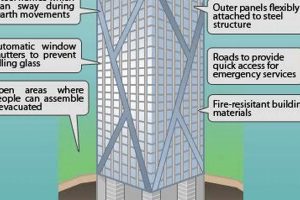
Skyscrapers, towering structures that dominate skylines around the world, have a rich history marked by architectural innovation and engineering marvels. These vertical wonders have reshaped urban landscapes, revolutionized construction techniques, and left an indelible mark on human civilization.
The allure of skyscrapers lies in their ability to accommodate a growing population within a limited urban footprint. They offer unparalleled views, increased energy efficiency, and enhanced connectivity. Historically, skyscrapers have played a pivotal role in the development of cities, serving as symbols of economic prosperity and technological advancement.
To delve deeper into the captivating history of skyscrapers, let’s explore their origins, architectural evolution, engineering challenges, and the impact they have had on society. From the Home Insurance Building in Chicago to the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, each skyscraper tells a unique story of human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of reaching new heights.
1. Origins
The late 19th century marked a pivotal era in the history of architecture and engineering, witnessing the genesis of skyscrapers. This period saw a convergence of factors that laid the foundation for these towering structures to emerge and reshape skylines around the world.
One of the key drivers was the rapid urbanization and population growth in major cities during this time. As cities became more densely populated, there was a growing need for buildings that could accommodate a large number of people and businesses within a limited footprint. This led to the development of taller and more efficient buildings.
Technological advancements also played a crucial role in the emergence of skyscrapers. The invention of the elevator in the 1850s made it possible to transport people and goods quickly and efficiently to higher floors. Additionally, the development of new construction techniques, such as the use of steel frames, allowed for the construction of taller and more stable buildings.
Understanding the origins of skyscrapers is essential for comprehending their historical significance and architectural evolution. By tracing the roots of skyscrapers to the late 19th century, we gain insights into the factors that shaped their development and the technological breakthroughs that made them possible.
2. Engineering feats
Engineering feats played a pivotal role in the history of skyscrapers, pushing the boundaries of architectural design and construction. These innovative techniques enabled the creation of taller, stronger, and more efficient buildings that redefined the urban landscape.
- Steel frames: The use of steel frames provided a lightweight and durable structure for skyscrapers, allowing them to reach unprecedented heights. The steel frame acts as a skeleton, supporting the weight of the building and resisting wind forces.
- Elevators: The invention of elevators made it possible to transport people and goods quickly and efficiently to higher floors, overcoming the limitations of traditional staircases and enabling the vertical expansion of buildings.
- Concrete: The development of reinforced concrete, a composite material combining steel and concrete, revolutionized skyscraper construction. Concrete’s strength and versatility made it suitable for constructing massive foundations, columns, and floor slabs.
- Wind engineering: As skyscrapers soared higher, engineers had to address the challenges of wind loads and structural stability. Advanced wind engineering techniques, such as wind tunnel testing and computer modeling, were developed to analyze and mitigate wind-induced vibrations and ensure the safety of these towering structures.
These engineering feats, combined with architectural innovation and economic factors, paved the way for the construction of iconic skyscrapers that became symbols of progress and architectural prowess. By exploring the groundbreaking engineering techniques that made skyscrapers possible, we gain a deeper understanding of the challenges and triumphs that shaped the history of these architectural marvels.
3. Architectural styles
Architectural styles have played a significant role in shaping the history of skyscrapers, influencing their form, function, and aesthetic appeal. The evolution of architectural styles has been closely intertwined with advancements in engineering techniques and the changing needs of society.
In the early days of skyscraper construction, architects drew inspiration from historical architectural styles, such as Gothic and Beaux-Arts. These styles were characterized by elaborate ornamentation, spires, and intricate facades. As skyscrapers grew taller, architects began to explore more modern styles that emphasized simplicity, functionality, and the use of new materials, such as glass and steel.
The International Style, which emerged in the early 20th century, had a profound impact on skyscraper design. This style emphasized clean lines, geometric forms, and the use of glass curtain walls. Many iconic skyscrapers, such as the Seagram Building in New York City and the Lever House in London, exemplify the principles of the International Style.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainable design in skyscraper construction. Architects are now designing skyscrapers that are energy-efficient, environmentally friendly, and responsive to the needs of their occupants. This has led to the development of new architectural styles that incorporate green features, such as rooftop gardens, solar panels, and rainwater harvesting systems.
Understanding the evolution of architectural styles in skyscraper design is essential for appreciating the rich history of these iconic structures. By examining the interplay between architectural styles, engineering advancements, and societal needs, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces that have shaped the skylines of cities around the world.
4. Economic drivers
Economic factors have played a significant role in shaping the history of skyscrapers. The construction and development of these towering structures require substantial financial resources and are often driven by economic growth and prosperity.
- Real estate speculation and land value: The desire to maximize profits from real estate has been a major driver behind the constr
uction of skyscrapers. In cities with limited land availability, building upwards allows developers to increase the value of their land by creating more rentable or saleable space. For example, the rapid development of skyscrapers in Dubai was fueled in part by speculation in the real estate market. - Economic booms and recessions: Periods of economic growth and prosperity often lead to increased demand for office and residential space, driving the construction of skyscrapers. Conversely, economic downturns can result in a decrease in demand and a slowdown in skyscraper construction. The construction boom in skyscraper development in China during the early 21st century was driven by the country’s rapid economic growth.
- Availability of financing: The construction of skyscrapers requires significant financial resources, which are often obtained through a combination of private investment, government subsidies, and bank loans. The availability of financing can influence the timing and scale of skyscraper development.
- Government policies and incentives: Government policies and incentives can play a role in encouraging or discouraging the construction of skyscrapers. For example, tax breaks or zoning regulations that favor high-rise development can stimulate skyscraper construction.
Understanding the economic drivers behind skyscraper construction and development provides insights into the complex interplay between financial factors and the built environment. Economic factors have shaped the skylines of cities around the world and continue to influence the design, construction, and use of skyscrapers.
5. Cultural impact
Skyscrapers, with their towering heights and impressive architectural designs, have become iconic symbols of progress and innovation, leaving a lasting cultural impact on societies worldwide. Their presence in major cities has shaped perceptions, influenced art and literature, and fostered a sense of pride and identity.
- Symbols of economic prosperity and technological advancement: Skyscrapers are often seen as reflections of a city’s economic vitality and technological prowess. They represent a community’s ambition, optimism, and belief in the future. For example, the construction of the Empire State Building in New York City during the Great Depression served as a symbol of resilience and hope.
- Architectural marvels and design inspiration: Skyscrapers have pushed the boundaries of architectural design, showcasing innovative and daring concepts. Their unique shapes, intricate facades, and use of new materials have inspired architects, artists, and designers worldwide. The Chrysler Building in New York City, with its Art Deco spire, is a prime example of how skyscrapers have influenced architectural aesthetics.
- Cultural landmarks and tourist attractions: Skyscrapers have become cultural landmarks that define a city’s skyline and attract tourists from around the globe. They offer breathtaking views, observation decks, and unique experiences, making them popular destinations for visitors. The Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the tallest building in the world, is a prime example of a skyscraper that has become a global icon.
- Sources of civic pride and identity: Skyscrapers can foster a sense of civic pride and identity among residents and visitors alike. They represent a city’s achievements and aspirations, becoming symbols of community and belonging. The Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, are iconic landmarks that embody the country’s economic growth and national identity.
In conclusion, skyscrapers have had a profound cultural impact, shaping perceptions, inspiring creativity, and fostering a sense of pride and identity. Their presence in cities worldwide has transformed skylines, influenced art and literature, and become enduring symbols of progress and innovation.
6. Urban planning
Skyscrapers have played a pivotal role in urban planning and the transformation of cityscapes throughout history. Their construction has necessitated careful planning and coordination to ensure the efficient use of land, minimize congestion, and create livable and sustainable urban environments.
- Zoning regulations: Skyscrapers have influenced zoning regulations, which govern the height, density, and use of buildings in specific areas. Zoning laws aim to balance the need for high-rise development with concerns about overshadowing, wind patterns, and the preservation of historic neighborhoods. For example, the 1916 Zoning Resolution in New York City established height limits and setback requirements to ensure adequate sunlight and air circulation.
- Transportation planning: The construction of skyscrapers has had a significant impact on transportation planning. High-rise buildings generate increased pedestrian and vehicular traffic, requiring the expansion and improvement of public transportation systems, such as subways, buses, and commuter rail lines. In some cities, skyscrapers have also led to the development of underground pedestrian networks to connect buildings and reduce street congestion.
- Public space and green areas: Skyscrapers can affect the availability of public space and green areas in urban environments. Large-scale developments may require the demolition of existing parks or open spaces, leading to concerns about the loss of green space and the impact on the quality of life for residents. Urban planners work to mitigate these effects by incorporating green roofs, rooftop gardens, and public plazas into skyscraper designs.
- Mixed-use developments: Skyscrapers have contributed to the rise of mixed-use developments, which combine residential, commercial, and retail spaces in a single building. This approach promotes walkability, reduces reliance on cars, and creates more vibrant and diverse urban environments. For example, the Hudson Yards development in New York City integrates residential towers, office buildings, retail stores, and cultural venues into a single large-scale project.
The relationship between skyscrapers and urban planning is a complex and dynamic one. As cities continue to grow and evolve, urban planners will need to address the challenges and opportunities presented by these towering structures to create sustainable, livable, and equitable urban environments.
7. Sustainability
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainability in the design and construction of skyscrapers. This shift towards sustainable practices is driven by a combination of environmental concerns, economic factors, and changing societal values.
- Green Building Certifications: Green building certifications, such as LEED and BREEAM, have become widely adopted as a way to measure and verify the sustainability of skyscrapers. These certifications evaluate buildings based on their energy efficiency, water use, indoor environmental quality, and other sustainability factors.
- Energy Efficiency: Skyscrapers consume a significant amount of energy, particularly for h
eating, cooling, and lighting. Modern skyscrapers are incorporating energy-efficient technologies, such as double-glazed windows, LED lighting, and efficient HVAC systems, to reduce their energy consumption and carbon footprint. - Renewable Energy: Some skyscrapers are also incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, to generate their own clean energy. This helps to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and promote sustainable practices.
- Water Conservation: Water conservation is another important aspect of sustainable skyscraper design. Low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and drought-tolerant landscaping are some of the strategies used to reduce water consumption in these high-rise buildings.
The increasing focus on sustainability in skyscraper design is a positive trend that helps to mitigate the environmental impact of these towering structures. By incorporating sustainable practices, modern skyscrapers are becoming more energy-efficient, environmentally friendly, and healthier for occupants and the surrounding community as a whole.
8. Case studies
Case studies of iconic skyscrapers provide valuable insights into the evolution of skyscraper design, engineering, and construction. By examining these architectural marvels up close, we can gain a deeper understanding of the key concepts that have shaped skyscraper history.
- Architectural Innovation: Iconic skyscrapers often showcase groundbreaking architectural concepts and designs. The Burj Khalifa, for example, features a unique Y-shaped plan that enhances structural stability and maximizes views. By studying such case studies, we can learn from the innovative solutions employed by architects to overcome design challenges.
- Engineering Feats: Skyscrapers push the boundaries of engineering. The Taipei 101, known for its ability to withstand typhoons, demonstrates the advanced engineering techniques used to ensure the safety and stability of these towering structures. Case studies allow us to delve into the engineering principles and innovations that make such feats possible.
- Cultural Significance: Skyscrapers are often symbols of a city’s identity and cultural heritage. The Empire State Building, an Art Deco masterpiece, embodies the spirit of New York City. Case studies help us understand how skyscrapers reflect the cultural values and aspirations of the communities they are built in.
- Sustainable Practices: Modern skyscrapers increasingly incorporate sustainable design elements. The One World Trade Center, for example, features energy-efficient systems and rainwater harvesting. Case studies of sustainable skyscrapers provide practical examples of how eco-friendly practices can be integrated into high-rise architecture.
By examining iconic skyscrapers around the world, we gain a deeper understanding of the key concepts that have shaped skyscraper history. These case studies serve as valuable tools for architects, engineers, urban planners, and anyone interested in the evolution of these architectural wonders.
9. Future Trends
The history of skyscrapers is a testament to human ingenuity and the constant pursuit of architectural innovation. As we look towards the future, it is exciting to speculate on the trends that will shape the next generation of skyscrapers.
- Sustainability: As environmental concerns become increasingly pressing, skyscrapers will need to become more sustainable. This includes incorporating energy-efficient technologies, using renewable energy sources, and reducing water consumption. Some skyscrapers are already experimenting with vertical gardens and green roofs to improve air quality and reduce the urban heat island effect.
- Technology: Technological advancements will continue to play a major role in skyscraper design and construction. New materials, such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, promise to make buildings stronger and lighter. Smart technologies will be used to optimize building performance, improve occupant comfort, and enhance security.
- Mixed-use developments: Skyscrapers will increasingly be designed as mixed-use developments, combining residential, commercial, and retail spaces. This trend towards vertical communities will help to create more vibrant and sustainable urban environments. It also allows for better utilization of space and reduces the need for long commutes.
- Customization: Mass customization will become more common in skyscraper construction. This means that buildings will be tailored to the specific needs of their occupants, from the layout of the interior spaces to the amenities and services offered. 3D printing and other advanced manufacturing techniques will make it possible to create unique and customized building components.
The future of skyscraper design and construction is full of possibilities. By embracing sustainability, technology, mixed-use development, and customization, we can create skyscrapers that are more environmentally friendly, technologically advanced, and responsive to the needs of their occupants. These trends will undoubtedly shape the skylines of cities around the world in the years to come.
Skyscraper History FAQs
This section addresses frequently asked questions (FAQs) about the history of skyscrapers, providing concise and informative answers to common concerns and misconceptions.
Question 1: When were the first skyscrapers built?
The first buildings that can be considered skyscrapers emerged in the late 19th century, with the Home Insurance Building in Chicago (1885) and the New York World Building (1890) being notable examples.
Question 2: What were the key factors that enabled the construction of skyscrapers?
The development of new technologies, such as the elevator and steel-frame construction, along with the increasing demand for office space in dense urban areas, were key factors that made the construction of skyscrapers possible.
Question 3: How have architectural styles influenced skyscraper design?
Skyscrapers have showcased various architectural styles over time, from the ornate Gothic Revival and Art Deco styles of early skyscrapers to the sleek modernism of the International Style and the sustainable designs of contemporary skyscrapers.
Question 4: What is the tallest skyscraper in the world?
As of 2023, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai holds the title of the tallest skyscraper in the world, standing at an impressive height of 828 meters (2,717 feet).
Question 5: How do skyscrapers impact urban planning?
Skyscrapers have significantly influenced urban planning by altering city skylines, affecting transportation systems, and prompting the development of zoning regulations to manage their impact on the urban environment and ensure sustainable development.
Question 6: What are the future trends in skyscraper design and construction?
Future skyscraper designs are expected to focus on sustainability, incorporating energy-efficient technologies and sustainable materials. Technological advancements, mixed-use developments, and custo
mization will also shape the next generation of skyscrapers.
In conclusion, the history of skyscrapers is a fascinating journey of architectural innovation, engineering feats, and their impact on urban environments. These FAQs provide a brief overview of key aspects of skyscraper history, addressing common questions and highlighting future trends.
To learn more about skyscraper history, explore the other sections of this article for a comprehensive understanding of this captivating topic.
Tips Related to Skyscraper History
Delving into the history of skyscrapers offers valuable insights into architectural advancements and urban development. Here are some tips to enhance your understanding and appreciation of this fascinating topic:
Tip 1: Explore Iconic Skyscrapers:
Study renowned skyscrapers like the Empire State Building, Burj Khalifa, and Petronas Towers. Examine their architectural styles, engineering marvels, and cultural significance.
Tip 2: Understand the Role of Technology:
Recognize the impact of technological innovations, such as the elevator, steel-frame construction, and sustainable materials, on the evolution of skyscrapers.
Tip 3: Analyze Urban Planning Impacts:
Explore how skyscrapers have influenced urban planning, including zoning regulations, transportation systems, and the creation of mixed-use developments.
Tip 4: Trace the Historical Context:
Understand the economic, social, and cultural factors that have driven the construction of skyscrapers in different eras.
Tip 5: Appreciate Architectural Styles:
Identify the architectural styles that have shaped skyscraper design, from Gothic Revival to Art Deco and contemporary sustainable designs.
Tip 6: Consider Sustainability Trends:
Examine the increasing focus on sustainability in modern skyscraper construction, including energy efficiency, renewable energy sources, and green building certifications.
Tip 7: Explore Case Studies:
Analyze specific skyscraper case studies to gain in-depth knowledge of their design, engineering, and impact on the surrounding environment.
Tip 8: Stay Updated on Future Trends:
Keep abreast of emerging trends in skyscraper design and construction, such as the use of advanced materials, smart technologies, and customized building designs.
In conclusion, by following these tips, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of skyscraper history, appreciate the architectural marvels and engineering feats, and stay informed about future trends shaping the skylines of cities around the globe.
Skyscraper History
Skyscrapers, with their towering heights and architectural marvels, stand as testaments to human ingenuity and the pursuit of vertical expansion. Throughout history, they have reshaped skylines, revolutionized construction techniques, and left an indelible mark on urban landscapes. Their evolution is a captivating story of innovation, engineering feats, and cultural significance.
The exploration of skyscraper history unveils the intricate interplay between technology, economics, and architectural vision. From the early skyscrapers that pushed the boundaries of engineering to the modern skyscrapers that prioritize sustainability and mixed-use developments, these structures have consistently adapted to meet the changing needs of society. Understanding their history allows us to appreciate the remarkable achievements of architects, engineers, and builders, and to envision the possibilities that lie ahead.