Zaha Hadid was an Iraqi-British architect, known for her groundbreaking designs and innovative use of concrete and steel. Her distinctive style, characterized by fluid, curvilinear forms and dynamic structures, has left a lasting impact on the world of architecture.
Hadid’s skyscrapers are particularly notable for their sculptural qualities and bold, futuristic aesthetic. They often feature complex, interwoven geometries and cantilevered elements that seem to defy gravity. Her designs not only push the boundaries of architectural expression but also explore new possibilities for urban living and sustainability.
Some of Hadid’s most iconic skyscraper projects include the Al Wakrah Stadium in Qatar, the Guangzhou Opera House in China, and the MAXXI Museum in Rome. These buildings have garnered widespread recognition for their architectural prowess and have become landmarks in their respective cities.
1. Sculptural forms
The sculptural forms of Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers are a defining characteristic of her work. Her buildings are often described as fluid, curvilinear, and dynamic, and they often resemble sculptures more than traditional buildings. This approach to design sets her work apart from that of many other architects and has made her one of the most recognizable figures in contemporary architecture.
Hadid’s use of sculptural forms is not merely an aesthetic choice. Her designs are carefully conceived to create specific effects and experiences for the people who use them. For example, the swooping curves of the Guangzhou Opera House in China are designed to create a sense of movement and energy, while the more restrained forms of the MAXXI Museum in Rome are intended to evoke a sense of calm and contemplation.
The sculptural forms of Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers have a number of practical benefits as well. For example, the curved surfaces of the Al Wakrah Stadium in Qatar help to reduce wind resistance, making the building more energy-efficient. Similarly, the cantilevered roof of the London Aquatics Centre helps to create a more spacious and open interior.
Hadid’s sculptural forms are not without their challenges. They can be difficult and expensive to construct, and they can sometimes be impractical for everyday use. However, Hadid’s work has shown that sculptural forms can be used to create beautiful, sustainable, and inspiring buildings.
2. Fluid lines
Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers are renowned for their distinctive fluid lines. These lines create a sense of movement and energy, and they help to give her buildings a unique and sculptural quality. Fluid lines are a key part of Hadid’s design vocabulary, and they can be seen in all of her work, from her early projects to her later masterpieces.
- Continuous curves: Hadid’s fluid lines are often continuous, creating a sense of movement and flow. This can be seen in the swooping curves of the Guangzhou Opera House in China, and in the gently undulating facade of the Al Wakrah Stadium in Qatar.
- Intersecting lines: Hadid also uses fluid lines to create complex and intersecting forms. This can be seen in the MAXXI Museum in Rome, where the building’s facade is made up of a series of intersecting curves. These lines create a sense of tension and drama, and they help to give the building a unique and dynamic appearance.
- Organic forms: Hadid’s fluid lines are often inspired by organic forms, such as plants and animals. This can be seen in the sinuous curves of the London Aquatics Centre, which resemble the shape of a wave. Hadid’s organic forms help to create a sense of connection between her buildings and the natural world.
- Dynamic shapes: Hadid’s fluid lines create dynamic and sculptural forms. This can be seen in theing tower of the CCTV Headquarters in Beijing, and in the flowing curves of the Heydar Aliyev Center in Azerbaijan. Hadid’s dynamic shapes help to give her buildings a sense of movement and energy, and they make them stand out from the ordinary.
Hadid’s fluid lines are a key part of her design aesthetic. They help to create buildings that are both beautiful and functional, and they have made her one of the most influential architects of our time.
3. Dynamic Structures
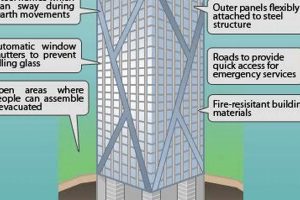
Dynamic structures are a key feature of Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers. They are designed to respond to the forces of nature, such as wind and earthquakes, in a way that creates a more efficient and sustainable building. Hadid’s dynamic structures are often characterized by their use of curves and angles, which help to distribute weight and stress more evenly throughout the building.
- Lightweight materials: Hadid’s skyscrapers often use lightweight materials, such as steel and glass, which help to reduce the overall weight of the building and make it more resistant to earthquakes. For example, the Al Wakrah Stadium in Qatar uses a steel frame that is designed to sway in the wind, which helps to dissipate energy and reduce the risk of damage.
- Aerodynamic shapes: Hadid’s skyscrapers often have aerodynamic shapes that help to reduce wind resistance and make the building more energy-efficient. For example, the Guangzhou Opera House in China has a curved roof that is designed to channel wind around the building and reduce drag.
- Base isolation systems: Hadid’s skyscrapers often use base isolation systems, which are designed to isolate the building from the ground and reduce the effects of earthquakes. For example, the MAXXI Museum in Rome uses a base isolation system that consists of a series of rubber bearings that are placed between the building and the ground.
- Active control systems: Hadid’s skyscrapers often use active control systems, which are designed to counteract the effects of wind and earthquakes in real time. For example, the London Aquatics Centre uses a system of sensors and actuators that are used to adjust the building’s structure in response to changes in wind speed and direction.
Hadid’s dynamic structures are a key part of her design aesthetic. They help to create buildings that are both beautiful and sustainable, and they have made her one of the most influential architects of our time.
4. Complex geometries
Complex geometries are a defining characteristic of Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers. Her buildings often feature intricate and unconvention
al shapes, which can be difficult to design and construct. However, Hadid’s mastery of complex geometries has allowed her to create some of the most iconic and innovative buildings of our time.
- Curvilinear forms: Hadid’s skyscrapers often feature curvilinear forms, which can be difficult to design and construct. However, Hadid’s use of curvilinear forms creates a sense of movement and fluidity, and it helps to give her buildings a unique and sculptural quality. For example, the Guangzhou Opera House in China features a curved roof that resembles a giant wave, while the Al Wakrah Stadium in Qatar features a swirling, vortex-like facade.
- Intersecting planes: Hadid’s skyscrapers often feature intersecting planes, which can create complex and dynamic forms. This can be seen in the MAXXI Museum in Rome, where the building’s facade is made up of a series of intersecting planes. These planes create a sense of tension and drama, and they help to give the building a unique and striking appearance.
- Faceted surfaces: Hadid’s skyscrapers often feature faceted surfaces, which can create a sense of depth and texture. This can be seen in the London Aquatics Centre, where the building’s facade is made up of a series of faceted panels. These panels create a sense of movement and energy, and they help to give the building a unique and eye-catching appearance.
- Organic forms: Hadid’s skyscrapers often feature organic forms, which can create a sense of connection to the natural world. This can be seen in the Heydar Aliyev Center in Azerbaijan, where the building’s facade is inspired by the shape of a leaf. Hadid’s use of organic forms helps to create a sense of harmony between her buildings and the surrounding environment.
Hadid’s mastery of complex geometries has allowed her to create some of the most innovative and iconic buildings of our time. Her buildings are a testament to her creativity and her commitment to pushing the boundaries of architectural design.
5. Cantilevered elements
Cantilevered elements are a defining feature of Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers. They are structural elements that project beyond the main body of the building, and they are often used to create dramatic and visually striking effects. Hadid’s use of cantilevered elements is a key part of her design aesthetic, and it has helped to make her one of the most influential architects of our time.
There are a number of reasons why Hadid uses cantilevered elements in her skyscrapers. First, they allow her to create buildings that are visually striking and memorable. The swooping curves and dramatic angles of her cantilevered elements create a sense of movement and energy, and they help to make her buildings stand out from the ordinary. Second, cantilevered elements can be used to create more space within a building. By extending the floor plates beyond the main body of the building, Hadid can create more usable space without increasing the overall footprint of the building. Third, cantilevered elements can be used to improve the structural stability of a building. By distributing the weight of the building more evenly, cantilevered elements can help to reduce the risk of collapse.
Hadid has used cantilevered elements in a number of her most famous skyscrapers, including the Al Wakrah Stadium in Qatar, the Guangzhou Opera House in China, and the MAXXI Museum in Rome. These buildings are all characterized by their bold and innovative use of cantilevered elements, and they have helped to establish Hadid as one of the most important architects of our time.
6. Sustainable design
Sustainable design is an essential component of Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers. She believed that buildings should be designed to minimize their environmental impact and to create a positive social and economic legacy. Hadid’s commitment to sustainable design is evident in all of her work, from her early projects to her later masterpieces.
One of the most important aspects of sustainable design is energy efficiency. Hadid’s skyscrapers are designed to be energy-efficient in a number of ways. For example, the Al Wakrah Stadium in Qatar uses a system of solar panels to generate renewable energy. The Guangzhou Opera House in China uses a rainwater collection system to reduce water consumption. And the MAXXI Museum in Rome uses a geothermal heating and cooling system to reduce energy consumption.
In addition to energy efficiency, Hadid’s skyscrapers are also designed to be sustainable in terms of their materials and construction methods. For example, the Al Wakrah Stadium is made from recycled materials, and the Guangzhou Opera House is built on a brownfield site. Hadid’s commitment to sustainable design has earned her a number of awards and accolades, including the Pritzker Architecture Prize in 2004. She is an inspiration to architects around the world, and her work is a testament to the power of sustainable design.
7. Urban landmarks
Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers are often seen as urban landmarks, iconic structures that define a city’s skyline and become symbols of its identity. This is due to a number of factors, including their unique and innovative designs, their use of cutting-edge materials and construction methods, and their ability to create a sense of place and community.
- Distinctive design: Hadid’s skyscrapers are known for their bold and distinctive designs, which often set them apart from other buildings in the surrounding area. This can make them landmarks in their own right, even if they are not the tallest or most prominent buildings in the city.
- Innovative materials and construction methods: Hadid’s skyscrapers often use innovative materials and construction methods, which can make them visually striking and memorable. For example, the Al Wakrah Stadium in Qatar is made from a lightweight steel frame that is designed to sway in the wind, while the Guangzhou Opera House in China is built on a brownfield site using recycled materials.
- Sense of place and community: Hadid’s skyscrapers often create a sense of place and community, becoming focal points for social and cultural activities. For example, the MAXXI Museum in Rome is a popular destination for art lovers, while the London Aquatics Centre is a popular venue for sporting events and community gatherings.
Hadid’s skyscrapers are not just buildings; they are works of art that can transform the urban landscape and create a sense of place and community. They are a testament to her creativity and her commitment to pushing the boundaries of architectural design.
8. Global recognition
Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers have achieved global recognition for their innovative designs and their ability to create a sense of place and community. Her work has been celebrated by critics and architects alike, and she has been awarded numerous prestigious
prizes, including the Pritzker Architecture Prize in 2004.
There are a number of reasons why Hadid’s skyscrapers have achieved such global recognition. First, her designs are unique and visually striking. She is not afraid to experiment with new forms and materials, and her buildings are often seen as works of art in their own right. Second, Hadid’s skyscrapers are often built in prominent locations, such as city centers and waterfront areas. This helps to ensure that they are seen by a large number of people and become landmarks in their own right.
The global recognition of Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers has had a number of positive effects. First, it has helped to raise her profile as an architect and has led to her being commissioned to design buildings all over the world. Second, it has helped to promote the city of London as a center for architectural innovation. Third, it has helped to inspire a new generation of architects to push the boundaries of architectural design.
The global recognition of Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers is a testament to her talent and creativity as an architect. Her buildings are not just works of art; they are also important landmarks that have helped to shape the urban landscape of the 21st century.
9. Architectural legacy
Zaha Hadid, the Iraqi-British architect, left behind an architectural legacy that is defined by innovation, experimentation, and a commitment to pushing the boundaries of design. Her skyscrapers, in particular, stand as testaments to her unique vision and her ability to create buildings that are both visually striking and socially responsible.
- Innovation in design
Hadid’s skyscrapers are known for their bold and innovative designs. She was not afraid to experiment with new forms and materials, and her buildings often challenged conventional notions of what a skyscraper could be. For example, the Al Wakrah Stadium in Qatar is a striking example of her innovative approach to design. The stadium’s undulating roof is made of a lightweight steel frame that is designed to sway in the wind, giving the building a sense of movement and dynamism.
- Commitment to sustainability
Hadid was also committed to sustainability, and her skyscrapers often incorporate features that reduce their environmental impact. For example, the Guangzhou Opera House in China uses a rainwater collection system to reduce water consumption, and the MAXXI Museum in Rome uses a geothermal heating and cooling system to reduce energy consumption.
- Sense of place and community
Hadid’s skyscrapers often create a sense of place and community. They are often located in prominent locations, and their unique designs make them landmarks in their own right. For example, the London Aquatics Centre is a popular destination for sporting events and community gatherings, and the Heydar Aliyev Center in Azerbaijan is a major cultural center.
- Global recognition
Hadid’s skyscrapers have achieved global recognition for their innovative designs and their ability to create a sense of place and community. Her work has been celebrated by critics and architects alike, and she has been awarded numerous prestigious prizes, including the Pritzker Architecture Prize in 2004.
Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers are a testament to her talent and creativity as an architect. Her buildings are not just works of art; they are also important landmarks that have helped to shape the urban landscape of the 21st century.
FAQs about Zaha Hadid Skyscrapers
Zaha Hadid was an Iraqi-British architect known for her innovative and groundbreaking designs. Her skyscrapers are particularly notable for their bold and futuristic aesthetic, as well as their complex geometries and use of sustainable materials. Here are answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about Zaha Hadid skyscrapers:
Question 1: What are the key characteristics of Zaha Hadid skyscrapers?
Answer: Hadid’s skyscrapers are known for their fluid, curvilinear forms, dynamic structures, complex geometries, cantilevered elements, sustainable design, and their ability to create urban landmarks.
Question 2: What is the architectural style of Zaha Hadid skyscrapers?
Answer: Hadid’s skyscrapers are often described as belonging to the deconstructivist architectural style. Deconstructivism is an architectural movement that emerged in the late 1980s and is characterized by its use of fragmentation, non-linear forms, and the rejection of traditional notions of symmetry and order.
Question 3: What are some examples of Zaha Hadid skyscrapers?
Answer: Some of Hadid’s most famous skyscraper projects include the Al Wakrah Stadium in Qatar, the Guangzhou Opera House in China, and the MAXXI Museum in Rome. These buildings are all characterized by their bold and innovative designs, and they have become landmarks in their respective cities.
Question 4: How sustainable are Zaha Hadid skyscrapers?
Answer: Hadid was committed to sustainable design, and her skyscrapers often incorporate features that reduce their environmental impact. For example, the Guangzhou Opera House in China uses a rainwater collection system to reduce water consumption, and the MAXXI Museum in Rome uses a geothermal heating and cooling system to reduce energy consumption.
Question 5: What are the benefits of Zaha Hadid skyscrapers?
Answer: Hadid’s skyscrapers offer a number of benefits, including their unique and innovative designs, their ability to create urban landmarks, and their commitment to sustainability. Her buildings are also often praised for their sculptural qualities and their ability to create a sense of place and community.
Question 6: What are the challenges of designing Zaha Hadid skyscrapers?
Answer: Designing Zaha Hadid skyscrapers can be challenging due to their complex geometries and use of innovative materials and construction methods. However, Hadid’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of architectural design has resulted in some of the most iconic and innovative buildings of our time.
Summary: Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers are architectural marvels that push the boundaries of design and sustainability. Their unique and innovative designs have made them landmarks in cities around the world, and their commitment to sustainability has earned them widespread recognition.
Transition to the next article section: Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers are a testament to her creativity and her commitment to pushing the boundaries of architectural design. They are a source of inspiration for architects and designers around the world, and they will continue to shape the urban landscape for years to come.
Tips for designing Zaha Hadid skyscrapers
Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers are known for their bold and innovative designs. They are often characterized by their fluid, curvilinear forms, dynamic structures, and complex geometries. If you are interested in designing Zaha Hadid-inspired skyscrapers, here are a few tips to help you get started:
Tip 1: Use fluid, curvilinear forms
Hadid’s skyscrapers are often characterized by their fluid, curvilinear forms. These forms can be created using a variety of techniques, such as computer-aided des
ign (CAD) software or parametric design. When using fluid, curvilinear forms, it is important to consider the overall shape of the building and how it will interact with its surroundings.
Tip 2: Create dynamic structures
Hadid’s skyscrapers are also known for their dynamic structures. These structures are often designed to respond to the forces of nature, such as wind and earthquakes. When designing a dynamic structure, it is important to consider the materials that you will be using and how they will perform under different loads.
Tip 3: Use complex geometries
Hadid’s skyscrapers often feature complex geometries. These geometries can be created using a variety of techniques, such as parametric design or 3D modeling. When using complex geometries, it is important to consider the structural implications of your design and how it will be constructed.
Tip 4: Use innovative materials
Hadid was known for her use of innovative materials in her designs. These materials often had unique properties that allowed her to create new and exciting forms. When selecting materials for your Zaha Hadid-inspired skyscraper, consider their strength, durability, and sustainability.
Tip 5: Consider sustainability
Hadid was committed to sustainability, and her skyscrapers often incorporate features that reduce their environmental impact. For example, many of her buildings use recycled materials and rainwater collection systems. When designing your Zaha Hadid-inspired skyscraper, consider ways to incorporate sustainable features into your design.
Summary: Designing Zaha Hadid-inspired skyscrapers can be a challenging but rewarding experience. By following these tips, you can create buildings that are both beautiful and sustainable.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: Zaha Hadid was a visionary architect who pushed the boundaries of design. Her skyscrapers are a testament to her creativity and her commitment to sustainability. By following these tips, you can create Zaha Hadid-inspired skyscrapers that will stand the test of time.
Conclusion
Zaha Hadid’s skyscrapers are architectural marvels that push the boundaries of design and sustainability. Their unique and innovative designs have made them landmarks in cities around the world, and their commitment to sustainability has earned them widespread recognition. Hadid’s legacy as an architect is secure, and her buildings will continue to inspire architects and designers for years to come.
Hadid’s work challenges us to rethink what is possible in architecture. Her buildings are not just structures; they are works of art that create a sense of place and community. They are a reminder that architecture can be both beautiful and sustainable, and that it has the power to transform our cities.
As we look to the future, it is important to remember Hadid’s commitment to innovation and sustainability. By following her example, we can create buildings that are both beautiful and sustainable, and that will make a positive contribution to our world.