Skyscrapers, defined as high-rise buildings exceeding 150 meters (492 feet) in height, are architectural marvels that have reshaped skylines worldwide. They serve as vertical cities, accommodating a multitude of functions, including residential, commercial, and recreational spaces.
The construction of skyscrapers has been driven by several factors, including the need for increased urban density, advancement in engineering techniques, and the desire for architectural prominence. They offer numerous advantages, such as efficient land utilization, reduced transportation demand, and stunning panoramic views. Historically, skyscrapers have played a pivotal role in shaping urban centers, becoming landmarks and symbols of economic prosperity.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the various aspects of skyscrapers, exploring their design, construction, and impact on society. We will also examine notable examples of skyscrapers and discuss the future of these architectural wonders.
1. Height
The extraordinary height of skyscrapers is an integral aspect that sets them apart from other buildings and defines their very essence. This verticality has far-reaching implications, shaping their design, function, and impact on the urban environment.
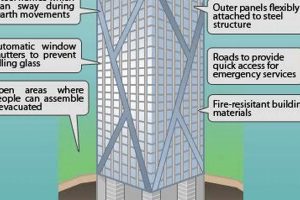
- Structural Innovation: To achieve such towering heights, skyscrapers require innovative engineering solutions and advanced construction techniques. These include reinforced concrete, steel frames, and advanced wind-bracing systems, enabling them to withstand lateral forces and seismic activity.
- Land Optimization: Skyscrapers offer a solution to the increasing demand for urban space by maximizing vertical development. They allow for high-density construction, accommodating a large population within a limited footprint. This efficient land utilization helps preserve valuable green spaces and reduces urban sprawl.
- Panoramic Views: The height of skyscrapers provides unparalleled panoramic views of the surrounding cityscape. These views are not only aesthetically pleasing but also offer practical advantages, such as enhanced natural lighting and reduced energy consumption for interior spaces.
- Architectural Landmark: Skyscrapers have become iconic landmarks, shaping the identity of cities and skylines worldwide. Their height and unique designs make them instantly recognizable symbols of urban progress and economic prosperity.
In conclusion, the height of skyscrapers is not merely a physical attribute but a defining characteristic that influences their design, functionality, and cultural significance. These towering structures stand as testaments to human ingenuity and the pursuit of vertical frontiers, transforming the urban landscape and contributing to the economic and cultural fabric of cities around the globe.
2. Design
In the realm of skyscrapers, design plays a paramount role in shaping their captivating forms and iconic identities. Architectural ingenuity and innovation converge to create structures that transcend mere functionality, becoming symbols of urban progress and cultural expression.
- Form and Function: Skyscrapers exemplify the harmonious integration of form and function. Their designs optimize space utilization while creating visually striking silhouettes. Structural elements, such as buttresses and setbacks, not only enhance stability but also contribute to their architectural aesthetic.
- Facade Engineering: The facades of skyscrapers are testaments to engineering prowess and artistic expression. Advanced materials, such as glass, metal, and composites, enable the creation of intricate patterns, textures, and effects. These facades not only enhance the building’s appearance but also contribute to energy efficiency and sustainability.
- Wind Engineering: Given their towering heights, skyscrapers must withstand significant wind forces. Wind engineering plays a crucial role in shaping their designs, ensuring structural integrity and occupant comfort. Aerodynamic features, such as tapered profiles and windbreaks, minimize wind resistance and enhance stability.
- Cultural Influences: Skyscrapers often reflect the cultural and architectural heritage of their. Design elements, such as traditional motifs, local materials, and historical references, are incorporated to create a sense of place and connect the building to its surroundings.
In conclusion, the design of skyscrapers is a symphony of architectural ingenuity and innovation, where form and function converge to create iconic structures. These buildings not only reshape skylines but also serve as canvases for artistic expression, reflecting the cultural and technological advancements of their time. As we continue to push the boundaries of design and engineering, skyscrapers will undoubtedly continue to captivate and inspire.
3. Function
The diverse functions of skyscrapers are a defining characteristic that sets them apart from traditional buildings. This versatility allows them to cater to the multifaceted needs of urban populations and create vibrant, self-contained communities within the vertical realm.
- Vertical Cities: Skyscrapers have evolved into vertical cities, accommodating a wide range of functions within a single structure. Residential units, offices, retail spaces, and recreational facilities coexist seamlessly, creating a dynamic and efficient urban environment.
- Mixed-Use Developments: Mixed-use skyscrapers combine different functions, such as residential, commercial, and hospitality, under one roof. This integrated approach promotes convenience, reduces commuting time, and fosters a sense of community.
- Vertical Transportation: Advanced vertical transportation systems, such as elevators and sky lobbies, enable efficient movement within skyscrapers. These systems seamlessly connect different zones, ensuring smooth and rapid transit for occupants.
- Amenity-Rich Living: Modern skyscrapers offer an array of amenities to enhance the living experience of residents. Rooftop gardens, fitness centers, swimming pools, and concierge services are becoming increasingly common, creating a luxurious and convenient lifestyle.
In conclusion, the diverse functions of skyscrapers transform them into microcosms of urban life, where living, working, shopping, and leisure activities converge. This multifunctional aspect not only optimizes space utilization but also contributes to the sustainability and vibrancy of cities, making skyscrapers essential components of modern urban landscapes.
4. Engineer
ing
Engineering plays a critical role in the construction and safety of all skyscrapers. Advanced engineering techniques are employed to ensure that these towering structures can withstand various forces and maintain structural integrity. These techniques include:
- Wind Engineering: Skyscrapers are subjected to strong wind forces, especially at higher altitudes. Wind engineering involves designing the building to minimize wind resistance and prevent excessive sway. Techniques such as aerodynamic shaping and wind tunnels are used to optimize the building’s form and mitigate wind-induced vibrations.
- Seismic Engineering: In earthquake-prone areas, skyscrapers must be designed to withstand seismic forces. This involves incorporating earthquake-resistant features, such as base isolation systems and energy-dissipating devices, which help reduce the impact of ground shaking on the building.
- Structural Analysis: Engineers use advanced computer modeling and analysis techniques to simulate the behavior of skyscrapers under various loading conditions. This helps identify potential structural weaknesses and optimize the design to ensure the building’s stability and safety.
The engineering techniques used in skyscrapers are crucial because they ensure the safety and well-being of occupants and the surrounding community. By understanding the importance of engineering in skyscrapers, we can appreciate the complexity and ingenuity involved in constructing these architectural marvels.
5. Density
Skyscrapers have become an essential solution in addressing the increasing need for urban density, especially in major metropolitan areas where land is scarce and expensive. Their ability to accommodate a large population within a limited footprint has led to several key implications and benefits:
- Efficient Land Utilization: Skyscrapers allow for more efficient use of land compared to traditional low-rise buildings. By concentrating residential, commercial, and other functions vertically, skyscrapers reduce urban sprawl and preserve valuable green spaces.
- Increased Population Density: Skyscrapers can accommodate a significantly higher population density than other building types. This increased density helps reduce traffic congestion, as residents and workers can live and work in the same area, minimizing commuting needs.
- Compact Urban Environments: The compact nature of skyscrapers promotes walkability and creates more vibrant and lively urban environments. With essential amenities and services within close proximity, residents can easily access their daily needs on foot.
- Reduced Infrastructure Costs: By concentrating a large population in a smaller area, skyscrapers can reduce the need for extensive infrastructure development, such as roads, utilities, and public transportation networks.
In summary, the density of skyscrapers plays a crucial role in addressing land scarcity, accommodating a growing population, promoting sustainable urban development, and reducing infrastructure costs. As cities continue to grow, skyscrapers will likely remain an integral part of urban planning strategies, ensuring efficient land use and creating livable and sustainable urban environments.
6. Sustainability
In the realm of skyscrapers, sustainability has emerged as a guiding principle, shaping the design and construction of these architectural giants to minimize their environmental impact. Modern skyscrapers are increasingly incorporating sustainable features to reduce energy consumption, conserve water, and promote overall environmental responsibility.
- Energy Efficiency: Energy-efficient lighting systems, double-glazed windows, and optimized building insulation are employed to reduce energy consumption. Some skyscrapers utilize renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, to further minimize their carbon footprint.
- Water Conservation: Water-efficient fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and greywater reuse techniques are implemented to conserve water. These measures reduce the strain on municipal water supplies and contribute to the preservation of natural resources.
- Green Materials: Sustainable materials, such as recycled steel, low-VOC paints, and FSC-certified wood, are used in the construction and interior design of skyscrapers. These materials minimize the environmental impact associated with material extraction, production, and disposal.
- Waste Management: Comprehensive waste management plans are implemented to reduce, reuse, and recycle waste generated during construction and operation. Some skyscrapers incorporate composting systems and waste-to-energy conversion technologies to further minimize their environmental impact.
The integration of sustainable features in modern skyscrapers not only reduces their environmental impact but also contributes to the overall livability and well-being of occupants. These buildings provide healthier indoor environments, reduce operating costs, and enhance the reputation of businesses and organizations that occupy them. As the world becomes increasingly aware of the need for sustainable practices, skyscrapers will continue to play a vital role in shaping more environmentally responsible urban landscapes.
7. Urbanization
Skyscrapers have become synonymous with urbanization, transforming the skylines of cities worldwide and serving as catalysts for urban development. Their towering presence not only reshapes the physical landscape but also influences the economic, social, and cultural dynamics of urban centers.
- Vertical Expansion: Skyscrapers enable cities to grow vertically, maximizing land use and accommodating a growing population within a limited footprint. This vertical expansion reduces urban sprawl and preserves valuable green spaces, contributing to more sustainable and compact urban environments.
- Economic Hubs: Skyscrapers often house corporate headquarters, financial institutions, and other businesses, creating vibrant economic centers within cities. They attract investment, generate employment opportunities, and contribute to the overall economic growth and prosperity of urban areas.
- Cultural Landmarks: Iconic skyscrapers become landmarks that define a city’s identity and cultural heritage. Their unique designs and architectural innovations attract tourists and contribute to the city’s global recognition and appeal.
- Mixed-Use Developments: Modern skyscrapers often incorporate mixed-use developments, combining residential, commercial, and recreational spaces within a single structure. This creates diverse and vibrant urban neighborhoods that cater to a wide range of needs and lifestyles.
In summary, skyscrapers play a multifacete
d role in urbanization, shaping the physical, economic, social, and cultural fabric of cities. They optimize land use, drive economic growth, create cultural landmarks, and foster vibrant mixed-use communities. As urbanization continues to shape the world’s population distribution, skyscrapers will undoubtedly remain central to the evolution and transformation of urban centers.
8. Economics
Skyscrapers serve as prominent symbols of economic prosperity and growth in cities worldwide. Their towering presence often reflects a thriving financial sector and a favorable business environment. Here are a few key facets that connect skyscrapers to economic development:
- Corporate Headquarters: Skyscrapers often house the headquarters of major corporations, banks, and financial institutions. These companies choose to locate in skyscrapers for their prestige, visibility, and accessibility to key business districts. By attracting these businesses, skyscrapers contribute to the city’s economic vitality and job market.
- Investment Opportunities: Skyscrapers represent significant investment opportunities for developers and real estate investors. The construction and ownership of skyscrapers can generate substantial returns, attracting capital and stimulating economic growth. Moreover, skyscrapers can increase property values in surrounding areas, leading to further economic development.
- Tourism and Hospitality: Iconic skyscrapers often become tourist destinations in their own right. Visitors flock to these architectural marvels to experience breathtaking views and unique experiences. As a result, skyscrapers can boost tourism revenue and support local businesses, including hotels, restaurants, and entertainment venues.
- Mixed-Use Developments: Modern skyscrapers often incorporate mixed-use developments, combining residential, commercial, and retail spaces. This creates vibrant and self-contained communities that attract businesses and residents alike. Mixed-use skyscrapers promote economic diversification and reduce reliance on a single industry.
In conclusion, skyscrapers play a crucial role in driving economic growth and prosperity in cities. They attract businesses, investments, and tourism, creating job opportunities and stimulating economic activity. As symbols of urban progress and affluence, skyscrapers continue to shape the economic landscapes of cities worldwide.
9. Culture
The cultural significance of skyscrapers extends beyond their economic and functional roles. They have become iconic landmarks, embodying the ambition, creativity, and technological advancements of the societies that build them. Skyscrapers transcend their physical presence and evolve into symbols of cultural identity and national pride.
The Empire State Building in New York City, for instance, stands as a testament to American resilience and the pursuit of architectural excellence. The Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur symbolize Malaysia’s economic and architectural innovation. Burj Khalifa in Dubai represents the United Arab Emirates’ unwavering ambition to push the boundaries of engineering and design.
Understanding the cultural significance of skyscrapers provides valuable insights into the motivations and aspirations of the societies that create them. It highlights the importance of architecture as a reflection of cultural values and aspirations. Moreover, it underscores the role of skyscrapers in shaping a city’s identity and attracting global recognition.
FAQs on Skyscrapers
Skyscrapers, architectural marvels that define skylines worldwide, have captured the imagination and sparked numerous questions. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions that delve into the fascinating world of skyscrapers:
Question 1: What defines a skyscraper?
Skyscrapers are generally defined as high-rise buildings exceeding 150 meters (492 feet) in height. They are distinguished by their towering stature and vertical orientation, often accommodating a mix of residential, commercial, and recreational spaces.
Question 2: What is the tallest skyscraper in the world?
As of 2023, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, holds the title of the tallest skyscraper in the world, standing at an impressive height of 828 meters (2,717 feet).
Question 3: How do skyscrapers withstand strong winds and earthquakes?
Skyscrapers employ advanced engineering techniques to ensure structural integrity and withstand various forces. Wind engineering minimizes wind resistance and sway, while seismic engineering incorporates earthquake-resistant features to mitigate the impact of ground shaking.
Question 4: Are skyscrapers efficient in terms of energy consumption?
Modern skyscrapers increasingly prioritize energy efficiency through sustainable design. Features such as energy-efficient lighting, double-glazed windows, and optimized insulation help reduce energy consumption.
Question 5: How do skyscrapers impact urban environments?
Skyscrapers play a significant role in shaping urban environments. They optimize land use, accommodate growing populations, and create vibrant mixed-use communities. However, careful urban planning is crucial to address potential challenges, such as overshadowing and wind effects on the street level.
Question 6: What is the future of skyscrapers?
The future of skyscrapers is expected to focus on sustainability, innovation, and well-being. Advanced materials, renewable energy sources, and smart building technologies will continue to transform skyscraper design and construction, aiming to create more sustainable, resilient, and human-centric vertical cities.
These FAQs provide a glimpse into the multifaceted world of skyscrapers, highlighting their architectural significance, engineering prowess, and impact on urban environments. As we continue to push the boundaries of vertical construction, skyscrapers will undoubtedly remain symbols of human ingenuity and ambition, shaping the skylines and communities of tomorrow.
…
Tips on Skyscrapers
Skyscrapers, as architectural marvels that dominate skylines, require careful planning and execution to ensure their success. Here are essential tips to consider when designing, constructing, and managing skyscrapers:
Tip 1: Prioritize Structural Integrity
Skyscrapers must withstand various forces, including wind and seismic activity. Employ advanced engineering techniques, such as wind engineering and seismic isolation, to ensure structural stability and occupant safety.
Tip 2: Optimize Energy Efficiency
Incorporate sustainable design principles to minimize energy consumption. Use energy-efficient lighting, insulation, and renewable energy sources to reduce operating costs and environmental impact.
Tip 3: Enhance Indoor Air Quality
Provide proper ventilation and air filtration systems to maintain healthy indoor air quality for occupants. Consider green building materials and low-VOC finishes to minimize air pollution.
Tip 4: Consider Mixed-Use Developments
Create vibrant and self-contained communities by incorporating mixed-use developments. Integrate residential, comme
rcial, and recreational spaces to promote walkability and reduce reliance on private vehicles.
Tip 5: Focus on Tenant Comfort
Design skyscrapers with tenant comfort in mind. Provide ample natural light, ergonomic workspaces, and amenities that enhance occupant well-being and productivity.
Tip 6: Integrate Smart Building Technologies
Implement smart building technologies to improve efficiency, safety, and occupant experience. Utilize sensors, automation, and data analytics to optimize energy consumption, enhance security, and provide personalized services.
Tip 7: Encourage Sustainable Practices
Promote sustainability throughout the skyscraper’s lifecycle. Encourage waste reduction, water conservation, and responsible waste management practices among occupants and management.
Tip 8: Plan for Future Adaptability
Design skyscrapers with flexibility and adaptability in mind. Anticipate future changes in technology, tenant needs, and urban environments to ensure the building remains relevant and functional over its lifetime.
By incorporating these tips into skyscraper design and management, architects, engineers, and building owners can create sustainable, resilient, and human-centric vertical cities that meet the needs of present and future generations.
Conclusion
Skyscrapers, architectural marvels that redefine skylines and reshape urban landscapes, have left an indelible mark on human civilization. Their towering heights, innovative designs, and multifunctional capabilities have transformed the way we live, work, and interact with our surroundings. From maximizing land use and accommodating growing populations to serving as symbols of economic prosperity and cultural ambition, skyscrapers have become essential components of modern cities.
As we continue to push the boundaries of architectural innovation and sustainability, the future of skyscrapers holds exciting possibilities. The integration of smart technologies, sustainable materials, and human-centric design principles will undoubtedly shape the next generation of vertical cities. These skyscrapers will not only be architectural wonders but also beacons of environmental consciousness and well-being. By embracing innovation and collaboration, we can create skyscrapers that meet the evolving needs of our planet and its inhabitants, ensuring that these architectural giants continue to inspire and elevate urban living for generations to come.