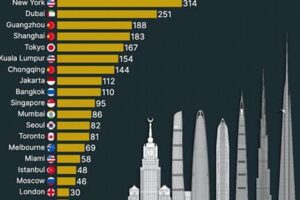
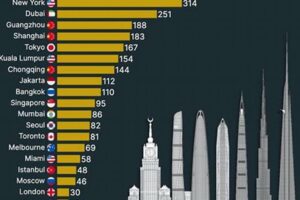
The term “skyscrapers per city” refers to the number of high-rise buildings within a particular urban area. It serves as an indicator of a city’s economic development, architectural innovation, and overall urban landscape.
The presence of skyscrapers in a city offers several advantages. Firstly, they provide increased floor space, allowing for the efficient use of valuable land resources. Secondly, skyscrapers enhance a city’s skyline, creating a distinctive and recognizable identity. Thirdly, they contribute to urban sustainability by promoting efficient land use and reducing urban sprawl.
The construction of skyscrapers has a rich historical context. The early 20th century witnessed the emergence of the first skyscrapers in major cities like New York and Chicago. These early buildings were marvels of engineering and architectural design, pushing the boundaries of what was considered structurally possible. Over time, technological advancements and innovative design concepts have led to the development of even taller and more sophisticated skyscrapers, transforming the skylines of cities worldwide.
1. Urban Density
Urban density is a key aspect influencing the number of skyscrapers per city. It refers to the concentration of people and buildings within a specific urban area. High urban density often drives the construction of skyscrapers as a means to accommodate a growing population and optimize land use.
- Land scarcity: In densely populated cities with limited land availability, building upwards becomes a necessity. Skyscrapers allow for increased floor space and efficient land utilization, enabling cities to accommodate more people and businesses within a constrained area.
- Economic benefits: High-rise buildings can generate substantial revenue through rent, office space, and retail. The increased density attracts businesses and investment, fueling economic growth and prosperity.
- Transportation efficiency: Dense urban areas with skyscrapers often have well-developed public transportation systems. This connectivity reduces the need for personal vehicles, mitigating traffic congestion and promoting sustainable commuting.
- Urban planning: Urban planners play a crucial role in managing urban density and skyscraper development. By regulating building heights, zoning, and infrastructure, they ensure the harmonious integration of skyscrapers into the urban fabric while preserving the city’s character and livability.
In summary, urban density is a primary driver behind the proliferation of skyscrapers per city. It presents challenges and opportunities for urban planners and policymakers, requiring careful planning and management to harness the benefits of high-rise buildings while ensuring sustainable and livable urban environments.
2. Architectural Innovation and Skyscrapers per City
Architectural innovation plays a pivotal role in the development and construction of skyscrapers per city. It encompasses the groundbreaking ideas, novel designs, and advanced technologies that push the boundaries of architectural possibilities, enabling the creation of ever-taller and more sustainable high-rise buildings.
One of the key drivers of architectural innovation in skyscrapers is the need to address the challenges posed by urban density and land scarcity. As cities grow vertically, architects and engineers must devise innovative solutions to maximize space utilization and create livable and sustainable urban environments. This has led to the development of new structural systems, such as diagrid structures and supertall core designs, which allow for the construction of skyscrapers that are both strong and efficient.
Moreover, architectural innovation in skyscrapers extends beyond structural considerations. It encompasses the integration of green building technologies, such as solar panels and rainwater harvesting systems, which enhance the sustainability and energy efficiency of high-rise buildings. Additionally, architects are exploring innovative facade designs that incorporate natural ventilation and daylighting, creating healthier and more comfortable indoor environments for occupants.
The practical significance of architectural innovation in skyscrapers per city is immense. It enables the creation of iconic landmarks that define a city’s skyline and contribute to its cultural identity. Innovative skyscraper designs also have the potential to transform urban landscapes, fostering economic growth and attracting investment. Furthermore, the sustainable features incorporated into modern skyscrapers contribute to reducing the environmental impact of urbanization and promoting sustainable urban development.
3. Economic Growth
Skyscrapers per city serve as a prominent indicator of economic growth and prosperity. The construction of high-rise buildings is often driven by strong economic conditions and reflects a city’s overall financial health.
- Increased Business Activity: Skyscrapers provide ample space for businesses to operate and expand, accommodating large corporations and international firms. The presence of numerous high-rise buildings in a city attracts businesses seeking to establish a presence in a thriving economic hub.
- Job Creation: The construction and maintenance of skyscrapers generate significant employment opportunities in various sectors, including architecture, engineering, construction, and real estate. These projects provide jobs for skilled workers, boosting the local economy.
- Tourism and Investment: Iconic skyscrapers become landmarks that attract tourists and investors alike. The unique architectural designs and observation decks of these buildings often draw visitors, generating revenue for the city. Additionally, skyscrapers can serve as a symbol of a city’s economic prowess, attracting foreign investment and business partnerships.
- Increased Tax Revenue: The construction and occupancy of skyscrapers contribute to increased property and business taxes for the city. This revenue can be used to fund essential public services, infrastructure development, and social programs, further driving economic growth.
In summary, skyscrapers per city are not merely architectural marvels but also indicators of economic vitality. They facilitate business activity, create jobs, attract investment, and generate revenue, contributing to the overall prosperity and economic growth of the city.
4. Land Use Efficiency and Sky
scrapers per City
Skyscrapers per city play a crucial role in promoting land use efficiency, a fundamental concept in urban planning and development. Land use efficiency refers to the optimal utilization of, ensuring that it is used wisely and sustainably to meet the needs of a growing population.
The construction of skyscrapers allows for increased density and vertical growth within a limited land area. By building upwards, cities can accommodate more people and businesses without sprawling outwards, preserving valuable land resources for other uses such as parks, green spaces, and essential infrastructure.
Skyscrapers contribute to land use efficiency by:
- Maximizing Vertical Space: Skyscrapers utilize the vertical dimension to create additional floor space, allowing for a higher concentration of population and economic activity within a smaller footprint.
- Mixed-Use Development: Many skyscrapers are designed with mixed-use functionality, incorporating residential, commercial, and retail spaces within a single building. This approach optimizes land use by accommodating diverse activities in one location.
- Transit-Oriented Development: Skyscrapers are often constructed near public transportation hubs, encouraging residents and workers to use sustainable modes of transport. This reduces urban sprawl and promotes compact, walkable neighborhoods.
Examples of cities that have successfully implemented skyscrapers for land use efficiency include:
- New York City: Known for its iconic skyline, New York City has a high concentration of skyscrapers, allowing it to accommodate a vast population and diverse economic activities within a relatively small land area.
- Tokyo: Despite being one of the most densely populated cities in the world, Tokyo has managed to preserve green spaces and improve air quality through the construction of numerous skyscrapers, promoting vertical growth and efficient land use.
- Hong Kong: With limited land available for development, Hong Kong has embraced skyscrapers as a way to maximize space utilization. The city has one of the highest skyscraper densities in the world and has successfully implemented mixed-use developments to enhance land use efficiency.
In conclusion, skyscrapers per city play a significant role in promoting land use efficiency by maximizing vertical space, encouraging mixed-use development, and supporting transit-oriented development. By optimizing land use, cities can create more sustainable and livable urban environments while preserving valuable land resources for essential purposes.
5. Sustainability and Skyscrapers per City
The concept of sustainability plays a crucial role in the development and management of skyscrapers within urban environments. As cities strive to become more sustainable and environmentally responsible, skyscrapers are increasingly being designed and constructed with sustainability principles in mind.
- Energy Efficiency: Skyscrapers can be designed to incorporate energy-efficient features such as double-glazed windows, efficient lighting systems, and renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines. These measures reduce energy consumption and minimize the environmental impact of high-rise buildings.
- Water Conservation: Sustainable skyscrapers employ water-saving fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and greywater recycling technologies to reduce water usage and conserve this precious resource.
- Green Building Materials: The construction of skyscrapers can utilize sustainable building materials such as recycled steel, low-VOC (volatile organic compound) paints, and sustainably sourced wood to minimize the environmental impact of construction and operation.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Sustainable skyscrapers prioritize the health and well-being of occupants by providing access to natural light, fresh air, and green spaces within the building. This can contribute to improved air quality, reduced stress levels, and enhanced productivity.
Examples of sustainable skyscrapers that incorporate these principles include:
- Burj Khalifa, Dubai: This iconic skyscraper utilizes double-glazed windows, solar panels, and a rainwater harvesting system to reduce its environmental impact.
- One World Trade Center, New York City: This LEED-certified skyscraper features a high-performance curtain wall system that reduces energy consumption and provides natural light to its occupants.
- The Edge, Amsterdam: This innovative skyscraper incorporates a sloping glass facade that maximizes natural light and offers panoramic views of the city while minimizing energy usage.
By embracing sustainability, skyscrapers per city can contribute to the creation of more livable, environmentally friendly, and resilient urban environments. As the world continues to urbanize, sustainable skyscrapers will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of our cities.
6. Cultural Identity
Skyscrapers, with their towering heights and iconic designs, have become symbols of urban identity and cultural expression. The number of skyscrapers per city is not merely a measure of economic development but also a reflection of the city’s cultural values, aspirations, and unique character.
- Architectural Heritage and Local Culture: Skyscrapers often incorporate elements of traditional architecture or local cultural motifs into their designs, creating a harmonious blend of the past and present. For example, the Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur draw inspiration from Islamic art, while the Bank of China Tower in Hong Kong resembles a bamboo stalk, reflecting the city’s Chinese heritage.
- Urban Skyline as Cultural Canvas: The skyline of a city, shaped by its skyscrapers, becomes a canvas for cultural expression. It can symbolize the city’s economic power, technological advancements, or artistic aspirations. The futuristic skyscrapers of Dubai, for instance, showcase the city’s ambition and desire to push architectural boundaries.
- Skyscrapers as Cultural Landmarks: Iconic skyscrapers often become cultural landmarks, representing the identity and spirit of the city. The Empire State Building in New York City and the Eiffel Tower in Paris are prime examples of skyscrapers that have transcended their functional purpose and become symbols of their respective cities.
- Skyscrapers and Urban Identity: The presence and density of skyscrapers can shape the way people perceive and experience a city. They can create a sense of grandeur, excitement, and global connectivity, while also influencing the city’s social dynamics and urban fabric.
In conclusion, the connection between cultural identity and skyscrapers per city is multifaceted
and profound. Skyscrapers are not just vertical structures but cultural expressions that reflect the values, aspirations, and unique character of the cities they inhabit.
7. Urban Planning
Urban planning plays a crucial role in determining the number of skyscrapers per city. It involves the thoughtful arrangement and regulation of land use, infrastructure, and public spaces to create livable, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing urban environments. In the context of skyscrapers, effective urban planning is essential for ensuring their harmonious integration into the urban fabric and mitigating their potential negative impacts.
One of the key aspects of urban planning is regulating building heights and densities to prevent overcrowding and ensure adequate sunlight and ventilation. Zoning laws and height restrictions are used to control the distribution and concentration of skyscrapers within a city. This planning ensures that skyscrapers do not overshadow neighboring buildings or create wind tunnels that can affect pedestrian comfort. For example, in New York City, zoning regulations limit the height of buildings in certain districts to preserve the city’s iconic skyline and protect the views of landmarks like the Empire State Building and Central Park.
Urban planning also involves the provision of adequate infrastructure to support the increased population and activities brought by skyscrapers. This includes expanding transportation networks, upgrading utilities, and creating green spaces and public amenities to cater to the needs of residents and workers in high-rise buildings. Well-planned infrastructure ensures that skyscrapers contribute positively to the city’s overall livability and quality of life.
Furthermore, urban planning considers the long-term impact of skyscrapers on the urban environment. It assesses the potential effects of high-rise buildings on air quality, energy consumption, and waste generation. By incorporating sustainable design principles and green building practices into urban planning regulations, cities can promote the construction of environmentally friendly skyscrapers that minimize their ecological footprint.
In summary, urban planning is a critical component of skyscrapers per city. It ensures the orderly and sustainable development of high-rise buildings, promotes their harmonious integration into the urban environment, and maximizes their benefits while mitigating potential negative impacts. By carefully planning for skyscrapers, cities can create vibrant, livable, and sustainable urban environments that enhance the quality of life for all residents.
Skyscrapers per City FAQs
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions regarding the topic of skyscrapers per city. The questions and answers provide concise and informative explanations to enhance understanding.
Question 1: What is the significance of skyscrapers per city?
Skyscrapers per city serve as an indicator of economic growth, architectural innovation, and urban development. They provide increased floor space, enhance a city’s skyline, and contribute to urban sustainability by promoting efficient land use.
Question 2: How do skyscrapers impact urban density?
Skyscrapers play a crucial role in increasing urban density by providing vertical living and working spaces. They allow for a more efficient use of land, accommodating a growing population within a limited geographical area.
Question 3: What are the environmental implications of skyscrapers?
While skyscrapers can contribute to energy consumption and waste generation, modern designs incorporate sustainable features to minimize their environmental impact. Green building practices, energy-efficient technologies, and rainwater harvesting systems are increasingly employed to reduce the ecological footprint of high-rise buildings.
Question 4: How do skyscrapers influence a city’s cultural identity?
Skyscrapers serve as iconic landmarks and symbols of urban identity. Their architectural designs often reflect cultural values and aspirations, shaping the city’s skyline and contributing to its unique character.
Question 5: What role does urban planning play in regulating skyscrapers?
Urban planning is essential for managing the development of skyscrapers. Zoning laws, height restrictions, and infrastructure planning ensure the harmonious integration of high-rise buildings into the urban fabric, mitigating potential negative impacts on sunlight, ventilation, and overall livability.
Question 6: How can skyscrapers contribute to sustainable urban development?
Skyscrapers can promote sustainable urban development by incorporating green building practices, such as energy efficiency, water conservation, and waste reduction. They can also contribute to reducing urban sprawl and preserving valuable land resources for essential purposes.
In conclusion, skyscrapers per city represent a complex and multifaceted topic with significant implications for urban development, sustainability, and cultural identity. Understanding the various aspects and addressing common concerns through these FAQs provides a comprehensive overview of this important subject.
Transition to the next article section: The following section will delve deeper into the architectural and engineering challenges associated with constructing skyscrapers, exploring innovative design solutions and the pursuit of sustainable high-rise buildings.
Skyscraper Design and Construction Tips
Designing and constructing skyscrapers requires careful planning, innovative engineering, and adherence to strict safety standards. Here are some essential tips to consider:
Tip 1: Structural Integrity: Skyscrapers must withstand various forces, including wind, seismic activity, and gravitational loads. Structural engineers employ advanced techniques like diagrid structures and reinforced concrete cores to ensure the building’s stability and integrity.
Tip 2: Wind Resistance: Tall buildings are susceptible to wind forces. Architects incorporate aerodynamic designs, wind tunnels, and tuned mass dampers to minimize wind-induced vibrations and enhance structural stability.
Tip 3: Fire Safety: Skyscrapers pose unique fire safety challenges. Fire-resistant materials, compartmentalization, and advanced fire suppression systems are crucial for containing and extinguishing fires.
Tip 4: Sustainable Design: Modern skyscrapers embrace sustainable practices to reduce their environmental impact. Green building certifications, energy-efficient lighting, and rainwater harvesting systems contribute to eco-friendly high-rise developments.
Tip 5: Urban Integration: Skyscrapers should harmoniously integrate with the urban fabric. Careful planning ensures adequate sunlight, ventilation, and access to public transportation, creating a livable and vibrant urban environment.
Tip 6: Innovation and Aesthetics: Architectural innovation drives the design of captivating and iconic skyscrapers. Unique facades, sky gardens, and observation decks enhance the aesthetic appeal and create memorable landmarks.
Tip 7: Advanced Construction Techniques: Prefabrication, modular construction, and the use of high-strength materials expedite the construction process, reduce costs, and improve safety on skyscraper projects.
Tip 8: Tenant Comfo
rt and Well-being: Skyscrapers should provide comfortable and healthy indoor environments for occupants. Natural light, fresh air ventilation, and amenities like fitness centers contribute to tenant satisfaction and productivity.
By adhering to these tips, architects, engineers, and urban planners can create skyscrapers that are structurally sound, environmentally friendly, aesthetically pleasing, and contribute positively to the urban landscape.
Conclusion: Skyscrapers continue to shape the skylines of cities worldwide, pushing the boundaries of architectural design and engineering innovation. By embracing these tips, we can ensure that future skyscrapers are not only vertical marvels but also symbols of sustainable urban development and human ingenuity.
Skyscrapers
The exploration of “skyscrapers per city” reveals their multifaceted impact on urban development, sustainability, and cultural identity. These vertical giants serve as indicators of economic growth, architectural prowess, and a city’s unique character.
Skyscrapers have transformed urban landscapes, providing increased floor space, enhancing skylines, and promoting efficient land use. Their construction involves cutting-edge engineering and design solutions that address challenges such as structural stability, wind resistance, and fire safety. As cities strive for sustainability, modern skyscrapers incorporate green building practices to minimize their environmental footprint.
Moreover, skyscrapers have become iconic landmarks, reflecting the cultural values and aspirations of the cities they inhabit. Their architectural designs often draw inspiration from local heritage and traditions, contributing to a city’s unique identity. Urban planning plays a crucial role in regulating skyscraper construction, ensuring harmonious integration into the urban fabric and mitigating potential negative impacts.
As we look to the future, skyscrapers will continue to evolve, driven by innovation and a commitment to sustainable urban development. By embracing advanced construction techniques, architects and engineers can create skyscrapers that are not only structurally sound but also environmentally friendly and aesthetically pleasing.
Skyscrapers per city serve as a testament to human ingenuity and our ability to push the boundaries of architecture and engineering. They shape the skylines of our cities, contribute to economic growth, and reflect the cultural identity of urban centers worldwide.
As we continue to build upwards, let us strive to create skyscrapers that are not only vertical marvels but also symbols of sustainable urban development and human progress.