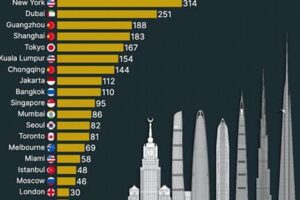
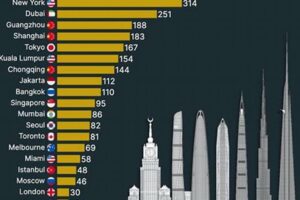
Skyscrapers, towering structures that define modern skylines, have become a prominent feature in many European cities, transforming their urban landscapes and contributing to their economic and cultural development. These architectural marvels, reaching unprecedented heights, offer breathtaking views, provide ample office and residential space, and serve as landmarks that symbolize progress and innovation.
The presence of skyscrapers in European cities brings numerous benefits. They optimize land usage in densely populated areas, accommodating a substantial number of people and businesses within a limited footprint. Moreover, skyscrapers enhance a city’s prestige and global recognition, attracting tourism and investment. They also promote sustainability by incorporating energy-efficient designs and reducing urban sprawl.
The history of skyscrapers in Europe dates back to the early 20th century, with the construction of buildings like the Torre Velasca in Milan and the Warsaw Trade Tower in Poland. However, the most significant growth in skyscraper development occurred after the 1950s, particularly in cities such as London, Paris, and Frankfurt. Today, many European cities boast impressive skylines dotted with iconic skyscrapers, such as The Shard in London, the Tour Montparnasse in Paris, and the Commerzbank Tower in Frankfurt.
1. Height
In the context of “european cities with skyscrapers,” the height of these structures is a defining characteristic that significantly contributes to their impact on the urban landscape and beyond. Skyscrapers, with their towering heights, dominate the skyline, becoming iconic landmarks that symbolize progress, innovation, and economic power. Their sheer size commands attention and reshapes the way we perceive and interact with the city.
The height of skyscrapers offers several advantages. Firstly, it allows for efficient land use in densely populated urban centers. By building upwards, cities can accommodate a large number of people and businesses within a relatively small footprint. This vertical growth helps alleviate urban sprawl, preserving green spaces and reducing traffic congestion.
Moreover, the height of skyscrapers enhances a city’s prestige and global recognition. Towering structures become symbols of a city’s ambition and modernity, attracting tourism and investment. They create a distinct and memorable skyline that can be easily identified and associated with a particular city. For example, the Shard in London, with its distinctive pyramid shape, has become synonymous with the city’s financial district, while the Eiffel Tower in Paris is a globally recognized icon.
In addition to their symbolic and practical value, the height of skyscrapers also presents engineering and architectural challenges. Constructing these towering structures requires innovative engineering solutions to ensure stability and safety. Architects must carefully consider factors such as wind resistance, seismic activity, and building materials to create skyscrapers that can withstand the forces of nature and provide a safe and comfortable environment for occupants.
In conclusion, the height of skyscrapers in European cities is not merely a physical attribute but a key factor that shapes their urban identity, economic development, and global perception. These soaring structures dominate the skyline, symbolizing progress, innovation, and the ambition of the cities they inhabit.
2. Density
In the context of European cities with skyscrapers, density plays a crucial role in optimizing land use within densely populated urban environments. Skyscrapers, by their very nature, allow cities to accommodate a large number of people and businesses within a relatively small footprint. This vertical growth strategy offers several advantages and implications:
- Efficient Land Utilization: Skyscrapers maximize land use by building upwards, reducing urban sprawl and preserving valuable green spaces. This is particularly important in densely populated European cities where land is scarce and expensive. For example, London, a city with a population of over 9 million people, has embraced high-rise development to accommodate its growing population while preserving its green spaces, such as Hyde Park and Regent’s Park.
- Reduced Traffic Congestion: By concentrating people and businesses in vertical structures, skyscrapers help reduce traffic congestion by minimizing the need for long commutes. This is achieved by creating mixed-use developments that integrate residential, commercial, and retail spaces within the same building or complex. This approach promotes walkability and reduces reliance on cars, contributing to a more sustainable and livable urban environment.
- Enhanced Public Transportation: Densely populated areas with skyscrapers often have well-developed public transportation systems, such as subways, buses, and trains. This efficient public transportation infrastructure supports the movement of large numbers of people within the city, reducing traffic congestion and promoting accessibility for all. For example, cities like Paris and Frankfurt have extensive metro systems that seamlessly connect skyscraper districts with other parts of the city.
- Economic Vitality: Skyscrapers can act as catalysts for economic growth and vitality. They attract businesses, investors, and skilled workers, creating a vibrant and diverse urban economy. The concentration of businesses and services in close proximity fosters innovation, collaboration, and economic opportunities. For instance, the Canary Wharf development in London, a cluster of skyscrapers housing financial institutions and businesses, has transformed the city’s economic landscape.
In conclusion, the density achieved through skyscrapers in European cities is not merely a matter of maximizing space but a strategic approach to optimizing land use, reducing traffic congestion, enhancing public transportation, and fostering economic vitality. By building upwards, these cities can accommodate their growing populations, preserve green spaces, and create vibrant and sustainable urban environments.
3. Prestige
Skyscrapers have become synonymous with global cities, enhancing their recognition and appeal on the world stage. These towering structures symbolize a city’s ambition, modernity, and economic power, attracting tourists, investors, and businesses alike.
- Landmark Status
Skyscrapers are often iconic landmarks that define a city’s skyline and become symbols of its identity. The Eiffel Tower in Paris, the Shard in London, and the Co
mmerzbank Tower in Frankfurt are just a few examples of skyscrapers that have become instantly recognizable symbols of their respective cities. - Tourism and Economic Growth
Skyscrapers attract tourists from around the world, who come to admire their architectural prowess and enjoy the panoramic views they offer. This influx of tourism generates revenue and supports local businesses. For example, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai has become a major tourist destination, attracting millions of visitors each year and contributing significantly to the city’s economy. - Investment and Business Opportunities
Cities with impressive skylines are often seen as attractive investment destinations. Skyscrapers provide modern and prestigious office spaces for multinational corporations and financial institutions, fostering economic growth and job creation. London’s Canary Wharf, once a neglected docklands area, has been transformed into a thriving business district thanks to its cluster of skyscrapers. - Cultural and Artistic Hubs
Skyscrapers can also serve as cultural and artistic hubs, housing museums, art galleries, and performance spaces. The One World Trade Center in New York City, for example, includes a performing arts center and a museum dedicated to the history of the Twin Towers. These cultural amenities enhance the city’s appeal and make it a more vibrant and desirable place to live and visit.
In conclusion, the prestige associated with skyscrapers contributes significantly to the global recognition and appeal of European cities. These towering structures not only reshape skylines but also attract tourism, investment, and businesses, while fostering cultural and artistic endeavors. As a result, skyscrapers have become integral to the identity and prosperity of many European cities.
4. Sustainability
In the context of European cities with skyscrapers, sustainability plays a crucial role in shaping the development and impact of these towering structures. Skyscrapers, by their very nature, have the potential to consume significant energy and contribute to urban sprawl. However, innovative design strategies and thoughtful urban planning can mitigate these concerns, creating sustainable skyscrapers that enhance the livability and environmental performance of European cities.
- Energy Efficiency
Modern skyscrapers incorporate energy-efficient technologies and design features to minimize their environmental impact. These include high-performance building envelopes that reduce heat loss and gain, efficient lighting systems, and renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines. For example, the Torre Hadid in Milan, Italy, utilizes a double-skin facade that acts as a thermal buffer, reducing energy consumption by 40%. - Reduced Urban Sprawl
Skyscrapers, by building upwards, help reduce urban sprawl by accommodating a significant number of people and businesses within a compact footprint. This vertical growth strategy preserves valuable green spaces and agricultural land, promoting a more sustainable and livable urban environment. For example, the high-density development of skyscrapers in London’s Canary Wharf has helped protect the city’s green belt, a vital recreational and ecological resource for the city’s residents. - Green Building Certifications
Many skyscrapers in European cities have achieved green building certifications, such as LEED or BREEAM, which recognize their commitment to sustainability. These certifications assess buildings based on their energy efficiency, water usage, indoor environmental quality, and other factors. By meeting these rigorous standards, skyscrapers demonstrate their commitment to environmental responsibility and contribute to the overall sustainability of the urban environment. - Mixed-Use Developments
Skyscrapers are often part of mixed-use developments that integrate residential, commercial, and retail spaces within the same building or complex. This approach promotes walkability, reduces reliance on cars, and creates vibrant and sustainable neighborhoods. For example, the MAXXI Museum in Rome, Italy, is a mixed-use development that combines exhibition spaces, a library, offices, and a restaurant, fostering cultural exchange and reducing the need for long commutes.
In conclusion, the sustainability of European cities with skyscrapers is not merely an afterthought but a fundamental consideration that shapes their design, construction, and operation. By incorporating energy-efficient technologies, reducing urban sprawl, achieving green building certifications, and promoting mixed-use developments, these skyscrapers contribute to a more sustainable and livable urban environment, ensuring the long-term prosperity and well-being of European cities.
5. History
The history of skyscraper architecture in Europe is intricately linked to the development of European cities with skyscrapers. Skyscrapers, as we know them today, are a relatively recent phenomenon in Europe, with their origins in the late 19th century. However, the roots of skyscraper architecture can be traced back to earlier periods, and the evolution of this architectural form has played a significant role in shaping the skylines and urban landscapes of European cities.
- Early Influences: The concept of tall buildings has existed for centuries in Europe, with structures such as castles, cathedrals, and towers serving as prominent landmarks in many cities. These early structures influenced the development of skyscraper architecture by demonstrating the possibilities of building tall and the use of innovative construction techniques.
- Industrial Revolution: The Industrial Revolution in the 19th century brought about new technologies and materials that made the construction of taller buildings possible. The use of steel frames and elevators allowed architects to design buildings that were both tall and structurally sound.
- Art Nouveau and Art Deco: The Art Nouveau and Art Deco movements in the late 19th and early 20th centuries had a significant impact on skyscraper architecture. These styles emphasized ornamentation, curved lines, and geometric motifs, which were incorporated into the design of many early skyscrapers, giving them a distinctive and elegant appearance.
- Post-World War II Reconstruction: After the devastation of World War II, many European cities embarked on ambitious reconstruction projects. Skyscrapers played a central role in these efforts, as they offered a way to quickly and efficiently provide much-needed office and residential space in densely populated urban areas.
The evolution of skyscraper architecture in Europe has continued in the postwar period, with new technologies and design trends leading to the construction of ever taller and more innovative buildings. Today, skyscrapers are a defining feature of many European cities, symbolizing progress, economic power, and architectural achievement.
6. Diversity
The diversity of architectural styles and designs showc
ased in European cities with skyscrapers is a testament to the creativity and innovation of architects and engineers. This diversity has played a significant role in shaping the unique character and identity of each city, contributing to their cultural and architectural heritage.
One of the key factors that has contributed to the diversity of skyscraper architecture in Europe is the rich architectural history of the continent. European cities have been home to a wide range of architectural styles over the centuries, from Gothic to Renaissance to Baroque. This diversity of styles has provided a foundation for architects to draw upon when designing skyscrapers, resulting in a wide range of buildings that reflect different eras and influences.
Another factor that has contributed to the diversity of skyscraper architecture in Europe is the influence of different cultures and traditions. European cities have been shaped by a variety of cultural influences, from the Roman Empire to the Middle Ages to the present day. This has resulted in a mix of architectural styles that can be seen in the skyscrapers of European cities, from the classical lines of the Torre Velasca in Milan to the futuristic form of the Gherkin in London.
The diversity of skyscraper architecture in European cities has a number of practical benefits. It creates a visually interesting and stimulating urban environment, and it helps to preserve the architectural heritage of European cities. Additionally, the diversity of skyscraper architecture can help to attract tourism and investment, as visitors are drawn to cities with unique and iconic buildings.
In conclusion, the diversity of architectural styles and designs showcased in European cities with skyscrapers is a reflection of the continent’s rich architectural history and cultural diversity. This diversity has contributed to the creation of a visually interesting and stimulating urban environment, and it has helped to preserve the architectural heritage of European cities.
7. Economic Drivers
Skyscrapers have become powerful economic drivers for European cities, attracting investment, tourism, and business. The presence of iconic skyscrapers in a city’s skyline can enhance its prestige and global recognition, making it a more attractive destination for investors and tourists alike.
For example, the construction of the Shard in London has attracted significant investment in the surrounding area, leading to the development of new businesses, hotels, and residential properties. Similarly, the Torre Picasso in Madrid has become a symbol of the city’s financial district, attracting major banks and corporations to locate their headquarters there.
Skyscrapers can also be a major draw for tourists. The Eiffel Tower in Paris, one of the world’s most recognizable landmarks, attracts millions of visitors each year. These visitors contribute to the local economy by spending money on hotels, restaurants, and other tourist attractions.
In addition to attracting investment and tourism, skyscrapers can also help to attract businesses. The presence of a skilled workforce and modern infrastructure in skyscraper districts makes them attractive locations for businesses of all sizes. For example, the Canary Wharf development in London has become a major hub for financial services firms, while the La Dfense district in Paris is home to many technology companies.
Overall, the economic benefits of skyscrapers for European cities are significant. Skyscrapers can attract investment, tourism, and business, which can lead to job creation, increased tax revenue, and a higher standard of living for residents.
FAQs on European Cities with Skyscrapers
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions surrounding European cities with skyscrapers, providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: What are the tallest skyscrapers in Europe?
Answer: As of 2023, the tallest skyscraper in Europe is the Lakhta Center in Saint Petersburg, Russia, standing at 462 meters (1,516 feet) tall. Other notable skyscrapers include the Mercury City Tower in Moscow, the One Canada Square in London, and the Torre PwC in Madrid.
Question 2: Which European city has the most skyscrapers?
Answer: Moscow currently has the highest number of skyscrapers in Europe, with over 50 buildings exceeding 150 meters (492 feet) in height. Other cities with a significant number of skyscrapers include London, Paris, Frankfurt, and Istanbul.
Question 3: Are skyscrapers common in European cities?
Answer: While skyscrapers are not as ubiquitous in Europe as they are in cities like New York or Hong Kong, they have become increasingly common in major European cities in recent decades. Skyscrapers are often seen as symbols of economic prosperity and modernity, and they can contribute to a city’s skyline and overall identity.
Question 4: What are the benefits of building skyscrapers in European cities?
Answer: Skyscrapers offer several advantages for European cities, including increased density and efficient land use, reduced urban sprawl, enhanced prestige and global recognition, and the potential for sustainable design and energy efficiency. They can also serve as hubs for business, finance, and tourism.
Question 5: Are there any concerns or challenges associated with skyscrapers in European cities?
Answer: While skyscrapers can provide many benefits, there are also potential challenges to consider. These include the need for careful planning and urban design to ensure compatibility with the surrounding environment, the potential impact on historical and cultural heritage, and the importance of sustainable construction practices.
Question 6: What is the future of skyscrapers in European cities?
Answer: The future of skyscrapers in European cities is likely to be shaped by factors such as technological advancements in sustainable design and construction, the increasing demand for urban density and efficiency, and the ongoing evolution of architectural styles and urban planning.
In summary, skyscrapers have become a notable feature of many European cities, offering both benefits and challenges. As cities continue to grow and evolve, skyscrapers are likely to remain a part of the urban landscape, albeit with a focus on sustainable and context-sensitive design.
This concludes our exploration of frequently asked questions on European cities with skyscrapers.
Transition to the next article section:
Click here to learn more about the history and development of skyscrapers in Europe.
Tips for Designing and Constructing Skyscrapers in European Cities
Skyscrapers have become an integral part of the skyline of many European cities. However, designing and constructing skyscrapers in these cities presents unique challenges and opportunities. Here are a few tips to consider:
Tip 1: Consider the historical and cultural context.
When designing a skyscraper in a European city, it is important to consider the historical and cultural context of the surroundings. The skyscraper should be designed in a way that is respectful of the existing architecture and urban fabric.
Tip 2: Prioritize sustainability.
Skyscrapers can be energy-intensive buildings. Therefore, it is import
ant to prioritize sustainability in the design and construction process. This can be done by using energy-efficient materials and technologies, and by incorporating green features such as rooftop gardens and rainwater harvesting systems.
Tip 3: Create a mixed-use development.
Skyscrapers can be used to create mixed-use developments that include residential, commercial, and retail space. This can help to create a more vibrant and sustainable urban environment.
Tip 4: Invest in public transportation.
Skyscrapers can attract a large number of people to a small area. Therefore, it is important to invest in public transportation to ensure that people can easily access the skyscraper and the surrounding area.
Tip 5: Create a sense of place.
Skyscrapers should be designed to create a sense of place. This can be done by creating public spaces at the base of the skyscraper, and by incorporating public art and other amenities.
By following these tips, architects and developers can design and construct skyscrapers that are sensitive to the unique challenges and opportunities of European cities.
Conclusion:
Skyscrapers can be a valuable addition to European cities. However, it is important to design and construct them in a way that is respectful of the historical and cultural context, and that prioritizes sustainability and livability.
Conclusion
Skyscrapers have become an increasingly prominent feature of European cities, reshaping skylines and contributing to economic growth, cultural vibrancy, and sustainable development. Their presence has brought numerous benefits, including efficient land use, reduced urban sprawl, enhanced prestige and global recognition, and the potential for incorporating sustainable design and energy efficiency.
As European cities continue to evolve, skyscrapers will likely remain an integral part of their urban fabric. However, it is crucial to approach their design and construction with careful planning and consideration for the historical, cultural, and environmental context. By embracing sustainable practices, prioritizing mixed-use developments, investing in public transportation, and creating a sense of place, architects, developers, and urban planners can ensure that skyscrapers continue to contribute positively to the identity and prosperity of European cities.