A skyscraper city is a metropolitan area with an abundance of high-rise buildings, typically defined as buildings with over 40 floors or rising at least 150 meters (492 feet) in height. These cities are often characterized by dense populations, vibrant economies, and iconic skylines.
Skyscraper cities offer several advantages. They can accommodate large populations in a relatively small geographic area, reducing urban sprawl and preserving green spaces. High-rise buildings also promote energy efficiency by reducing the surface area exposed to the elements and maximizing natural light. Additionally, skyscraper cities serve as hubs for business, finance, and culture, attracting investment and fostering innovation.
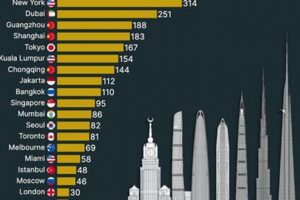
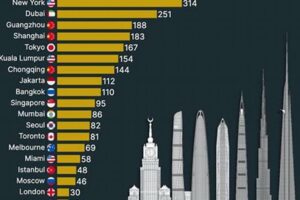
Notable skyscraper cities around the world include New York City, Tokyo, Shanghai, Hong Kong, and Dubai. Each city boasts a unique architectural style and cultural identity, showcasing the diverse expressions of urban development in the modern era.
1. Verticality
In the context of skyscraper cities, verticality plays a crucial role in optimizing land use and accommodating dense populations. Skyscrapers extend upwards, defying the limitations of horizontal space. This architectural strategy offers several benefits and implications:
- Efficient land utilization: Skyscrapers allow cities to accommodate more people and businesses within a limited geographic area. By building upwards, cities can preserve green spaces, parks, and other vital urban amenities.
- Reduced urban sprawl: Vertical development helps curb urban sprawl, the uncontrolled expansion of cities into surrounding areas. By concentrating development upwards, cities can maintain their boundaries and promote sustainable urban growth.
- Enhanced density: High-rise buildings increase population density, creating vibrant and diverse urban environments. Densely populated areas foster a sense of community, support public transportation, and encourage walking and cycling.
- Energy efficiency: Tall buildings can be designed to maximize natural light and ventilation, reducing energy consumption. They also provide opportunities for green building practices, such as rooftop gardens and rainwater harvesting systems.
In conclusion, the verticality of skyscraper cities is a key factor in their ability to accommodate large populations, promote sustainable urban growth, and create vibrant and efficient urban environments.
2. Density
In skyscraper cities, density is a defining characteristic that shapes the urban landscape and social dynamics. High-rise buildings allow cities to accommodate large populations within a compact area, offering several advantages and implications:
- Efficient land use: By building upwards, skyscraper cities can preserve valuable land for parks, green spaces, and other urban amenities. This efficient use of land helps create livable and sustainable urban environments.
- Reduced urban sprawl: Dense development helps curb urban sprawl, the uncontrolled expansion of cities into surrounding areas. By concentrating development upwards, cities can maintain their boundaries and promote sustainable urban growth.
- Enhanced community: Densely populated areas foster a sense of community and belonging. High-rise buildings often include mixed-use developments that integrate residential, commercial, and cultural spaces, promoting interaction and vibrancy.
- Public transportation: Densely populated areas support efficient public transportation systems, reducing reliance on cars and promoting sustainable mobility.
- Economic vitality: High-rise buildings often house businesses and commercial activities, contributing to the economic vitality of skyscraper cities. Densely populated areas create a large consumer base and support a diverse range of businesses.
In conclusion, the density achieved through high-rise buildings is a crucial component of skyscraper cities. It allows for efficient land use, reduces urban sprawl, enhances community, supports public transportation, and contributes to economic vitality. Understanding this connection is essential for planning and managing sustainable and livable urban environments.
3. Efficiency
In the context of skyscraper cities, dense construction plays a crucial role in promoting energy efficiency and sustainability. High-rise buildings, when designed and constructed thoughtfully, can minimize energy consumption and environmental impact.
- Reduced energy demand: Dense construction reduces the surface area of buildings exposed to the elements, minimizing heat loss and gain. This reduces the need for heating and cooling, leading to lower energy consumption.
- Efficient building systems: High-rise buildings can incorporate energy-efficient systems, such as LED lighting, smart HVAC systems, and renewable energy sources like solar panels. These systems optimize energy use and reduce operating costs.
- Natural light and ventilation: Dense construction often involves designing buildings to maximize natural light and ventilation. This reduces the reliance on artificial lighting and mechanical ventilation, further reducing energy consumption.
- Green building practices: Skyscraper cities often adopt green building practices and certifications, such as LEED and BREEAM. These practices promote sustainable construction methods, energy efficiency, and water conservation, contributing to the overall sustainability of the city.
In conclusion, the dense construction characteristic of skyscraper cities offers significant opportunities for energy efficiency and sustainability. By reducing energy demand, incorporating efficient building systems, maximizing natural resources, and adopting green building practices, skyscraper cities can create a more sustainable and environmentally friendly urban environment.
4. Economic hubs
Skyscraper cities serve as economic hubs, attracting businesses and investment from around the world. This phenomenon can be attributed to several key factors:
- Concentration of resources: Skyscraper cities often house major financial institutions, corporate headquarters, and specialized industries. Thi
s concentration of resources creates a favorable environment for businesses to operate and collaborate. - Skilled workforce: Skyscraper cities attract and retain a highly skilled workforce, providing businesses with access to qualified professionals in various fields.
- World-class infrastructure: Skyscraper cities typically boast advanced infrastructure, including transportation networks, communication systems, and energy grids, which support business operations and facilitate trade.
- Global connectivity: Many skyscraper cities are major transportation hubs, with international airports and seaports, enabling businesses to connect with global markets.
The presence of economic hubs is a defining characteristic of skyscraper cities and contributes to their overall success and prosperity. Businesses benefit from the concentration of resources, skilled workforce, and world-class infrastructure, while the city itself benefits from increased economic activity, job creation, and tax revenue.
Examples of prominent economic hubs include New York City, London, Tokyo, and Hong Kong. These cities are renowned for their financial markets, corporate headquarters, and thriving business communities.
Understanding the connection between skyscraper cities and economic hubs is crucial for urban planners and policymakers seeking to foster economic growth and prosperity in their cities.
5. Cultural centers
Skyscraper cities are often cultural hubs, housing a wide range of museums, art galleries, and performance venues. This cultural richness contributes to the vibrancy and attractiveness of these cities, as well as offering several key benefits:
- Preservation of cultural heritage: Museums and art galleries play a crucial role in preserving and showcasing a city’s cultural heritage. They house valuable artifacts, artwork, and historical documents that tell the story of the city’s past and present.
- Promotion of artistic expression: Performance venues provide platforms for artists to showcase their work and connect with audiences. This fosters creativity, innovation, and cultural exchange.
- Community building: Cultural centers serve as gathering places for people to engage with art, history, and culture. They promote a sense of community and belonging, and encourage social interaction and dialogue.
- Economic benefits: Cultural institutions attract visitors and contribute to the local economy. They create jobs, generate tourism revenue, and enhance the city’s overall image and reputation.
The presence of cultural centers is a defining characteristic of skyscraper cities. They contribute to the city’s identity, foster creativity and innovation, and enhance the quality of life for residents and visitors alike. Examples of prominent cultural hubs include New York City, London, Paris, and Tokyo, which are renowned for their world-class museums, art galleries, and performance venues.
6. Architectural marvels
In the context of skyscraper cities, architectural marvels are not merely iconic structures but integral components that contribute to the city’s identity and functionality. Skyscrapers showcase innovative designs and engineering feats, pushing the boundaries of architectural possibilities and transforming the urban landscape.
The pursuit of architectural marvels in skyscraper cities stems from several factors. Firstly, the vertical nature of these cities demands innovative structural solutions to optimize space and maximize height. Secondly, skyscrapers serve as symbols of economic power and urban ambition, leading architects and engineers to strive for unique and awe-inspiring designs.
The impact of architectural marvels extends beyond aesthetics. They serve as technological testbeds, advancing construction techniques and materials. These advancements contribute to the overall efficiency, sustainability, and safety of high-rise buildings. Moreover, architectural marvels attract global attention and tourism, boosting the city’s economy and reputation.
Examples of architectural marvels in skyscraper cities abound. The Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the tallest building in the world, exemplifies innovative engineering with its record-breaking height and complex structural design. The Shanghai Tower in China boasts a unique twisting form that reduces wind resistance and offers panoramic views. New York City’s Empire State Building, an Art Deco masterpiece, has been an enduring symbol of the city’s architectural heritage.
Understanding the connection between architectural marvels and skyscraper cities is crucial for urban planners, architects, and policymakers. It highlights the importance of design excellence, innovation, and engineering prowess in shaping livable, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing urban environments. By embracing architectural marvels, skyscraper cities can continue to push the boundaries of human ingenuity and create iconic landmarks that define their skylines for generations to come.
7. Iconic skylines
In the context of skyscraper cities, iconic skylines are more than just visually striking features; they are integral to the city’s identity and contribute to its overall appeal and functionality.
The clustering of high-rises in skyscraper cities creates distinctive urban landscapes that set them apart from other metropolitan areas. These skylines serve as symbols of economic power, architectural prowess, and cultural heritage. They attract tourists, boost real estate values, and enhance the overall quality of life for residents.
The Empire State Building in New York City, the Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur, and the Burj Khalifa in Dubai are just a few examples of iconic skyscrapers that have come to define their respective cities. These structures have become synonymous with urban ambition and serve as landmarks that people from all over the world recognize.
Understanding the connection between iconic skylines and skyscraper cities is crucial for urban planners, architects, and policymakers. It highlights the importance of design excellence, innovation, and sustainability in shaping livable, vibrant, and aesthetically pleasing urban environments.
FAQs about Skyscraper Cities
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions about skyscraper cities, providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: What defines a skyscraper city?
A skyscraper city is an urban center characterized by a high concentration of high-rise buildings, typically defined as buildings with over 40 floors or rising at least 150 meters (492 feet) in height.
Question 2: Why do cities build skyscrapers?
Skyscrapers offer several advantages. They maximize space utilization, accommodate large populations in dense urban areas, promote energy efficiency, and serve as hubs for business, finance, and culture.
Question 3: Are skyscraper cities sustainable?
Skyscraper cities can
be sustainable if designed and managed thoughtfully. Dense construction reduces energy consumption, and green building practices promote resource conservation. However, careful planning is crucial to mitigate potential environmental impacts.
Question 4: How do skyscraper cities impact urban life?
Skyscrapers can shape urban life in various ways. They can increase population density, promote mixed-use developments, and enhance connectivity. However, they can also affect wind patterns, cast shadows, and create microclimates.
Question 5: What are the challenges of managing skyscraper cities?
Skyscraper cities require comprehensive planning and management to address issues such as traffic congestion, housing affordability, and infrastructure maintenance. They also need to balance economic development with social equity and environmental sustainability.
Question 6: What are the future trends for skyscraper cities?
Skyscraper cities continue to evolve, with trends such as smart building technologies, vertical green spaces, and mixed-use developments. They are also expected to play a key role in addressing global challenges like climate change and urbanization.
In summary, skyscraper cities are complex and multifaceted urban environments that offer unique opportunities and challenges. Understanding their characteristics and impacts is crucial for sustainable and livable urban development.
Transition to the next article section: The Benefits and Challenges of Skyscraper Cities
Tips for Thriving in Skyscraper Cities
Skyscraper cities offer unique opportunities and challenges. Here are some tips for navigating and enjoying these vertical urban environments:
Tip 1: Embrace Vertical Living
Skyscrapers offer a different perspective on urban life. Embrace the verticality by using elevators and sky bridges to explore different levels of buildings and enjoy panoramic views.
Tip 2: Take Advantage of Amenities
Many skyscraper complexes feature amenities such as fitness centers, swimming pools, and rooftop gardens. Utilize these amenities to enhance your well-being and socialize with neighbors.
Tip 3: Explore Mixed-Use Developments
Skyscrapers often incorporate mixed-use developments, combining residential, commercial, and retail spaces. Take advantage of the convenience and variety offered by these integrated environments.
Tip 4: Use Public Transportation
Skyscraper cities typically have efficient public transportation systems. Utilize subways, buses, and trains to navigate the city and reduce traffic congestion.
Tip 5: Be Aware of Microclimates
Skyscrapers can create microclimates, affecting wind patterns and temperatures. Stay informed about weather conditions and dress accordingly.
Tip 6: Consider Sustainability
Skyscrapers can have a significant environmental impact. Choose buildings with green features, such as energy-efficient lighting and water conservation systems.
Tip 7: Find Community Spaces
While skyscrapers can be dense, there are often hidden community spaces. Explore parks, plazas, and rooftop gardens to connect with nature and other residents.
Tip 8: Enjoy the Views
One of the best things about skyscraper cities is the stunning views. Take advantage of observation decks, rooftop restaurants, and high-floor apartments to appreciate the cityscape.
Summary
Skyscraper cities offer a unique and dynamic urban experience. By embracing vertical living, utilizing amenities, and navigating the challenges, you can thrive in these extraordinary environments.
Conclusion
The skyscraper city, characterized by its towering high-rises and dense urban fabric, has emerged as a dominant model of contemporary urban development. Throughout this exploration, we have examined the multifaceted nature of skyscraper cities, delving into their advantages and challenges, their impact on urban life, and strategies for thriving within these vertical environments.
Skyscraper cities offer a unique blend of opportunities and complexities. They maximize space utilization, accommodate growing populations, and serve as hubs for business, finance, and culture. However, they also require careful planning and management to address issues such as traffic congestion, housing affordability, and environmental sustainability.
The future of skyscraper cities lies in embracing innovation and sustainability. Smart building technologies, green design, and mixed-use developments will shape the next generation of these urban centers. By integrating these advancements, skyscraper cities can continue to evolve as dynamic and livable environments that meet the challenges of the 21st century.
As we look ahead, it is imperative to recognize the significance of skyscraper cities as testaments to human ingenuity and architectural prowess. They stand as symbols of urban ambition and economic power, while also presenting opportunities for sustainable and equitable urban development. By embracing the unique characteristics of skyscraper cities and working collaboratively to address their challenges, we can harness their potential to create thriving and resilient urban environments for future generations.