Architecture skyscraper design encompasses the conceptualization and realization of high-rise buildings, often exceeding 150 meters in height. These architectural marvels combine engineering prowess with aesthetic vision, pushing the boundaries of vertical construction.
Skyscrapers have played a pivotal role in shaping urban landscapes, accommodating growing populations and serving as symbols of economic prosperity. Their designs prioritize space optimization, incorporating sustainable features and advanced technologies to ensure structural integrity and energy efficiency.
Delving into the intricacies of architecture skyscraper design, this article will explore the historical evolution of these architectural wonders, examining iconic structures and analyzing the design principles that govern their creation. Furthermore, it will delve into the challenges and considerations involved in conceiving and constructing these towering giants, showcasing the ingenuity and innovation that drive this specialized field.
1. Height Optimization
In architecture skyscraper design, height optimization is a crucial aspect that involves maximizing the usable space of a building while maintaining its structural integrity. This vertical expansion is driven by several factors, including the need to accommodate growing populations, optimize land use in densely populated urban areas, and create iconic landmarks that define skylines.
Achieving height optimization requires careful consideration of various elements. The structural system must be robust enough to withstand the increased forces exerted by greater heights, such as wind loads and seismic activity. Innovative engineering techniques, such as diagrid structures and supercolumns, are often employed to achieve this stability. Moreover, architects must optimize floor plans to maximize space efficiency and minimize wasted areas.
Height optimization has significant practical implications. It allows for the creation of more usable space without expanding the building’s footprint, reducing land consumption and preserving valuable urban areas. Additionally, taller buildings can offer panoramic views, enhancing the quality of life for occupants and creating desirable real estate.
2. Structural Integrity
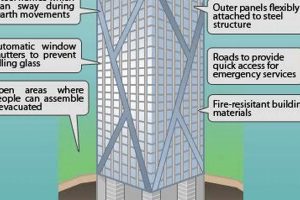
In architecture skyscraper design, structural integrity is paramount, ensuring the stability and safety of these towering structures. It involves the ability of a building to withstand various forces and environmental conditions without compromising its safety or functionality.
The structural integrity of a skyscraper is achieved through a combination of innovative engineering techniques and high-quality materials. Engineers must carefully consider the building’s height, weight, and shape to ensure it can resist strong winds, earthquakes, and other potential threats. They employ structural systems such as diagrid structures, moment-resisting frames, and outrigger systems to distribute forces efficiently and maintain stability.
Ensuring structural integrity is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, it safeguards the lives of occupants and the public. A structurally sound building can withstand extreme events and prevent catastrophic failures. Moreover, it protects the building’s contents, including valuable equipment and infrastructure. Additionally, structural integrity contributes to the building’s durability and longevity, reducing maintenance costs and ensuring its continued use over time.
3. Space Efficiency
In architecture skyscraper design, space efficiency is a critical consideration that involves optimizing the use of available space within a building’s vertical structure. It plays a vital role in maximizing usable floor area, accommodating a greater number of occupants or functions, and creating more efficient and sustainable buildings.
Achieving space efficiency in skyscraper design requires careful planning and innovative solutions. Architects employ various strategies, such as optimizing floor plans, reducing circulation areas, and incorporating multi-functional spaces. They also utilize advanced construction techniques, such as modular construction and prefabrication, to streamline the building process and minimize material waste.
The importance of space efficiency in architecture skyscraper design cannot be overstated. It allows for the creation of more livable and functional spaces within the constraints of limited land availability in urban areas. Space-efficient skyscrapers can accommodate a larger population, reducing urban sprawl and preserving valuable green spaces. Moreover, efficient use of space can lead to reduced construction costs, lower energy consumption, and improved building performance.
4. Sustainability
Sustainability has become an imperative consideration in architecture skyscraper design, as these towering structures have a significant impact on the environment. Architects and engineers are continuously exploring innovative ways to reduce the ecological footprint of skyscrapers while maintaining their functionality and aesthetic appeal.
- Energy Efficiency: Skyscrapers consume a substantial amount of energy for lighting, heating, cooling, and other operations. Sustainable design strategies focus on reducing energy consumption through the use of energy-efficient appliances, lighting systems, and building envelopes that minimize heat loss and gain. For example, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai utilizes a double-skin facade that acts as a thermal buffer, reducing the building’s energy needs by 30%.
- Water Conservation: Water usage in skyscrapers can be significant, particularly for irrigation and sanitary purposes. Sustainable design incorporates water-saving fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and greywater recycling systems to reduce water consumption. The Taipei 101 in Taiwan has implemented a rainwater collection system that supplies water for irrigation and toilet flushing, saving over 20 million gallons of water annually.
- Material Selection: The choice of building materials has a significant environmental impact. Sustainable skyscrapers prioritize the use of recycled and renewable materials, such as steel, glass, and bamboo. These materials have a lower embodied carbon footprint compared to traditional materials like concrete and can be reused or recycled at the end of the building’s life cycl
e. - Waste Management: Construction and operation of skyscrapers generate a substantial amount of waste. Sustainable design incorporates waste management strategies, such as recycling programs, waste sorting systems, and the use of modular construction techniques that reduce waste on-site. The Empire State Building in New York City has implemented a comprehensive waste management program that diverts over 80% of its waste from landfills.
By embracing sustainability in architecture skyscraper design, architects and engineers can create buildings that are not only iconic but also environmentally responsible. These sustainable skyscrapers contribute to a greener and more livable urban environment, ensuring the well-being of future generations.
5. Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency plays a crucial role in architecture skyscraper design, as these towering structures consume a substantial amount of energy for lighting, heating, cooling, and other operations. Sustainable design strategies focus on reducing energy consumption while maintaining functionality and aesthetic appeal.
- Building Envelope: The building envelope, including the facade, windows, and roof, plays a vital role in energy efficiency. Architects design envelopes that minimize heat loss and gain, utilizing materials with high thermal resistance and incorporating shading devices to reduce solar heat gain. For example, the Shanghai Tower in China has a double-skin facade that acts as a thermal buffer, reducing the building’s energy needs by 30%.
- Lighting Systems: Lighting accounts for a significant portion of energy consumption in skyscrapers. Sustainable design incorporates energy-efficient lighting systems, such as LED lighting and daylighting strategies that maximize natural light penetration. The Empire State Building in New York City has upgraded its lighting system to LED, resulting in a 70% reduction in energy consumption.
- HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are major energy consumers in skyscrapers. Sustainable design employs efficient HVAC systems that utilize variable air volume (VAV) technology and heat recovery systems to minimize energy consumption. The Burj Khalifa in Dubai has a centralized HVAC system that optimizes airflow and reduces energy use.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, can further enhance the energy efficiency of skyscrapers. These systems generate clean energy on-site, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering operating costs. The One World Trade Center in New York City has installed wind turbines that generate approximately 5% of the building’s energy needs.
By implementing these energy-efficient strategies, architects and engineers can create skyscrapers that are not only iconic but also environmentally responsible. Energy-efficient skyscrapers contribute to a greener and more sustainable urban environment, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the impact of climate change.
6. Aesthetic Appeal
Aesthetic appeal is an integral aspect of architecture skyscraper design, transcending mere visual appearance to encompass the emotional and experiential qualities of these towering structures. It involves the deliberate manipulation of form, materials, and lighting to create buildings that are not only functional but also visually captivating and emotionally resonant.
The pursuit of aesthetic appeal in skyscraper design serves several important purposes. Firstly, it contributes to the overall identity and character of a city’s skyline. Iconic skyscrapers become landmarks that define the urban landscape and evoke a sense of pride and belonging among residents. For example, the Empire State Building in New York City is instantly recognizable and has become an enduring symbol of the city’s architectural heritage.
Furthermore, aesthetic appeal can influence the desirability and value of skyscrapers as living and working spaces. Buildings that are visually appealing and well-integrated into their surroundings tend to attract tenants and command higher rental rates. The Burj Khalifa in Dubai, with its sleek and futuristic design, has become a highly sought-after address for businesses and residents alike.
7. Urban Integration
Urban integration is a crucial aspect of architecture skyscraper design, as these towering structures have a significant impact on the surrounding urban fabric. It involves the thoughtful consideration of a skyscraper’s relationship with its context, ensuring that it complements and enhances the existing urban environment.
Integrating skyscrapers into the urban fabric requires a holistic approach that considers various factors, including:
- Contextual Sensitivity: Skyscrapers should be designed in a way that respects and responds to the surrounding architectural styles and historical context. This can involve incorporating traditional design elements or materials, or creating a harmonious contrast that complements the existing cityscape.
- Connectivity and Accessibility: Skyscrapers should be well-connected to public transportation and pedestrian networks, ensuring easy access for occupants and visitors. This can involve designing integrated transit hubs or creating direct connections to nearby streets and sidewalks.
- Public Spaces: Skyscrapers can create or enhance public spaces at their base, providing gathering places and amenities for the community. This can involve incorporating plazas, parks, or retail areas that activate the street level and contribute to the vibrancy of the urban environment.
- Sustainability: Urban integration also involves considering the environmental impact of skyscrapers and their contribution to the overall sustainability of the city. This can involve designing energy-efficient buildings, incorporating green spaces, and promoting sustainable transportation options.
Successful urban integration of skyscrapers can bring numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Urban Vitality: Skyscrapers can create new focal points and attract businesses and residents, contributing to the overall vitality and economic prosperity of the city.
- Improved Connectivity: Well-integrated skyscrapers can improve connectivity and accessibility within the city, making it easier for people to move around and access different areas.
- Increased Public Spaces: Skyscrapers can provide opportunities to create new public spaces at their base, offering places for recreation, relaxation, and community events.
- Sustainable Urban Development: Urban integration promotes sustainable urban development by encouraging the efficient use of land and resources, and by reducing the environmental impact of skyscrapers.
In conclusion, urban integration is a critical aspect of architecture skyscraper design, as it ensures that these towering structures contribute positively to the surrounding urban environment. B
y considering contextual sensitivity, connectivity, public spaces, and sustainability, architects and urban planners can create skyscrapers that are not only iconic landmarks but also valuable assets to the city.
8. Technological Advancements
Technological advancements play a pivotal role in the ever-evolving field of architecture skyscraper design, pushing the boundaries of what is structurally feasible and aesthetically captivating.
- Materials and Construction Techniques: Innovations in materials and construction techniques have revolutionized skyscraper design. Advanced materials like ultra-high-strength concrete and lightweight composite panels allow for the creation of taller, more slender structures. Prefabricated components and modular construction methods streamline the building process, reducing costs and construction time.
- Structural Systems: Technological advancements have led to the development of innovative structural systems that can withstand the immense forces acting on skyscrapers. Diagrid structures, exoskeletons, and tuned mass dampers provide enhanced stability and seismic resistance, enabling architects to design skyscrapers that soar to new heights.
- Facade Engineering: Advanced facade systems contribute to the energy efficiency and aesthetic appeal of skyscrapers. Double-skin facades, solar panels integrated into the building envelope, and smart glass that adjusts to changing light conditions optimize thermal performance and reduce energy consumption.
- Digital Design and Analysis Tools: Sophisticated software tools have transformed the design and analysis of skyscrapers. Building information modeling (BIM) allows architects and engineers to create virtual models of the building, enabling them to simulate performance, identify potential issues, and optimize the design.
Technological advancements will continue to shape the future of architecture skyscraper design, allowing architects to create structures that are taller, more sustainable, and more visually stunning than ever before.
Architecture Skyscraper Design FAQs
This section addresses frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to architecture skyscraper design, providing concise and informative answers to common concerns and misconceptions.
Question 1: What are the key considerations in architecture skyscraper design?
Architecture skyscraper design involves a complex interplay of factors, including structural integrity, height optimization, space efficiency, sustainability, energy efficiency, aesthetic appeal, urban integration, and technological advancements. Architects and engineers must carefully balance these considerations to create safe, functional, and visually stunning skyscrapers that enhance the urban environment.
Question 2: How do architects ensure the structural integrity of skyscrapers?
Ensuring structural integrity is paramount in architecture skyscraper design. Engineers employ innovative structural systems, such as diagrid structures and outrigger systems, to distribute forces efficiently and maintain stability. High-quality materials, such as ultra-high-strength concrete and lightweight composite panels, are used to withstand the immense forces acting on skyscrapers.
Question 3: How can skyscrapers be designed to be sustainable?
Sustainability is a crucial aspect of modern architecture skyscraper design. Architects incorporate energy-efficient lighting systems, double-skin facades for thermal insulation, and rainwater harvesting systems to reduce resource consumption. They also prioritize the use of recycled and renewable materials to minimize environmental impact.
Question 4: How do skyscrapers contribute to the urban environment?
Skyscrapers play a significant role in shaping the urban environment. They can create new focal points, attract businesses and residents, and enhance connectivity. By incorporating public spaces and green areas at their base, skyscrapers can contribute to the vibrancy and livability of the city.
Question 5: What are the latest technological advancements influencing skyscraper design?
Technological advancements are constantly pushing the boundaries of skyscraper design. Advanced materials, such as ultra-high-strength concrete and lightweight composite panels, allow for taller and more slender structures. Building information modeling (BIM) software enables architects and engineers to optimize design and analyze performance virtually.
Question 6: How do architects balance aesthetic appeal with functionality in skyscraper design?
Aesthetic appeal is a subjective aspect of architecture skyscraper design. Architects strive to create visually captivating structures that complement the surrounding urban environment. However, they must also prioritize functionality, ensuring that the building meets the needs of its occupants and is safe and efficient to operate.
In conclusion, architecture skyscraper design is a multidisciplinary field that encompasses a wide range of considerations. By addressing these FAQs, we have shed light on the key factors that shape the design of these iconic structures, ensuring that they are safe, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing additions to the urban landscape.
Transition to the next article section:
Moving forward, we will delve deeper into the intricate details of architecture skyscraper design, exploring the engineering marvels, sustainable practices, and design principles that make these architectural wonders possible.
Tips for Architecture Skyscraper Design
In the realm of architecture, skyscraper design presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities. To achieve structural integrity, functional efficiency, and aesthetic appeal, architects and engineers must carefully consider various factors and employ innovative strategies.
Tip 1: Prioritize Structural Integrity
Skyscrapers are subjected to immense forces, including wind loads and seismic activity. Employ structural systems like diagrid structures and outrigger systems to distribute forces efficiently and ensure stability. Utilize high-quality materials, such as ultra-high-strength concrete and lightweight composite panels, to withstand these forces.
Tip 2: Maximize Space Efficiency
In urban areas with limited land availability, optimizing space is crucial. Employ innovative floor plans and multi-functional spaces to maximize usable area. Consider modular construction techniques and prefabrication to streamline the building process and minimize material waste.
Tip 3: Embrace Sustainability
Skyscrapers can have a significant environmental impact. Incorporate energy-efficient lighting systems, double-skin facades for thermal insulation, and rainwater harvesting systems to reduce resource consumption. Prioritize the use of recycled and renewable materials to minimize the building’s carbon footprint.
Tip 4: Enhance Urban Integration
Skyscrapers should complement and enhance the surrounding urban fabric. Create public spaces at the building’s base to promote community interaction. Ensure good connectivity to public transportation and pedestrian networks to facilitate accessibility and reduce traffic congestion.
Tip 5: Utilize Technological Advancements
Advanced materials, such as ultra-high-strength concrete and lightweight composite pane
ls, enable the construction of taller and more slender structures. Building information modeling (BIM) software helps optimize design and analyze performance virtually. Embrace these technologies to push the boundaries of skyscraper design.
Tip 6: Balance Functionality and Aesthetics
While aesthetic appeal is important, it should not compromise functionality. Collaborate with architects and engineers to create visually captivating structures that meet the needs of occupants and are safe and efficient to operate. Consider the building’s context and surrounding environment to ensure harmonious integration.
Tip 7: Focus on Long-Term Resilience
Skyscrapers are long-term investments. Design them with durability and adaptability in mind. Use high-quality materials and construction techniques to withstand the test of time. Consider future maintenance and upgrades to ensure the building remains safe and functional for generations to come.
Tip 8: Seek Professional Expertise
Skyscraper design is a complex undertaking. Engage the services of experienced architects, engineers, and consultants. Their expertise will ensure that your project meets all safety, sustainability, and performance standards.
By following these tips, architects and engineers can create skyscrapers that are not only visually stunning but also structurally sound, environmentally responsible, and seamlessly integrated into the urban fabric.
Conclusion
Architecture skyscraper design stands as a testament to human ingenuity and engineering prowess. By pushing the boundaries of structural integrity, maximizing space efficiency, embracing sustainability, and integrating seamlessly into urban environments, skyscrapers have transformed skylines and redefined the way we live and work in cities.
As we look towards the future, architecture skyscraper design will continue to evolve, driven by technological advancements, sustainability concerns, and the ever-changing needs of urban populations. By embracing innovation and collaboration, architects and engineers can create skyscrapers that are not only visually stunning but also structurally sound, environmentally responsible, and socially inclusive. These architectural marvels will continue to shape our cities and inspire future generations.