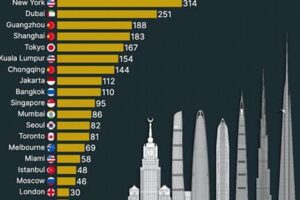
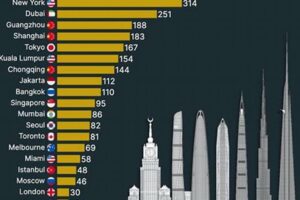
Skyscrapers are towering structures that dominate the skylines of major cities worldwide. They are marvels of engineering and architectural ingenuity, providing ample vertical space for commercial, residential, and other purposes. The skyscraper’s impact on the urban landscape is undeniable, shaping the way people live, work, and interact within the city.
Skyscrapers offer numerous advantages. They provide much-needed space in densely populated urban areas, allowing for efficient land use. Their height offers panoramic views, making them highly desirable for residential and commercial properties. Additionally, skyscrapers often incorporate sustainable design features, reducing their environmental impact and contributing to the overall well-being of the city.
The history of skyscrapers is intertwined with the development of cities. The first skyscrapers emerged in the late 19th century in response to the growing need for space in rapidly expanding urban centers. Over time, skyscrapers have evolved in design and function, reflecting advancements in technology and changing urban needs. Today, skyscrapers stand as symbols of progress, innovation, and the dynamic nature of modern cities.
1. Vertical Space
In the context of skyscrapers and cities, vertical space refers to the utilization of height to create additional usable area within a limited footprint. Skyscrapers, by their very nature, embody the concept of vertical space, extending upwards to maximize the use of available land.
The importance of vertical space in skyscrapers and cities is multifaceted. Firstly, it allows for increased population density without sprawling urban development. By building upwards, cities can accommodate more people and businesses within a smaller geographical area, promoting efficient land use and reducing urban sprawl.
Secondly, vertical space enables the creation of diverse and dynamic urban environments. Skyscrapers can house a mix of commercial, residential, and public spaces, fostering a vibrant street-level atmosphere and reducing the need for excessive commuting. This mixed-use approach promotes walkability, enhances community engagement, and contributes to the overall vitality of the city.
Thirdly, vertical space offers unique design possibilities and architectural innovation. Skyscrapers push the boundaries of engineering and architectural design, showcasing innovative structural systems, facade treatments, and sustainable features. These architectural marvels not only serve as functional buildings but also become iconic landmarks that define the city’s skyline and identity.
In conclusion, vertical space is a crucial aspect of skyscrapers and cities. It allows for efficient land use, creates diverse urban environments, and fosters architectural innovation. Understanding the significance of vertical space is essential for urban planning, architecture, and sustainable city development.
2. Urban Density
Urban density refers to the concentration of people and buildings within a specific urban area. It is a crucial factor in shaping the character and dynamics of cities, and skyscrapers play a significant role in influencing urban density.
- Increased Population Capacity: Skyscrapers allow cities to accommodate a larger population within a limited geographical area. By building upwards, cities can increase their population density without sprawling outwards, reducing urban sprawl and preserving green spaces.
- Mixed-Use Development: Skyscrapers often incorporate a mix of commercial, residential, and public spaces, creating diverse and vibrant urban environments. This mixed-use approach promotes walkability, reduces the need for excessive commuting, and fosters a sense of community within the city.
- Efficient Land Use: Skyscrapers maximize the use of available land by utilizing vertical space. This efficient land use allows cities to accommodate more people and businesses without compromising the overall livability and sustainability of the urban environment.
- Transportation and Infrastructure: High urban density around skyscrapers requires efficient transportation and infrastructure systems. This can lead to investments in public transportation, pedestrian-friendly streets, and other infrastructure improvements that benefit not only skyscraper residents but the entire city.
In conclusion, skyscrapers and urban density are closely intertwined. Skyscrapers enable cities to increase their population capacity, promote mixed-use development, and make efficient use of land. Understanding the connection between skyscrapers and urban density is essential for urban planning, architecture, and sustainable city development.
3. Architectural Innovation
Architectural innovation has been a driving force in the development of skyscrapers and has played a pivotal role in shaping the urban landscape. Skyscrapers, by their very nature, push the boundaries of architectural design and engineering, showcasing innovative structural systems, facade treatments, and sustainable features. These architectural marvels not only serve as functional buildings but also become iconic landmarks that define the city’s skyline and identity.
- Structural Systems:
Skyscrapers require innovative structural systems to withstand the immense forces imposed by their height and weight. Engineers have developed a range of structural systems, such as braced frames, moment-resisting frames, and diagrid structures, to ensure the stability and integrity of these towering structures. These systems not only provide structural support but also contribute to the unique architectural expression of skyscrapers.
- Facade Treatments:
The facades of skyscrapers are as diverse as their structural systems. Architects use innovative materials and techniques to create visually striking and energy-efficient facades. Glass curtain walls, metal paneling, and green walls are just a few examples of the innovative facade treatments employed in skyscraper design. These facades not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of the building but also contribute to its overall performance and sustainability.
- Sustainable Features:
Skyscrapers are increasingly incorporating sustainable design features to reduce their environmental impact and contribute to the overall well-being of the city. Green roofs, rainwater harvesting systems, and energy-efficient lighting are just a few examples of the sustainable features that are being integrated into skyscraper design. These fea
tures not only reduce the building’s carbon footprint but also create healthier and more comfortable indoor environments. - Mixed-Use Design:
Skyscrapers often incorporate a mix of commercial, residential, and public spaces, creating diverse and vibrant urban environments. This mixed-use approach promotes walkability, reduces the need for excessive commuting, and fosters a sense of community within the city. Mixed-use skyscrapers are becoming increasingly popular as cities seek to create more livable and sustainable urban environments.
In conclusion, architectural innovation is inextricably linked to the skyscraper and the city. Skyscrapers serve as a canvas for architectural experimentation and innovation, pushing the boundaries of design and engineering. The innovative structural systems, facade treatments, sustainable features, and mixed-use design of skyscrapers not only enhance the aesthetics and functionality of these buildings but also contribute to the overall vitality and sustainability of the city.
4. Economic Hubs
Skyscrapers, as towering symbols of urban development, play a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscape of cities. They serve as economic hubs, attracting businesses, industries, and a diverse workforce, contributing to the overall economic vitality and prosperity of the city.
The concentration of businesses in skyscrapers creates a favorable environment for collaboration, innovation, and economic growth. Skyscrapers offer ample space for offices, meeting rooms, and other facilities that facilitate business operations and foster a sense of community among professionals. The proximity of businesses within a skyscraper promotes networking opportunities, knowledge sharing, and the cross-pollination of ideas, leading to increased productivity and economic output.
Moreover, skyscrapers often house mixed-use developments, combining commercial, residential, and retail spaces within a single structure. This integration creates a vibrant and self-contained urban ecosystem where people can live, work, and enjoy amenities without the need for extensive commuting. Mixed-use skyscrapers attract a diverse population, including professionals, entrepreneurs, and residents, contributing to the city’s overall economic and social well-being.
Real-life examples of skyscrapers as economic hubs abound. The Empire State Building in New York City, standing at 102 stories, is home to a multitude of businesses, including law firms, financial institutions, and media companies. It is estimated that over 100,000 people work in the Empire State Building daily, contributing significantly to the city’s economy. Another prominent example is the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the world’s tallest building, which houses a mix of commercial, residential, and hospitality spaces, making it a thriving economic hub in the Middle East.
Understanding the connection between skyscrapers and economic hubs is crucial for urban planning and economic development strategies. By recognizing the role of skyscrapers in attracting businesses, fostering innovation, and creating vibrant mixed-use environments, cities can leverage these architectural marvels to drive economic growth and improve the overall quality of life for their residents.
5. Sustainable Design
In the context of skyscrapers and cities, sustainable design has emerged as a crucial approach to mitigate environmental impact and promote the well-being of urban populations. Skyscrapers, by their sheer scale and energy consumption, present unique challenges and opportunities for sustainable design practices.
- Energy Efficiency:
Skyscrapers can incorporate energy-efficient features such as high-performance glazing, LED lighting, and smart building management systems to reduce energy consumption. These measures not only lower operating costs but also contribute to a greener, more sustainable urban environment.
- Water Conservation:
Water conservation is another key aspect of sustainable design in skyscrapers. Rainwater harvesting systems, low-flow fixtures, and drought-tolerant landscaping can significantly reduce water usage. These strategies help preserve precious water resources and promote sustainable water management in dense urban environments.
- Material Sustainability:
The choice of building materials has a significant impact on the sustainability of skyscrapers. Architects and engineers are increasingly using recycled and renewable materials, such as bamboo, recycled steel, and low-carbon concrete, to reduce the environmental footprint of these towering structures.
- Indoor Environmental Quality:
Sustainable design in skyscrapers also focuses on improving indoor environmental quality for occupants. Natural ventilation, abundant daylighting, and the use of low-emitting materials help create healthier and more comfortable indoor spaces, enhancing the well-being of building users.
By embracing sustainable design principles, skyscrapers can transform into beacons of environmental consciousness, contributing to the creation of more sustainable and livable cities. It is through the integration of innovative technologies, mindful resource management, and a commitment to occupant well-being that skyscrapers can rise as symbols of both urban progress and environmental responsibility.
6. Cultural Landmarks
Skyscrapers, as towering symbols of urban development, often transcend their functional purpose and evolve into cultural landmarks that define the identity and character of a city. The connection between cultural landmarks and the skyscraper and the city is a symbiotic one, where each element enhances and complements the other.
Cultural landmarks embedded within skyscrapers create a unique urban experience. They attract visitors, locals, and tourists alike, fostering a sense of place and community. The Empire State Building in New York City, for example, is not only an iconic skyscraper but also a cultural landmark, featuring an observation deck that offers breathtaking views of the city and has been featured in countless films and television shows.
Skyscrapers can also serve as platforms for cultural expression and artistic endeavors. The Burj Khalifa in Dubai houses the At the Top observation deck, which hosts art exhibitions and cultural events, showcasing the convergence of architecture and art. Moreover, the Shanghai Tower in China features a spiral staircase designed by Chinese artist Zhang Huan, transforming the skyscraper into a public art installation.
Understanding the connection between cultural landmarks and the skyscraper and the city is crucial for urban planning and cultural development strategies. By recognizing the role of skyscrapers in shaping cultural identity and providing spaces for artistic expression, cities can leverage these architectural marvels to enhance their cultural vitality and attractiveness.
7. Social Spaces
Skyscrapers, with their towering heights and imposing presence, have a significant impact on the social fabric of cities. The connection between “Social Spaces” and “the skyscraper and the city” is multifaceted, as skyscrapers can both shape and be shaped by the social dynamics of urban environments.
One of the key ways in which skyscrapers influence social spaces is by creating new opportunities for interaction and community building. Public spaces within skyscrapers, such as lobbies, plazas, and observation decks, provide gathering places for people from all walks of life. These spaces can foster a sense of community and belonging, particularly in densely populated urban areas where traditional public spaces may be limited. For example, the public plaza at the base of the Rockefeller Center in New York City has become a popular meeting spot and a venue for public events, contributing to the vibrant social atmosphere of Midtown Manhattan.
Moreover, skyscrapers can promote social interaction by housing a mix of uses, such as residential, commercial, and retail spaces. This mixed-use approach creates a diverse and dynamic urban environment where people can live, work, shop, and socialize within a single building or complex. By bringing people together from different backgrounds and walks of life, skyscrapers can foster social connections and strengthen the social fabric of the city.
Understanding the connection between social spaces and the skyscraper and the city is crucial for urban planning and design. By incorporating social spaces into skyscraper developments, architects and urban planners can create more livable and sustainable cities that promote social interaction, community building, and a sense of place.
8. Urban Planning
The connection between “Urban Planning” and “the skyscraper and the city” is a reciprocal one, with each element influencing the development and character of the other. Urban planning shapes the physical environment of the city, including the placement and design of skyscrapers, while skyscrapers, in turn, have a profound impact on the social, economic, and environmental fabric of the city.
Urban planning plays a critical role in ensuring that skyscrapers are integrated harmoniously into the urban landscape. Planners consider factors such as zoning regulations, building codes, and infrastructure capacity to guide the development of skyscrapers in a way that promotes sustainability, livability, and aesthetic appeal. For example, zoning regulations may limit the height and density of skyscrapers in certain areas to prevent overcrowding and preserve the character of historic neighborhoods. Building codes ensure that skyscrapers are structurally sound and meet safety standards, while infrastructure planning ensures that there is adequate transportation, water, and energy supply to support the increased population density brought about by skyscrapers.
Skyscrapers, in turn, have a significant impact on the urban planning process. Their height and prominence make them landmarks that can shape the identity and image of a city. For example, the Empire State Building in New York City and the Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur have become iconic symbols of their respective cities. Skyscrapers can also influence land use patterns and transportation networks. The concentration of businesses and workers in skyscrapers creates demand for nearby housing, retail, and transportation services, which can lead to the development of mixed-use neighborhoods and the improvement of public transportation infrastructure.
Understanding the connection between urban planning and the skyscraper and the city is crucial for creating livable, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing urban environments. By carefully considering the placement, design, and integration of skyscrapers into the urban fabric, urban planners can harness the potential of these architectural marvels to enhance the quality of life for city dwellers.
9. Global Connectivity
In the modern world, global connectivity is inextricably linked to the skyscraper and the city. Skyscrapers, as towering symbols of urban development, play a pivotal role in facilitating global interconnectedness and fostering international collaboration.
One of the key ways in which skyscrapers contribute to global connectivity is by housing multinational corporations and international organizations. These entities often establish their headquarters or regional offices in skyscrapers, taking advantage of the central location, ease of access, and advanced infrastructure that these buildings provide. The concentration of global businesses in skyscrapers creates a hub for international commerce, finance, and trade, fostering cross-border collaboration and economic growth.
Skyscrapers also serve as gateways to global transportation networks. Many skyscrapers are located in close proximity to airports, train stations, and major highways, providing convenient access to international travel. This connectivity enables businesses and individuals to easily connect with global markets and partners, facilitating the exchange of goods, services, and ideas.
Moreover, skyscrapers often incorporate state-of-the-art communication and information technology infrastructure, enabling seamless global connectivity. High-speed internet, satellite communications, and video conferencing facilities allow businesses and individuals within skyscrapers to communicate and collaborate with clients and partners around the world in real-time. This advanced connectivity fosters innovation, drives economic productivity, and strengthens international cooperation.
Understanding the connection between global connectivity and the skyscraper and the city is crucial for urban planning and economic development strategies. By recognizing the role of skyscrapers in facilitating global interconnectedness, cities can leverage these architectural marvels to attract international businesses, promote economic growth, and enhance their position in the global economy.
FAQs on the Skyscraper and the City
This section provides answers to frequently asked questions about the skyscraper and its relationship with the city. These questions address common concerns and misconceptions, offering clear and informative responses.
Question 1: How do skyscrapers impact the urban environment?
Skyscrapers have a significant impact on the urban environment, both positive and negative. On the positive side, they can increase population density, reduce urban sprawl, and create new public spaces. On the negative side, they can cast shadows on neighboring buildings, block views, and contribute to wind tunnel effects.
Question 2: Are skyscrapers energy efficient?
Skyscrapers can be energy efficient, but it depends on their design and construction. Modern skyscrapers often incorporate sustainable features such as energy-efficient lighting, heating, and cooling systems, double-paned windows, and rainwater harvesting systems. These features can significantly reduce energy consumption and make skyscrapers more environmentally friendly.
Question 3: How do skyscrapers affect transportation?
Skyscrapers can have a significant impact on transportation. They can attract large numbers
of workers and visitors, which can lead to increased traffic congestion and demand for public transportation. However, skyscrapers can also be designed to promote sustainable transportation options, such as pedestrian-friendly streets, bike lanes, and public transportation hubs.
Question 4: Are skyscrapers safe?
Skyscrapers are generally safe, but their safety depends on their design, construction, and maintenance. Modern skyscrapers are designed to withstand high winds, earthquakes, and other natural disasters. They also have advanced fire safety systems and emergency evacuation plans.
Question 5: How do skyscrapers contribute to the economy?
Skyscrapers can contribute to the economy in several ways. They can provide office space for businesses, attract tourism, and generate tax revenue for the city. Skyscrapers can also create jobs in construction, maintenance, and other related industries.
Question 6: What is the future of skyscrapers?
The future of skyscrapers is bright. As cities continue to grow and densify, the demand for vertical space will only increase. Skyscrapers will continue to evolve in design and functionality, becoming more sustainable, energy-efficient, and technologically advanced.
In summary, skyscrapers have a complex and multifaceted relationship with the city. They can have both positive and negative impacts on the urban environment, transportation, and economy. However, with careful planning and design, skyscrapers can be used to create more livable, sustainable, and prosperous cities.
Transition to the next article section: The Impact of Skyscrapers on Urban Life
Tips on “the skyscraper and the city”
Skyscrapers are iconic structures that shape the skyline of modern cities. They offer numerous advantages, but also present unique challenges. Here are some tips to harness the benefits and mitigate the drawbacks of skyscrapers in urban environments:
Tip 1: Prioritize mixed-use development.
Skyscrapers should not be exclusively dedicated to a single use, such as office space. Mixed-use developments that incorporate residential, commercial, retail, and public spaces create a more vibrant and diverse urban environment. This approach promotes walkability, reduces traffic congestion, and fosters a sense of community.
Tip 2: Implement sustainable design features.
Skyscrapers can be energy-intensive and contribute to urban heat island effects. To mitigate these impacts, incorporate sustainable design features such as energy-efficient lighting and HVAC systems, double-paned windows, and rainwater harvesting systems. Green roofs and vertical gardens can also improve air quality and reduce the urban heat island effect.
Tip 3: Ensure adequate public transportation.
Skyscrapers can attract a large number of workers and visitors, putting a strain on transportation infrastructure. To avoid traffic congestion and promote sustainable transportation, invest in public transportation systems that connect skyscrapers to other parts of the city. Provide convenient access to bus stops, subway stations, and bike lanes.
Tip 4: Create public spaces at ground level.
Skyscrapers often occupy large footprints, reducing the availability of public spaces at ground level. To mitigate this, incorporate public plazas, parks, and other open spaces into the design of skyscraper developments. These spaces provide opportunities for recreation, social interaction, and community events.
Tip 5: Design for resilience.
Skyscrapers should be designed to withstand natural disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods. Use earthquake-resistant construction techniques, install backup power systems, and implement emergency evacuation plans. Resilient skyscrapers ensure the safety of occupants and minimize disruptions to the city in the event of a disaster.
Tip 6: Foster community engagement.
Skyscrapers can sometimes be perceived as isolated and exclusive. To foster community engagement, involve local residents in the planning and design process. Create opportunities for public input and feedback. Consider incorporating community spaces, such as libraries or daycare centers, into skyscraper developments.
Tip 7: Consider the long-term impact.
Skyscrapers are major investments with a long lifespan. When planning and constructing skyscrapers, consider their long-term impact on the city. Ensure that they align with the city’s overall development goals and contribute to a sustainable and livable urban environment.
By following these tips, cities can harness the benefits of skyscrapers while mitigating their potential drawbacks. Skyscrapers can become valuable assets that enhance urban life, promote economic growth, and contribute to a more sustainable and resilient city.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: The Future of Skyscrapers in the Urban Landscape
Conclusion
Skyscrapers, with their towering heights and iconic presence, have become synonymous with modern cities. They have reshaped urban skylines, influenced economic growth, and transformed social interactions. This article has explored the multifaceted relationship between “the skyscraper and the city,” examining its impact on urban density, architectural innovation, economic hubs, sustainability, cultural landmarks, social spaces, urban planning, and global connectivity.
Skyscrapers offer numerous advantages, including increased population capacity, efficient land use, and the creation of vibrant mixed-use environments. However, they also present challenges related to energy consumption, urban heat island effects, and transportation strain. By implementing sustainable design features, prioritizing mixed-use development, ensuring adequate public transportation, and fostering community engagement, cities can harness the benefits of skyscrapers while mitigating their drawbacks.
As cities continue to grow and densify, the demand for vertical space will only increase. Skyscrapers will continue to evolve in design and functionality, becoming more sustainable, energy-efficient, and technologically advanced. They have the potential to play a vital role in creating more livable, sustainable, and prosperous cities. By carefully considering the relationship between “the skyscraper and the city,” we can ensure that these architectural marvels continue to contribute positively to the urban landscape and enhance the quality of life for city dwellers.