Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia that is known for its modern architecture, including its skyscrapers. Skyscrapers are tall buildings that are typically used for commercial or residential purposes. The tallest skyscraper in Malaysia is the Petronas Towers, which is located in Kuala Lumpur. The Petronas Towers are 452 meters tall and have 88 floors. They were completed in 1998 and were the tallest buildings in the world until 2004.
Skyscrapers are important to Malaysia because they provide space for businesses to operate and for people to live. They also contribute to the country’s economy by attracting tourists and investment. In addition, skyscrapers can be a symbol of a country’s economic and technological progress.
The history of skyscrapers in Malaysia dates back to the early 20th century. The first skyscraper in Malaysia was the Sultan Abdul Samad Building, which was completed in 1936. The Sultan Abdul Samad Building is a 41-meter-tall building that has six floors. It was designed by British architect A.C. Norman and is a major landmark in Kuala Lumpur.
1. Height
Height is a defining characteristic of skyscrapers in Malaysia. These towering structures dominate the skylines of major cities like Kuala Lumpur, symbolizing the country’s economic and architectural prowess.
The height of skyscrapers is not merely an aesthetic consideration; it serves several practical purposes. Firstly, it allows for increased floor space, accommodating more offices, residential units, or commercial establishments within a limited land area. Secondly, greater height enhances visibility and creates a landmark status, attracting attention and boosting property values in the surrounding area.
Furthermore, the height of skyscrapers can contribute to sustainability. Taller buildings can incorporate wind turbines or solar panels at higher elevations, harnessing renewable energy sources more effectively. Additionally, they can employ gravity-based systems for water distribution and waste management, reducing energy consumption.
The iconic Petronas Towers, standing at 452 meters, exemplify the architectural significance of height in Malaysian skyscrapers. Their twin spires not only symbolize the country’s rapid economic growth in the 1990s but also serve as a testament to its engineering capabilities. Other notable examples include The Exchange 106, currently the tallest building in Southeast Asia, and Merdeka 118, which is set to become the second tallest building in the world upon its completion.
In conclusion, the height of skyscrapers in Malaysia is not just a matter of aesthetics but also plays a crucial role in maximizing space, enhancing visibility, promoting sustainability, and shaping the country’s architectural identity.
2. Architecture
Architecture plays a pivotal role in shaping the identity of Malaysia’s skyscrapers, contributing to their aesthetic appeal, functionality, and sustainability. The architectural styles employed in these towering structures reflect a blend of cultural influences, modern design principles, and innovative engineering solutions.
One of the most striking features of Malaysian skyscrapers is their incorporation of traditional motifs and elements. For instance, the design of the Petronas Towers draws inspiration from Islamic architecture, featuring geometric patterns and arches. The Kuala Lumpur Convention Centre, on the other hand, showcases a contemporary interpretation of Malay traditional architecture, with its intricate roof resembling a woven basket.
Beyond aesthetics, the architecture of Malaysian skyscrapers is driven by functionality. The buildings are designed to maximize space and natural light, creating efficient and comfortable environments for occupants. Advanced glazing systems and sunshades are employed to regulate temperature and reduce energy consumption. Moreover, skyscrapers in Malaysia often integrate green spaces and public areas, enhancing the well-being of building users and contributing to the overall urban environment.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between architecture and Malaysian skyscrapers lies in its implications for urban planning and sustainable development. By carefully considering the architectural design of these structures, architects and urban planners can create livable, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing urban environments. This understanding also enables the preservation and celebration of Malaysia’s cultural heritage while embracing modern architectural trends.
In conclusion, the architecture of Malaysian skyscrapers is a testament to the country’s cultural diversity, technological advancements, and commitment to sustainable development. By harmonizing aesthetics, functionality, and sustainability, these architectural marvels contribute to the nation’s economic growth, global recognition, and overall quality of life.
3. Function
Function plays a crucial role in shaping the design and utilization of skyscrapers in Malaysia. These towering structures serve a diverse range of functions, catering to the needs of businesses, residents, and the wider community. Understanding the function of Malaysian skyscrapers provides insights into their economic, social, and environmental impact.
One of the primary functions of skyscrapers in Malaysia is to provide commercial office space for businesses and corporations. These high-rise buildings offer modern and efficient work environments, facilitating collaboration, innovation, and business growth. The concentration of offices in skyscrapers creates central business districts, fostering economic activity and promoting urban development.
Residential skyscrapers are another significant functional category in Malaysia. These buildings offer luxury apartments and condominiums, providing comfortable and convenient living spaces for urban dwellers. High-rise residential developments often include amenities such as swimming pools, fitness centers, and retail outlets, creating self-contained communities within the city center.
Beyond commercial and residential functions, skyscrapers in Malaysia also serve public and community purposes. For example, the Kuala Lumpur Convention Centre is a state-of-the-art facility that hosts international conferences and exhibitions, contributing to the country’s tourism and business events industry. The Menara Kuala Lumpur, also known as the KL Tower, is a telecommunications tower that offers panoramic views of the city and serves as a popular tourist attraction.
Understanding the function of Malaysian skyscrapers is essential for urban planning and sustainable development. By carefully considering the mix of functions within these buildings, architects and urban planner
s can create vibrant and livable urban environments that meet the diverse needs of the population.
In conclusion, the function of skyscrapers in Malaysia extends beyond mere aesthetics or height. These buildings play a vital role in supporting economic growth, providing living spaces, and serving the needs of the community. Understanding the functional aspects of Malaysian skyscrapers is crucial for optimizing their design, utilization, and overall impact on the urban landscape.
4. Engineering
Engineering plays a critical role in the design, construction, and maintenance of skyscrapers in Malaysia, ensuring their structural integrity, safety, and sustainability. The engineering marvels behind these towering structures are a testament to Malaysia’s advanced technological capabilities and commitment to innovation.
- Structural Engineering
Structural engineers are responsible for designing the framework of skyscrapers, ensuring they can withstand various loads and forces, including gravity, wind, and seismic activity. In Malaysia, skyscrapers often incorporate innovative structural systems, such as diagrid structures and tuned mass dampers, to enhance stability and resilience.
- Geotechnical Engineering
Geotechnical engineers study the soil conditions and foundation systems of skyscrapers to ensure they have a stable base. In Malaysia, where skyscrapers are often built on soft soil, engineers employ techniques such as pile foundations and soil improvement to provide adequate support and prevent settlement.
- Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineers design and install the mechanical systems within skyscrapers, including HVAC, plumbing, and elevators. These systems ensure the comfort, safety, and energy efficiency of the building. In Malaysia, skyscrapers often utilize advanced mechanical systems, such as district cooling systems and rainwater harvesting, to reduce environmental impact and operating costs.
- Fire Protection Engineering
Fire protection engineers are responsible for designing and implementing fire safety systems in skyscrapers. In Malaysia, skyscrapers adhere to strict fire safety regulations, including compartmentalization, smoke control systems, and advanced fire suppression technologies. These measures ensure the safety of occupants and minimize the risk of fire damage.
The engineering marvels behind Malaysian skyscrapers are not just technical achievements but also contribute to the overall livability, sustainability, and economic growth of the country. These engineering feats showcase Malaysia’s commitment to innovation, technological advancement, and the well-being of its citizens.
5. Sustainability
Sustainability is a crucial aspect of modern architecture, and skyscrapers in Malaysia are no exception. These towering structures are designed and built with careful consideration for their environmental impact, resource consumption, and overall well-being of occupants. Understanding the connection between sustainability and Malaysian skyscrapers provides insights into the country’s commitment to eco-friendly development and sustainable urban growth.
- Green Building Design
Malaysian skyscrapers often incorporate green building design principles, such as energy-efficient lighting systems, water-saving fixtures, and sustainable materials. The Menara Mesiniaga in Kuala Lumpur, for example, is a LEED-certified building that features a double-skin facade to reduce heat gain and energy consumption.
- Renewable Energy Integration
Many skyscrapers in Malaysia harness renewable energy sources to reduce their carbon footprint. The Merdeka 118, set to become the second tallest building in the world, will incorporate solar panels and wind turbines to generate clean energy.
- Rainwater Harvesting and Water Efficiency
Water conservation is a key sustainability feature in Malaysian skyscrapers. Buildings like the KLCC Twin Towers and The Exchange 106 employ rainwater harvesting systems to collect and reuse rainwater for non-potable purposes, reducing their reliance on municipal water supply.
- Waste Management and Recycling
Skyscrapers in Malaysia implement comprehensive waste management and recycling programs to minimize their environmental impact. The Menara Hap Seng in Kuala Lumpur has a dedicated waste recycling center that sorts and processes recyclable materials, reducing waste sent to landfills.
The emphasis on sustainability in Malaysian skyscrapers not only benefits the environment but also contributes to the overall livability and well-being of occupants. Sustainable buildings provide healthier indoor environments, reduce operating costs, and enhance the image and reputation of businesses and developments. By embracing sustainability, Malaysia is positioning itself as a leader in green architecture and sustainable urban development.
6. Tourism
Skyscrapers in Malaysia have become iconic landmarks, attracting tourists from around the world. Their architectural marvels, observation decks, and luxurious amenities make them popular destinations for travelers seeking unique experiences and breathtaking views.
- Architectural Wonders
The towering heights and striking designs of Malaysian skyscrapers are a sight to behold. Tourists flock to admire the Petronas Towers, the world’s tallest twin towers, and The Exchange 106, Southeast Asia’s tallest building. These architectural wonders showcase Malaysia’s advanced engineering capabilities and provide a glimpse into the country’s modern architectural landscape.
- Observation Decks
Many skyscrapers in Malaysia offer observation decks that provide panoramic views of the city and its surroundings. The KL Tower, standing at 421 meters, offers breathtaking views of Kuala Lumpur from its observation deck. Tourists can also visit the SkyBridge connecting the Petronas Towers for a unique perspective of the city’s skyline.
- Luxury and Amenities
Skyscrapers in Malaysia often house luxury hotels, restaurants, and shopping malls. The Ritz-Carlton, Kuala Lumpur, located in The Exchange 106, offers opulent accommodations and stunning views. Tourists can indulge in world-class dining and shopping experiences within these skyscrapers, making them ideal destinations for discerning travelers.
- Cultural Immersion
Skyscrapers in Malaysia are not just architectural feats but also cultural landmarks. They often incorporate traditional design elements and motifs, reflecting the country’s rich heritage. Tourists can experience a blend of modernity and tradition by visiting these skyscrapers, gaining insights into Malaysia’s cultural identity.
In conclusion, the connection between tourism and Malaysian skyscrapers is undeniable. These towering structures serve as architectural marvels, observation platforms, and luxurious destinations, attracting tourists worldwide. They contribute to Malaysia’s tourism industry, showcase its
architectural prowess, and offer visitors a unique and unforgettable experience.
7. Investment
Investment plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of malaysia skyscrapers. These towering structures require substantial financial backing to bring them from architectural concepts to gleaming urban landmarks.
One of the primary reasons for investing in malaysia skyscrapers is their potential for high returns. Commercial skyscrapers, with their vast office spaces, offer attractive rental yields and long-term capital appreciation. Residential skyscrapers, on the other hand, cater to the growing demand for luxury living in urban centers, providing investors with rental income and potential capital gains.
Beyond financial returns, investing in malaysia skyscrapers also contributes to the country’s economic growth and development. Skyscrapers are often part of large-scale mixed-use developments that include retail, hospitality, and entertainment components. These developments create employment opportunities, boost tourism, and stimulate economic activity in surrounding areas.
Furthermore, investing in sustainable skyscrapers can yield environmental and social benefits. Green buildings, designed with energy efficiency and water conservation features, reduce operating costs and attract tenants who prioritize sustainability. Incorporating affordable housing units within skyscraper developments can also contribute to social equity and inclusivity in urban areas.
In conclusion, investment is a vital component of malaysia skyscrapers, driving their development, economic impact, and overall sustainability. Understanding the connection between investment and these architectural marvels is essential for stakeholders involved in real estate, urban planning, and the broader economic landscape of Malaysia.
8. Symbolism
Skyscrapers in Malaysia are not just architectural marvels; they are also powerful symbols that reflect the country’s aspirations, identity, and progress. These towering structures embody various facets of symbolism, each contributing to the overall narrative of Malaysia’s development.
- National Pride and Identity
Skyscrapers in Malaysia serve as symbols of national pride and achievement. Their impressive heights and striking designs evoke a sense of awe and admiration, reinforcing the country’s position on the global stage. The Petronas Towers, for example, have become iconic symbols of Malaysia, recognized worldwide as a testament to the nation’s architectural prowess and economic growth.
- Economic Power and Prosperity
Skyscrapers are often associated with economic power and prosperity. In Malaysia, the presence of numerous skyscrapers, particularly in the heart of Kuala Lumpur, reflects the country’s strong and growing economy. These buildings house major corporations, financial institutions, and multinational companies, contributing to the nation’s economic vitality and competitiveness.
- Modernity and Innovation
Skyscrapers represent Malaysia’s embrace of modernity and innovation. Their cutting-edge designs and incorporation of advanced technologies showcase the country’s commitment to progress and development. The use of sustainable features, such as energy-efficient systems and rainwater harvesting, demonstrates Malaysia’s commitment to environmental stewardship.
- Cultural Heritage and Diversity
While skyscrapers may often be seen as symbols of modernity, they can also reflect a country’s cultural heritage and diversity. In Malaysia, some skyscrapers incorporate traditional architectural elements and motifs, blending the past with the present. This fusion of styles creates a unique and distinctive identity for Malaysian skyscrapers, showcasing the country’s rich cultural tapestry.
In conclusion, the symbolism associated with skyscrapers in Malaysia extends beyond their physical presence. These towering structures embody the nation’s aspirations, economic growth, commitment to innovation, and cultural heritage. Understanding this symbolism provides a deeper appreciation of the role skyscrapers play in shaping Malaysia’s identity and its standing on the global stage.
FAQs about Malaysia Skyscrapers
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding malaysia skyscrapers, providing informative answers to enhance understanding and dispel any uncertainties.
Question 1: What are the tallest skyscrapers in Malaysia?
The Petronas Towers, standing at 452 meters tall, currently hold the title of the tallest skyscrapers in Malaysia. However, the Merdeka 118, upon its completion, is set to surpass the Petronas Towers as the tallest building in Southeast Asia.
Question 2: Are malaysia skyscrapers earthquake-proof?
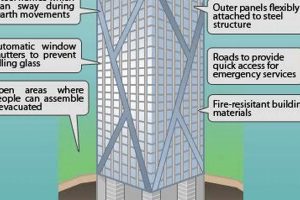
Skyscrapers in Malaysia are designed and constructed to withstand earthquakes. Engineers employ various techniques, such as base isolation systems and tuned mass dampers, to mitigate seismic forces and ensure the structural integrity of these buildings during earthquakes.
Question 3: Are malaysia skyscrapers energy-efficient?
Many malaysia skyscrapers incorporate sustainable design features to improve energy efficiency. These features may include double-glazed facades to reduce heat gain, energy-efficient lighting systems, and rainwater harvesting systems to conserve water.
Question 4: Are malaysia skyscrapers accessible to people with disabilities?
Malaysia’s building codes require skyscrapers to be accessible to people with disabilities. These buildings typically feature ramps, elevators, and accessible restrooms to ensure inclusivity and ease of access for all.
Question 5: What are the safety measures in place in malaysia skyscrapers?
Skyscrapers in Malaysia adhere to strict safety regulations. They are equipped with advanced fire safety systems, including sprinklers, smoke detectors, and fire escapes. Regular safety drills and inspections are conducted to ensure the preparedness of occupants in case of emergencies.
Question 6: What is the future of malaysia skyscrapers?
The future of malaysia skyscrapers lies in sustainable, innovative, and mixed-use developments. Architects and developers are exploring new technologies and design concepts to create skyscrapers that are environmentally friendly, technologically advanced, and cater to the evolving needs of businesses and residents.
In summary, malaysia skyscrapers are marvels of engineering, symbols of economic growth, and testaments to the country’s commitment to sustainability and accessibility. As the nation continues to progress, we can expect to see even more impressive and innovative skyscrapers gracing the skylines of Malaysian cities.
Understanding these FAQs provides a deeper appreciation of the design, construction, and impact of malaysia skyscrapers, fostering informed discussions and responsible decision-making regarding these architectural wonders.
Tips for Malaysia Skyscrapers
Malaysia’s skyscrapers are architectural marvels that contribute to the country’s economic growth and global recognition. To ensure the continued success and sustainability of these iconic structures, cons
ider the following tips:
Tip 1: Prioritize Sustainable Design
Incorporate green building principles to reduce energy consumption, conserve water, and minimize environmental impact. Consider features such as double-glazed facades, rainwater harvesting systems, and energy-efficient lighting.
Tip 2: Embrace Technological Advancements
Utilize cutting-edge technologies to enhance safety, efficiency, and occupant comfort. Implement smart building systems, advanced fire safety measures, and automated maintenance solutions to optimize building performance.
Tip 3: Ensure Accessibility and Inclusivity
Design skyscrapers to be accessible to people with disabilities and diverse needs. Provide ramps, elevators, accessible restrooms, and sensory-sensitive spaces to create an inclusive environment for all.
Tip 4: Promote Mixed-Use Developments
Integrate commercial, residential, retail, and hospitality components within skyscraper developments. Mixed-use buildings foster vibrant urban environments, reduce traffic congestion, and cater to the evolving needs of businesses and residents.
Tip 5: Encourage Collaboration and Innovation
Foster collaboration between architects, engineers, developers, and policymakers to push the boundaries of skyscraper design and construction. Encourage innovative approaches to sustainability, structural engineering, and architectural aesthetics.
Tip 6: Invest in Regular Maintenance and Retrofitting
Regular maintenance and timely retrofits are crucial to ensure the longevity and safety of skyscrapers. Conduct thorough inspections, address any structural issues promptly, and upgrade building systems to meet evolving safety codes and sustainability standards.
By adhering to these tips, Malaysia can continue to develop world-class skyscrapers that meet the needs of the present and future generations while contributing to the nation’s economic prosperity and global competitiveness.
Conclusion
Malaysia’s skyscrapers stand as testaments to the nation’s economic growth, architectural prowess, and commitment to sustainability. These towering structures have transformed skylines, fostered economic development, and enhanced the overall quality of life in Malaysian cities.
As Malaysia continues to progress, we can expect to see even more impressive and innovative skyscrapers gracing our urban landscapes. By embracing sustainable design, technological advancements, accessibility, and mixed-use developments, Malaysia can ensure that its skyscrapers continue to be symbols of progress, prosperity, and inclusivity for generations to come.