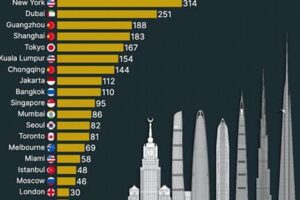
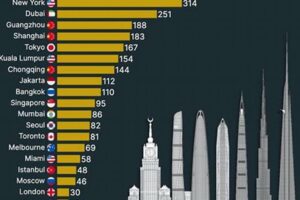
Skyscrapers are very tall buildings and are often used for commercial or residential purposes. They are typically found in large cities and are often seen as a symbol of economic prosperity. Skyscrapers have been built for centuries, but their popularity has increased dramatically in recent decades as cities have grown and land has become more scarce.
There are many different types of skyscrapers, but they all share some common features. Skyscrapers are typically built with a steel frame and have a concrete core. They are also typically clad in glass or metal. Skyscrapers are designed to be resistant to earthquakes and other natural disasters. They are also equipped with a variety of safety features, such as fire sprinklers and smoke detectors.
Skyscrapers have a number of advantages over other types of buildings. They are more efficient use of space, as they can accommodate more people and businesses in a smaller area. They are also more energy-efficient, as they can be designed to take advantage of natural light and ventilation. Skyscrapers can also be more environmentally friendly, as they can be built to LEED standards.
However, Skyscrapers also have some disadvantages. They can be expensive to build and maintain. They can also be difficult to evacuate in the event of an emergency. Additionally, Skyscrapers can cast a shadow over nearby buildings and can block views.
Skyscrapers are a significant part of the cityscape and are often seen as a symbol of economic prosperity. They are a marvel of engineering and continue to be built in cities around the world.
1. Height
Skyscrapers, with their towering heights, are a defining characteristic of modern cityscapes. Their verticality is not merely an architectural statement but also a response to the challenges and opportunities of urban environments.
- Efficient Land Use: Skyscrapers maximize land utilization in densely populated urban areas, allowing for more people and businesses to be accommodated within a limited footprint.
- Breathtaking Views: The height of skyscrapers offers unparalleled panoramic views of the city and its surroundings, creating a sense of grandeur and exclusivity for occupants.
- Vertical Communities: Skyscrapers foster a sense of community among their residents and workers, who share amenities, common spaces, and a unique urban lifestyle.
- Architectural Prowess: The construction of skyscrapers pushes the boundaries of engineering and design, showcasing innovative techniques and materials that redefine the limits of architectural possibilities.
The height of skyscrapers is not just a matter of aesthetics; it is a testament to human ingenuity and a reflection of the dynamic and ever-evolving nature of urban environments. As cities continue to grow and evolve, skyscrapers will remain a vital part of their fabric, reaching towards the heavens and shaping the skylines of the future.
2. Structure
The structural integrity of skyscrapers is paramount, ensuring the safety and longevity of these towering giants. Steel frames and concrete cores play a crucial role in providing the strength and stability necessary to withstand various forces and environmental conditions.
- Steel Frames:
Steel frames form the backbone of skyscrapers, providing exceptional strength and rigidity. The interlocking steel beams and columns create a robust framework that can resist high winds, earthquakes, and other lateral forces.
- Concrete Cores:
Concrete cores are the central load-bearing elements of skyscrapers. Made from reinforced concrete, these cores provide vertical support and stability, transferring the weight of the building down to the foundation.
- Composite Action:
The combination of steel frames and concrete cores creates a composite structure that maximizes strength and stability. The steel frame provides tensile strength, while the concrete core resists compression. This composite action ensures the skyscraper’s ability to withstand bending and other forces.
- Seismic Resistance:
In earthquake-prone areas, skyscrapers are designed with special structural features to resist seismic forces. Steel frames and concrete cores are reinforced with additional bracing and dampening systems to minimize lateral sway and protect the building from collapse.
The structural integrity of skyscrapers is a testament to the ingenuity and engineering prowess of architects and engineers. Steel frames and concrete cores work in harmony to create towering structures that are both safe and resilient, shaping the skylines of cities worldwide.
3. Facade
The facades of skyscrapers play a crucial role in shaping the aesthetics and functionality of these towering structures. Glass and metal facades, in particular, have become synonymous with modern skyscrapers, creating a dynamic interplay of light and shadow that transforms the urban landscape.
The use of glass facades allows for maximum natural light penetration, reducing the need for artificial lighting and creating brighter, more inviting interiors. The reflective properties of glass and metal facades create a shimmering effect, adding a touch of glamour and sophistication to the cityscape. This interplay of light and shadow adds depth and dimension to buildings, making them visually captivating and iconic.
Beyond aesthetics, glass and metal facades offer practical benefits as well. They provide excellent thermal insulation, helping to regulate the interior temperature of skyscrapers and reducing energy consumption. The reflective surfaces can also help mitigate the urban heat island effect, reducing the overall temperature of the city.
The facades of skyscrapers are not merely decorative elements; they are integral to the identity and functionality of these architectural marvels. Glass and metal facades, with their shimmering reflections and dynamic interplay of light and shadow, have become a defining characteristic of modern skyscrapers, shaping the skylines of cities around the world.
4. Function
Skyscrapers, with their towering heights and expansive floor plans, offer a unique opportunity to accommodate a multitude of uses wi
thin a single structure. This multifunctional aspect is a defining characteristic of skyscrapers and plays a significant role in their integration into the fabric of big city downtown buildings.
The combination of offices, residential units, and retail spaces within skyscrapers creates a vibrant and self-contained urban environment. Office workers, residents, and shoppers can easily access a wide range of amenities and services without having to venture far from the building. This mixed-use approach promotes walkability, reduces traffic congestion, and fosters a sense of community within the skyscraper and its surrounding area.
For example, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the tallest building in the world, houses a mix of residential apartments, corporate offices, a luxury hotel, and a shopping mall. This integration of diverse functions makes the Burj Khalifa a true vertical city, where residents and visitors can live, work, shop, and dine without ever having to leave the building.
The multifunctional nature of skyscrapers also allows for greater flexibility in urban planning. By combining multiple uses within a single structure, cities can optimize land use and create more compact and sustainable urban environments. This is especially important in densely populated downtown areas, where land is scarce and expensive.
In conclusion, the multifunctional aspect of skyscrapers is a key component of their integration into the fabric of big city downtown buildings. By accommodating a multitude of uses within a single structure, skyscrapers promote walkability, reduce traffic congestion, foster a sense of community, and optimize land use. This multifunctional approach is a defining characteristic of skyscrapers and contributes to their role as iconic landmarks and vibrant hubs of urban activity.
5. Density
Skyscrapers, with their towering heights, play a crucial role in maximizing land use within densely populated urban centers. By building upwards, skyscrapers can accommodate a significant number of people and businesses within a relatively small footprint, making them an essential component of “clipart skyscrapers big city downtown buildings”.
The density achieved by skyscrapers offers several advantages. Firstly, it reduces the urban sprawl that can occur when buildings are spread out over a large area. This helps to preserve green spaces, parks, and other amenities that are vital for the well-being of city residents. Secondly, dense urban environments promote walkability and reduce the need for car usage, leading to lower transportation costs and emissions.
Real-life examples of the practical significance of skyscraper density can be found in cities around the world. For instance, in New York City, skyscrapers have allowed the city to house millions of people and countless businesses within a relatively small geographic area. This density has fostered a vibrant and dynamic urban environment, with a diverse mix of residential, commercial, and cultural activities coexisting in close proximity.
Understanding the importance of density in the context of “clipart skyscrapers big city downtown buildings” is crucial for architects, urban planners, and policymakers. By maximizing land use through the construction of skyscrapers, cities can create more compact, sustainable, and livable environments. This approach promotes economic growth, social interaction, and environmental conservation, all of which are essential elements of thriving urban centers.
6. Sustainability
In the context of “clipart skyscrapers big city downtown buildings,” sustainability plays a crucial role in shaping the design and construction of modern skyscrapers. As cities strive to reduce their environmental impact and promote sustainable urban development, eco-friendly features have become an integral part of skyscraper design.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern skyscrapers incorporate energy-efficient lighting systems, appliances, and building materials to minimize energy consumption. This not only reduces operating costs but also contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with the growing demand for environmentally conscious building practices.
- Water Conservation: Rainwater harvesting systems collect and store rainwater for non-potable uses such as irrigation and toilet flushing. This helps reduce the strain on municipal water supplies, particularly in densely populated urban areas where water scarcity is a growing concern.
- Green Roofs and Facades: Green roofs and facades, covered with vegetation, provide insulation, reduce urban heat island effects, and improve air quality. They also create habitats for urban wildlife, contributing to biodiversity conservation within the concrete jungle of big cities.
- Sustainable Materials: Architects and builders are increasingly using sustainable materials, such as recycled steel and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) paints, in the construction of skyscrapers. These materials minimize the environmental impact of the building throughout its life cycle.
By incorporating these eco-friendly features, modern skyscrapers not only meet the demands of sustainable urban development but also contribute to the creation of healthier and more livable cities for future generations.
7. Connection between "Icons
Famous skyscrapers, like the Empire State Building and Burj Khalifa, have transcended their original purpose and become iconic landmarks, recognized worldwide. Their distinctive designs, towering heights, and cultural significance have made them symbols of architectural prowess and urban identity.
- Cultural Significance: Iconic skyscrapers often embody the spirit and aspirations of the cities they reside in. They serve as symbols of national pride, economic prosperity, and architectural achievement, shaping the cultural identity and heritage of urban centers.
- Architectural Innovation: These skyscrapers showcase groundbreaking engineering and design concepts, pushing the boundaries of architectural possibilities. Their innovative forms, structural systems, and facade designs inspire future generations of architects and engineers.
- Tourist Attractions: Iconic skyscrapers attract tourists from around the world. Observation decks, restaurants, and interactive exhibits provide visitors with breathtaking views and insights into the history and significance of these architectural marvels.
- Economic Drivers: Iconic skyscrapers often serve as catalysts for urban renewal and economic development. They attract businesses, investment, and tourism, creating jobs and stimulating the local economy.
In the context of “clipart skyscrapers big city downtown buildings,” iconic skyscrapers serve as aspirational models for architects and designers. They demonstrate the transformative power of architecture in shaping urban landscapes and creating landmarks that become symbols of cultural identity and global recognition.
8. Urban Impact
Skyscrapers, with their imposing heights and striking designs, are not just architectural marvels but also have a profound impact on the urban environment. Their presence transforms city skylines, influences microclimates, and contributes to the overall character of urban spaces.
- City Skylines: Skyscrapers redefine the vertical landscape of cities, creating iconic skylines that are recognized worldwide. They become symbols of urban identity and landmarks that shape the visual identity of a city from afar.
- Microclimates: Skyscrapers can influence local microclimates by creating wind tunnels, casting shadows, and altering temperature patterns. Tall buildings can channel winds, creating strong gusts at street level, while the dense concentration of buildings can reduce sunlight and increase humidity.
- Urban Character: Skyscrapers can influence the overall character of urban environments. Their presence can create a sense of grandeur, excitement, and dynamism. However, they can also contribute to feelings of congestion and alienation if not carefully integrated into the urban fabric.
- Sense of Place: Iconic skyscrapers can become landmarks that define a city’s sense of place. They create focal points, provide orientation, and contribute to the collective memory and identity of urban residents.
In the context of “clipart skyscrapers big city downtown buildings,” understanding the urban impact of skyscrapers is crucial for architects, urban planners, and policymakers. It helps them design and manage urban environments that are both visually striking and livable, creating cities that are not only impressive but also sustainable and human-centric.
Frequently Asked Questions about Skyscrapers
Skyscrapers, with their towering heights and impressive designs, are iconic structures that have become synonymous with big city skylines. However, there are many common questions and misconceptions surrounding these architectural marvels. This FAQ section aims to shed light on some of the most frequently asked questions about skyscrapers, providing informative answers to enhance your understanding of these remarkable structures.
Question 1: What is the tallest skyscraper in the world?
Currently, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, holds the title of the tallest skyscraper in the world, standing at an awe-inspiring height of 828 meters (2,717 feet).
Question 2: How are skyscrapers able to withstand strong winds and earthquakes?
Skyscrapers employ various structural engineering techniques to ensure their stability and resilience against strong winds and earthquakes. These techniques include the use of reinforced concrete cores, steel frames, and dampers, which work together to absorb and distribute forces, minimizing the risk of structural failure.
Question 3: Are skyscrapers energy-efficient?
Modern skyscrapers incorporate sustainable design features to enhance their energy efficiency. These features may include energy-efficient lighting systems, double-glazed windows, and building materials with high thermal insulation, reducing energy consumption and contributing to a greener urban environment.
Question 4: How do skyscrapers affect the surrounding urban environment?
Skyscrapers can have a significant impact on their surrounding urban environment. They may cast shadows on nearby buildings, alter wind patterns, and contribute to the urban heat island effect. However, careful urban planning and architectural design can mitigate these impacts, ensuring a harmonious integration of skyscrapers into the urban fabric.
Question 5: What are the safety features incorporated into skyscrapers?
Skyscrapers are designed with a comprehensive array of safety features to ensure the well-being of occupants and visitors. These features include fire sprinkler systems, smoke detectors, emergency staircases, and advanced fire suppression technologies, providing multiple layers of protection in the event of an emergency.
Question 6: How do skyscrapers contribute to the economy and urban development?
Skyscrapers play a vital role in urban development by providing space for businesses, offices, and residential units, accommodating a large population within a compact area. They act as economic hubs, attracting investment, generating employment opportunities, and contributing to the overall prosperity of the city.
These are just a few of the frequently asked questions about skyscrapers. Understanding these aspects provides valuable insights into the design, construction, and impact of these architectural wonders, helping us appreciate their significance in shaping our urban landscapes.
—————
Transition to the next article section:
Skyscrapers continue to captivate our imagination and push the boundaries of architectural innovation. As cities evolve and technology advances, we can expect to see even more remarkable and sustainable skyscrapers gracing our skylines in the years to come.
Skyscraper Design and Functionality Tips
Skyscrapers, as prominent landmarks in urban environments, require careful planning and innovative design to ensure their functionality and aesthetic appeal. Here are some valuable tips to consider when designing and constructing skyscrapers:
Tip 1: Structural Integrity: Prioritize the structural stability of the skyscraper by employing robust materials such as reinforced concrete and steel frames. Utilize advanced engineering techniques to withstand lateral forces, including wind and seismic activity.
Tip 2: Energy Efficiency: Integrate sustainable design features to minimize the building’s environmental impact. Consider energy-efficient lighting systems, double-glazed windows, and building materials with high thermal insulation properties.
Tip 3: Vertical Transportation: Plan for efficient vertical transportation systems, such as elevators and escalators, to facilitate the movement of occupants within the skyscraper. Optimize elevator placement and capacity to reduce waiting times and ensure smooth traffic flow.
Tip 4: Natural Light Optimization: Design the skyscraper to maximize natural light penetration, reducing the reliance on artificial lighting. Utilize large windows and incorporate reflective surfaces to distribute daylight throughout the interior spaces.
Tip 5: Safety and Security: Implement comprehensive safety and security measures, including fire sprinkler systems, smoke detectors, emergency staircases, and advanced fire suppression technologies. Ensure compliance with building codes and industry standards to maintain a safe environment for occupants.
Tip 6: Urban Integration: Consider the skyscraper’s integration into the surrounding urban environment. Design the building to complement the existing architectural landscape while minimizing negative impacts on neighboring structures and public spaces.
Tip 7: Multi-Use Functionality: Explore the possibility of incorporating multiple uses within the skyscraper, such as residential units, office spaces, retail stores, and public amenities. This diversity enhances the building’s functionality and contributes to a vibrant urban environment.
Tip 8: Aesthetic Appeal: Design the skyscraper with an aesthetically pleasing facade that reflects the city’s architectural style and cultural ident
ity. Utilize innovative materials and lighting techniques to create a visually striking landmark that becomes a symbol of urban pride.
By implementing these tips, architects and urban planners can create skyscrapers that are not only structurally sound and environmentally conscious but also enhance the functionality and aesthetics of the urban landscape.
—————–
Conclusion:
Skyscrapers are architectural marvels that continue to define the skylines of major cities around the world. Their design and functionality require careful consideration to ensure structural integrity, energy efficiency, safety, and integration with the surrounding urban environment. By adopting innovative approaches and incorporating sustainable practices, architects and urban planners can create skyscrapers that are not only iconic landmarks but also contribute to the overall well-being and prosperity of the city.
Conclusion
Skyscrapers, with their towering heights and iconic designs, have become defining features of modern urban landscapes. This exploration of “clipart skyscrapers big city downtown buildings” has provided insights into their architectural significance, structural marvels, and impact on urban environments.
Skyscrapers represent the ingenuity and ambition of architects and engineers, pushing the boundaries of design and construction. Their steel frames and concrete cores provide remarkable strength and stability, ensuring resilience against natural forces. The integration of glass and metal facades not only creates a striking aesthetic but also maximizes natural light and offers panoramic views.
Beyond their architectural prowess, skyscrapers play a crucial role in urban planning and development. Their density allows for efficient land use, accommodating a significant population and businesses within a limited footprint. Mixed-use skyscrapers foster vibrant and self-contained communities, promoting walkability and reducing traffic congestion.
Sustainability has become an integral part of modern skyscraper design, with eco-friendly features such as energy-efficient lighting, rainwater harvesting systems, and green roofs. These measures minimize environmental impact and contribute to the creation of more livable and sustainable cities.
Iconic skyscrapers transcend their functional purpose, becoming symbols of urban identity and cultural pride. They shape skylines, influence microclimates, and contribute to the overall character of cities. Careful urban planning and architectural design ensure that skyscrapers harmoniously integrate into the urban fabric, enhancing the visual appeal and livability of our cities.
As cities continue to evolve, skyscrapers will undoubtedly continue to play a prominent role, pushing the boundaries of architectural innovation and shaping the skylines of the future. By embracing sustainable practices, incorporating cutting-edge technologies, and prioritizing human well-being, architects and urban planners can create skyscrapers that are not only architectural marvels but also contribute to the prosperity and vitality of our urban environments.