exposure therapy, and medication when necessary.
Historically, humans have had an innate fear of heights due to evolutionary survival instincts. However, for some individuals, this fear can become excessive and debilitating, leading to the development of specific phobias like megalophobia. Understanding the psychological and physiological factors that contribute to this fear is crucial for developing effective treatments and coping mechanisms.
1. Height
The extreme height of skyscrapers is the primary trigger for megalophobia, the fear of skyscrapers. The sheer size and height of these structures can be overwhelming and anxiety-provoking for individuals with this specific phobia. The extreme height of skyscrapers can create a sense of vertigo and dizziness, leading to feelings of panic and a desire to escape the situation.
Understanding the connection between height and megalophobia is crucial for developing effective treatment plans. Exposure therapy, a common treatment for phobias, gradually exposes individuals to the feared stimulus in a controlled environment. In the case of megalophobia, this may involve gradually increasing exposure to skyscrapers, starting with smaller buildings and gradually working up to taller ones. By confronting their fear in a safe and supportive setting, individuals with megalophobia can learn to manage their anxiety and eventually overcome their fear of skyscrapers.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between height and megalophobia lies in the ability to develop targeted interventions and coping mechanisms. Individuals with megalophobia can benefit from strategies such as relaxation techniques, deep breathing exercises, and visualization to manage their anxiety when confronted with skyscrapers. Additionally, architectural design and urban planning can consider the needs of individuals with megalophobia by incorporating features that reduce feelings of vertigo and anxiety, such as gradual transitions between different heights and the use of calming colors and materials.
2. Dizziness
Dizziness and vertigo are common symptoms of megalophobia, the fear of skyscrapers. When individuals with megalophobia look down from tall buildings, they may experience a range of physical and psychological reactions, including:
- A sense of imbalance or unsteadiness
- Lightheadedness
- Nausea
- Rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Anxiety and panic
These reactions are caused by the body’s natural response to heights. When an individual looks down from a tall building, the brain receives conflicting signals from the eyes and the vestibular system, which is responsible for balance. This can lead to feelings of dizziness and vertigo. In addition, the fear and anxiety associated with megalophobia can further exacerbate these symptoms.
Understanding the connection between dizziness and megalophobia is important for several reasons. First, it can help individuals with megalophobia to understand and manage their symptoms. Second, it can help mental health professionals to develop more effective treatment plans. Third, it can help architects and urban planners to design buildings and public spaces that are less likely to trigger symptoms of megalophobia.
3. Anxiety
Anxiety is a central component of megalophobia, the fear of skyscrapers. When individuals with megalophobia are confronted with skyscrapers, they experience intense anxiety and panic. This anxiety can manifest in a variety of physical and psychological symptoms, including:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Trembling
- Nausea
- Lightheadedness
- Dizziness
- Feeling faint
- Chest pain
- Fear of losing control
- Fear of dying
The anxiety associated with megalophobia can be debilitating. It can interfere with an individual’s ability to work, socialize, and enjoy activities that involve skyscrapers or high altitudes. In severe cases, megalophobia can lead to agoraphobia, a fear of open spaces that can make it difficult to leave one’s home.
Understanding the connection between anxiety and megalophobia is important for several reasons. First, it can help individuals with megalophobia to understand and manage their symptoms. Second, it can help mental health professionals to develop more effective treatment plans. Third, it can help architects and urban planners to design buildings and public spaces that are less likely to trigger symptoms of megalophobia.
4. Avoidance
Avoidance is a common symptom of megalophobia, the fear of skyscrapers. People with this phobia may go to great lengths to avoid situations or places that involve tall buildings. For example, they may avoid:
Going to the top of tall buildings Looking out of windows on tall floors Driving or walking near tall buildings Living or working in tall buildings
- Social Avoidance
People with megalophobia may avoid social situations that involve tall buildings, such as parties or gatherings held on high floors. This can lead to isolation and loneliness.
- Occupational Avoidance
People with megalophobia may avoid jobs that require them to work in or around tall buildings, such as construction workers, window washers, or architects. This can limit their career opportunities.
- Recreational Avoidance
People with megalophobia may avoid activities that involve tall buildings, such as hiking, rock climbing, or sightseeing. This can limit their ability to enjoy leisure time and pursue their hobbies.
- Everyday Avoidance
People with megalophobia may avoid everyday activities
that involve tall buildings, such as going to the doctor’s office, taking the elevator, or crossing the street near a tall building. This can make it difficult to live a normal life.
Avoidance can have a significant impact on the lives of people with megalophobia. It can lead to social isolation, occupational problems, and difficulty enjoying leisure activities. In severe cases, avoidance can even lead to agoraphobia, a fear of open spaces that can make it difficult to leave one’s home.
5. Treatment
In the context of treating megalophobia, the fear of skyscrapers, therapy plays a crucial role in helping individuals overcome their anxiety and avoidance behaviors. Two widely recognized therapeutic approaches are exposure therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT).
- Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy gradually exposes individuals with megalophobia to the feared stimulus, in this case, skyscrapers. This controlled exposure helps them habituate to the anxiety-provoking situation and learn that it is not as dangerous as they perceive it to be. Exposure therapy can take place in real-life settings or through virtual reality simulations.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT helps individuals with megalophobia identify and challenge the negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to their fear. Through CBT, they learn to recognize and replace these irrational thoughts with more rational and adaptive ones. CBT also teaches coping mechanisms and strategies for managing anxiety.
The combination of exposure therapy and CBT has proven effective in reducing symptoms of megalophobia and improving the overall quality of life for individuals with this condition. By gradually facing their fear and challenging their negative thoughts, they can gradually overcome their fear of skyscrapers and engage in activities that were previously avoided.
6. Safety
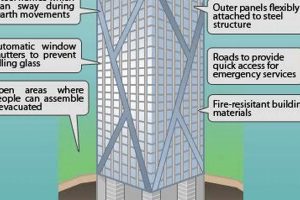
In the context of “fear of skyscrapers” or megalophobia, understanding building codes and safety regulations plays a significant role in reducing anxiety for individuals with this condition. By gaining knowledge about the rigorous standards and regulations that govern the construction and maintenance of skyscrapers, individuals can develop a sense of trust and confidence in the safety of these structures.
- Structural Integrity
Skyscrapers are designed and constructed to withstand various loads and forces, including high winds, earthquakes, and even potential terrorist attacks. Understanding the stringent structural requirements and the use of advanced engineering techniques can provide reassurance to individuals with megalophobia that these buildings are built to the highest safety standards.
- Fire Safety
Building codes mandate strict fire safety measures in skyscrapers, including fire-resistant materials, compartmentalization, and advanced fire suppression systems. Knowing that these measures are in place can reduce anxiety for individuals with megalophobia who may worry about the risk of fire or entrapment.
- Evacuation Plans
Skyscrapers have comprehensive evacuation plans and systems in place to ensure the safe and efficient evacuation of occupants in case of an emergency. Understanding these plans and practicing evacuation drills can give individuals with megalophobia a sense of preparedness and control, reducing their anxiety.
- Regular Inspections and Maintenance
Skyscrapers undergo regular inspections and maintenance to ensure their continued safety and integrity. These inspections cover various aspects, including structural components, fire safety systems, and mechanical equipment. Knowing that these regular checks are conducted can provide peace of mind to individuals with megalophobia.
By understanding the comprehensive safety measures and regulations surrounding skyscrapers, individuals with megalophobia can gradually challenge their negative thoughts and beliefs about these structures. This knowledge can empower them to confront their fear and engage in activities involving skyscrapers with greater confidence and reduced anxiety.
7. Support
In the context of “fear of skyscrapers” or megalophobia, support groups and online communities play a vital role in providing individuals with a sense of belonging and shared experiences.
- Peer Support
Support groups and online communities offer a platform for individuals with megalophobia to connect with others who share similar experiences and challenges. This sense of camaraderie and understanding can reduce feelings of isolation and stigma associated with the fear of skyscrapers.
- Shared Strategies
Within these support systems, individuals can share coping mechanisms, strategies, and advice on how to manage their fear of skyscrapers. Learning from others who have successfully overcome or are managing their megalophobia can provide hope and inspiration.
- Emotional Validation
Support groups and online communities offer a safe and non-judgmental space for individuals to express their fears and concerns about skyscrapers. Being listened to and understood by others who genuinely care can provide emotional validation and reduce feelings of shame or embarrassment.
- Challenging Negative Thoughts
Through interactions with supportive peers, individuals with megalophobia can challenge their negative thoughts and beliefs about skyscrapers. By sharing experiences and perspectives, they can gain a more balanced and realistic understanding of the risks and safety measures associated with tall buildings.
Overall, support groups and online communities provide individuals with megalophobia with a sense of belonging, shared experiences, and valuable resources to manage their fear of skyscrapers. These support systems can empower individuals to confront their fears, develop coping mechanisms, and improve their quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common concerns and misconceptions regarding the fear of skyscrapers, also known as megalophobia.
Question 1: Is megalophobia a common fear?
Yes, megalophobia is a relatively common specific phobia, affecting a significant portion of the population. Many individuals experience some degree of discomfort or anxiety around skyscrapers, but for those with megalophobia, this fear can be intense and debilitating.
Question 2: What are the symptoms of megalophobia?
Symptoms of megalophobia can vary but commonly include intense anxiety, panic, dizziness, nausea, and avoidance behaviors. Individuals with this phobia may experience significant distress and impairment in their daily lives due to their fear of skyscrapers.
Question 3: What causes megalophobia?
The exact cause of megalophobia is not fully understood, but a combination of factors is thought to play a role, including genetics, traumatic experiences, and environmental influences.
Some individuals may develop megalophobia after experiencing a negative event involving a skyscraper, while others may have a predisposition to developing phobias.
Question 4: How is megalophobia treated?
Effective treatments for megalophobia include exposure therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and medication in some cases. Exposure therapy gradually exposes individuals to skyscrapers in a controlled and supportive environment, helping them to habituate to their fear and develop coping mechanisms. CBT focuses on identifying and challenging negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to the phobia.
Question 5: Can megalophobia be cured?
While there is no known cure for megalophobia, it is a highly treatable condition. With proper treatment and support, individuals with megalophobia can significantly reduce their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Question 6: How can I support someone with megalophobia?
Supporting someone with megalophobia involves understanding their fear, providing emotional support, and encouraging them to seek professional help. Avoid dismissing their fears or pressuring them to face their phobia too quickly. Instead, offer, listen to their concerns, and help them to identify coping strategies.
Remember, megalophobia is a real and valid fear that can significantly impact an individual’s life. With the right support and treatment, individuals can overcome their fear and live fulfilling lives.
Transition to next section: Understanding the causes and symptoms of megalophobia is crucial for developing effective treatments and coping mechanisms. In the next section, we will delve deeper into the psychological and physiological factors that contribute to this fear.
Tips for Facing Fear of Skyscrapers (Megalophobia)
Managing megalophobia, the fear of skyscrapers, requires a combination of strategies and support. Here are some tips to help you cope with this fear:
Tip 1: Understand Your Fear
The first step in overcoming megalophobia is to understand the nature of your fear. Identify the specific triggers that provoke anxiety, such as the height, design, or location of skyscrapers. Understanding your fear can help you develop tailored coping mechanisms.
Tip 2: Practice Relaxation Techniques
When confronted with a skyscraper, practice deep breathing exercises or meditation to calm your anxiety. Focus on controlled breathing patterns and positive self-talk to reduce feelings of panic.
Tip 3: Gradually Face Your Fear
Avoidance only reinforces your fear. Gradually expose yourself to skyscrapers, starting with smaller buildings and gradually working your way up to taller ones. This controlled exposure helps you habituate to the feared stimulus.
Tip 4: Challenge Negative Thoughts
Megalophobia often involves irrational thoughts about the dangers of skyscrapers. Challenge these negative thoughts by gathering information about building codes, safety regulations, and the low probability of accidents.
Tip 5: Seek Professional Help
If self-help strategies prove insufficient, consider seeking professional help. Therapists can guide you through exposure therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, or other techniques to manage your fear effectively.
Tip 6: Join Support Groups
Connecting with others who share your fear can provide valuable support and encouragement. Support groups offer a safe space to share experiences, coping strategies, and emotional validation.
Tip 7: Reward Your Progress
Acknowledge and reward your accomplishments as you gradually face your fear. Celebrate small victories to stay motivated and reinforce positive behavior.
Tip 8: Focus on the Benefits
Remind yourself of the potential benefits of overcoming your fear of skyscrapers. Whether it’s enjoying scenic views, visiting iconic landmarks, or conquering a personal challenge, focus on the positive outcomes to stay inspired.
Remember, overcoming megalophobia is a gradual process that requires patience and effort. By implementing these tips and seeking support when needed, you can effectively manage your fear and live a fulfilling life.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: Understanding and addressing the fear of skyscrapers is crucial for improving mental well-being and quality of life. With the right strategies and support, individuals can overcome this phobia and experience the full benefits of urban environments.
Conclusion
Throughout this exploration of “fear of skyscrapers,” we have delved into its psychological and practical dimensions, offering evidence-based strategies for managing this specific phobia. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and effective treatments empowers individuals to take control of their fear and live fulfilling lives.
Overcoming megalophobia not only liberates individuals from the constraints of their fear but also opens up new possibilities for personal growth and enjoyment. By challenging negative thoughts, practicing relaxation techniques, and gradually facing their fear, individuals can unlock the freedom to experience the grandeur of skyscrapers and the vibrancy of urban environments.
Remember, seeking professional help is a valuable step when self-help strategies prove insufficient. Therapists can provide tailored support, guidance, and evidence-based interventions to help individuals overcome their fear of skyscrapers effectively.
As we move forward, continued research and awareness-raising efforts are crucial to destigmatize mental health conditions and empower individuals to seek the support they need. Together, we can create a society where individuals are equipped with the tools and resources to conquer their fears and live life to its fullest potential.