A list of skyscrapers refers to a compilation of high-rise buildings, typically exceeding a certain height threshold, such as 150 meters (492 feet) or 100 stories. These lists are often categorized by height, location, or architectural style, providing a comprehensive overview of the world’s most iconic and impressive skyscrapers.
Skyscrapers have revolutionized urban landscapes, offering numerous advantages. They optimize space in densely populated areas, accommodating a significant number of people and businesses within a limited footprint. Their height also provides panoramic views, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of cities and offering occupants breathtaking vistas. Moreover, skyscrapers serve as symbols of economic prosperity and architectural innovation, attracting tourism and investment.
Exploring the list of skyscrapers unveils the architectural marvels that shape skylines worldwide. From the towering Burj Khalifa in Dubai to the iconic Empire State Building in New York City, each skyscraper holds a unique story of engineering prowess and aesthetic vision. Delving into their designs, construction methods, and cultural significance offers a fascinating glimpse into the evolution of architecture and urban planning.
1. Height
Height is a defining characteristic of skyscrapers, influencing their overall presence and impact on the surrounding cityscape. Measured in meters or feet, it determines a skyscraper’s vertical dominance and establishes its place among the world’s tallest structures.
- Height Records: Skyscrapers compete for height supremacy, with new constructions constantly pushing the boundaries. The Burj Khalifa, standing at 828 meters, currently holds the title of the world’s tallest building, while others like the Shanghai Tower and the Makkah Royal Clock Tower follow closely behind.
- Engineering Challenges: Constructing skyscrapers at extreme heights presents significant engineering challenges. Architects and engineers must carefully consider factors such as wind resistance, structural stability, and material strength to ensure the safety and longevity of the building.
- Urban Planning: The height of skyscrapers affects urban planning and zoning regulations. They can alter wind patterns, cast shadows, and impact the overall aesthetics of a city’s skyline. Careful planning is necessary to ensure skyscrapers integrate harmoniously into the urban fabric.
- Economic Implications: Taller skyscrapers can accommodate more tenants, leading to higher rental rates and increased property values. They can also attract businesses and investment, contributing to economic growth and development in a city.
In the context of “list of skyscrapers,” height serves as a primary criterion for ranking and categorizing these architectural marvels. It provides a quantifiable measure of their vertical dominance and allows for comparisons between different skyscrapers. Moreover, height is often associated with prestige and technological advancement, making it an important factor in the design and construction of these iconic structures.
2. Location
The location of skyscrapers is inextricably linked to the concept of “list of skyscrapers.” Skyscrapers are predominantly situated in urban centers, where they shape cityscapes and serve as barometers of economic growth.
- Urban Dominance: Skyscrapers transform urban landscapes, becoming iconic landmarks that define a city’s skyline. They create vertical neighborhoods, offering panoramic views and optimizing space in densely populated areas.
- Economic Indicators: The presence of skyscrapers is often associated with economic prosperity and investment. Cities with numerous skyscrapers are perceived as thriving and attractive to businesses and residents alike.
- Land Value and Development: Skyscrapers can drive up land values and stimulate urban development. They attract businesses, residential units, and retail spaces, creating vibrant mixed-use neighborhoods.
- Transportation Hubs: Skyscrapers are often located near major transportation hubs, ensuring accessibility and connectivity for tenants and visitors. This proximity enhances the value and convenience of these high-rise buildings.
In the context of “list of skyscrapers,” location plays a crucial role in ranking and categorizing these structures. Skyscrapers are often listed according to their city or region, showcasing the architectural diversity and economic vitality of different urban centers. Location also influences the design and construction of skyscrapers, as factors such as seismic activity, wind patterns, and available infrastructure must be carefully considered.
3. Architecture
Architecture plays a paramount role in the context of “list of skyscrapers,” as it encompasses the unique designs, styles, and engineering feats that define these towering structures. Skyscrapers showcase a wide range of architectural prowess, from modern to neoclassical designs, pushing the boundaries of innovation and creativity.
- Modern Architecture: Modern skyscrapers embrace sleek lines, geometric forms, and innovative materials like glass and steel. They prioritize functionality, efficiency, and the integration of natural light, creating a sense of openness and spaciousness. Examples include the Seagram Building in New York City and the Burj Khalifa in Dubai.
- Neoclassical Architecture: Neoclassical skyscrapers draw inspiration from ancient Greek and Roman architecture, incorporating elements such as columns, pediments, and symmetrical facades. They exude grandeur and elegance, often serving as landmarks and civic buildings. Examples include the Empire State Building in New York City and the One Liberty Place in Philadelphia.
- Art Deco Architecture: Art Deco skyscrapers emerged in the 1920s and 1930s, characterized by geometric patterns, stylized ornamentation, and setbacks. They represent a fusion of modern and historical influences, adding a touch of glamour and sophistication to the urban landscape. Examples include the Chrysler Building in New York City and the Miami Tower in Miami.
- Postmodern Architecture: Postmodern skyscrapers challenge traditional design norms, incorporating playful elements, fragmented forms, and a mix of styles. They often make bold statements and reflect the eclecticism of the late 20th century. Examples include the AT&T Building in New York City and the Torre Agbar in Barcelona.
The architectural diversity of skyscrapers enhances the visual appeal o
f cities, making them dynamic and captivating. These structures serve as testaments to the ingenuity and artistic vision of architects and engineers, pushing the boundaries of design and innovation.
4. Purpose
The purpose of skyscrapers is a key aspect influencing their design, construction, and overall impact on urban landscapes. Skyscrapers serve diverse functions, including residential, commercial, and mixed-use, catering to a wide range of needs and activities.
Residential skyscrapers provide housing for individuals and families, offering panoramic views and convenient access to urban amenities. Commercial skyscrapers house offices, businesses, and retail spaces, creating vibrant commercial hubs within cities. Mixed-use skyscrapers combine residential and commercial functions, providing a convenient and integrated living and working environment.
The purpose of a skyscraper influences its design and amenities. Residential skyscrapers prioritize comfortable living spaces, often featuring balconies, fitness centers, and communal areas. Commercial skyscrapers emphasize efficient use of space, incorporating open floor plans, high-speed elevators, and modern infrastructure. Mixed-use skyscrapers combine elements of both residential and commercial design, creating dynamic and versatile spaces that cater to a diverse range of users.
Understanding the purpose of skyscrapers is crucial for creating functional and sustainable urban environments. By considering the intended use of a skyscraper, architects and urban planners can design buildings that meet the specific needs of occupants and contribute positively to the overall urban fabric.
5. Engineering
Engineering plays a crucial role in the context of “list of skyscrapers,” as it encompasses the innovative techniques and strategies employed to ensure the structural integrity and safety of these towering structures. Skyscrapers are subjected to various forces, including gravity, wind, and seismic activity, and engineering expertise is paramount in designing buildings that can withstand these forces and protect occupants.
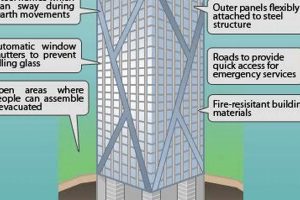
One of the key engineering challenges in skyscraper construction is ensuring stability against lateral forces, such as wind and earthquakes. Engineers employ various techniques to enhance stability, including the use of shear walls, moment-resisting frames, and outrigger systems. These structural elements work together to distribute and dissipate lateral forces, preventing excessive swaying and potential collapse.
Another important aspect of skyscraper engineering is the design of efficient and reliable elevator systems. High-rise buildings require elevators that can transport large numbers of people quickly and safely, and engineers must carefully consider factors such as elevator speed, capacity, and energy efficiency. Modern skyscrapers often incorporate advanced elevator systems, such as double-decker elevators and sky lobbies, to optimize vertical transportation and reduce wait times.
The engineering of skyscrapers also involves the integration of sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. Engineers strive to design buildings that minimize energy consumption, reduce carbon emissions, and promote occupant well-being. This can involve the use of energy-efficient lighting systems, rainwater harvesting systems, and green roofs.
Understanding the engineering principles behind skyscrapers is crucial for ensuring the safety and functionality of these iconic structures. By utilizing innovative engineering techniques, architects and engineers can create skyscrapers that are not only visually impressive but also safe, sustainable, and resilient.
6. Sustainability
In the context of “list of skyscrapers,” sustainability has become an increasingly important consideration, as these towering structures have the potential to significantly impact the environment. Architects and engineers are incorporating a range of green features into skyscraper designs to minimize their environmental footprint and promote occupant well-being.
- Energy Efficiency: Skyscrapers consume a substantial amount of energy for lighting, heating, cooling, and other operations. Green features such as energy-efficient lighting systems, double-glazed windows, and automated building management systems can significantly reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions.
- Water Conservation: Rainwater harvesting systems collect and store rainwater for non-potable uses such as irrigation and toilet flushing. Low-flow fixtures and water-efficient landscaping can further reduce water consumption.
- Green Roofs and Facades: Green roofs and facades incorporate vegetation into the building’s exterior. They provide insulation, reduce stormwater runoff, and improve air quality by absorbing pollutants and releasing oxygen.
- Sustainable Materials: Architects are increasingly using sustainable materials such as recycled steel, low-VOC paints, and FSC-certified wood in skyscraper construction. These materials minimize the environmental impact of the building’s materials and contribute to a healthier indoor environment.
By incorporating these and other green features, skyscrapers can reduce their environmental impact, promote occupant well-being, and contribute to a more sustainable built environment. As the demand for sustainable buildings continues to grow, skyscrapers are expected to play an increasingly important role in creating cities that are both environmentally responsible and livable.
7. Cultural Significance
Skyscrapers, with their towering heights and iconic designs, often transcend their functional purpose and become cultural landmarks and symbols of urban identity and architectural achievements. This cultural significance is deeply intertwined with the concept of “list of skyscrapers,” as it underscores the impact these structures have on shaping the identity and perception of cities.
When skyscrapers are included in a list, they are not merely cataloged as tall buildings but are recognized for their unique architectural features, historical importance, and the role they play in shaping the urban landscape. The Empire State Building, for example, is not just a skyscraper but an iconic symbol of New York City and a cultural touchstone that has been featured in countless works of art, literature, and film.
The cultural significance of skyscrapers extends beyond their individual identities. They also contribute to the collective identity of a city, becoming symbols of its economic power, technological advancements, and architectural prowess. The skyline of a city, with its collection of skyscrapers, can tell a story of the city’s history, its aspirations, and its place in the global landscape.
Understanding the cultural significance of skyscrapers is not only important for appreciating their architectural and historical value but also for comprehending the complex r
elationship between cities, their built environment, and the people who inhabit them. Skyscrapers serve as physical manifestations of human ambition, creativity, and the desire to push the boundaries of what is possible.
FAQs on List of Skyscrapers
This section addresses frequently asked questions related to the topic of skyscrapers, providing informative and concise answers to common queries.
Question 1: What is the tallest skyscraper in the world?
As of 2023, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai holds the title of the world’s tallest skyscraper, standing at an impressive height of 828 meters (2,717 feet).
Question 2: Which city has the most skyscrapers?
Hong Kong currently boasts the largest number of skyscrapers in the world, with over 480 buildings exceeding 150 meters (492 feet) in height.
Question 3: What are the main functions of skyscrapers?
Skyscrapers serve a variety of purposes, including residential, commercial, and mixed-use developments. They provide vertical space for living, working, and a range of other activities in densely populated urban areas.
Question 4: How do skyscrapers withstand strong winds and earthquakes?
Skyscrapers employ various engineering techniques to ensure stability against lateral forces. These include the use of shear walls, moment-resisting frames, and outrigger systems, which work together to distribute and dissipate forces and prevent excessive swaying.
Question 5: What are the sustainability features incorporated into modern skyscrapers?
To minimize environmental impact, modern skyscrapers often incorporate green features such as energy-efficient lighting systems, rainwater harvesting systems, green roofs and facades, and the use of sustainable building materials.
Question 6: How do skyscrapers contribute to the cultural identity of cities?
Skyscrapers have become iconic symbols of urban identity, representing economic power, technological advancements, and architectural prowess. The skyline of a city, with its collection of skyscrapers, tells a story of its history, aspirations, and place in the global landscape.
These FAQs provide a concise overview of key aspects related to skyscrapers, addressing common questions and offering informative answers to enhance understanding of these architectural marvels.
Proceed to the next section for further exploration of skyscrapers and their impact on urban landscapes.
Tips for Understanding “List of Skyscrapers”
Comprehending the concept and significance of “list of skyscrapers” requires a multifaceted approach. Here are some valuable tips to enhance your understanding:
Tip 1: Explore Different Categories
Lists of skyscrapers can be categorized based on height, location, architectural style, or function. Familiarize yourself with these categories to gain a comprehensive view of the diverse range of skyscrapers worldwide.
Tip 2: Study Architectural Features
Skyscrapers showcase a variety of architectural styles, from modern to neoclassical. Examine the unique design elements, materials, and structural systems employed in different skyscrapers to appreciate their architectural significance.
Tip 3: Consider Historical Context
The construction of skyscrapers is closely tied to historical events and economic conditions. Research the historical context surrounding the development of notable skyscrapers to understand their purpose and impact on the urban landscape.
Tip 4: Analyze Engineering Innovations
Skyscrapers require innovative engineering solutions to withstand various forces and ensure structural integrity. Explore the engineering techniques used in skyscraper construction, such as the use of shear walls and outrigger systems.
Tip 5: Evaluate Sustainability Features
Modern skyscrapers incorporate sustainable design elements to minimize environmental impact. Investigate the green features employed in skyscrapers, such as energy-efficient lighting, rainwater harvesting systems, and green roofs.
Tip 6: Recognize Cultural Significance
Skyscrapers have become iconic symbols of cities, reflecting economic power and architectural achievements. Understand the cultural significance of skyscrapers and their role in shaping urban identity.
These tips will help you delve deeper into the fascinating world of skyscrapers, unlocking a comprehensive understanding of their architectural, historical, engineering, and cultural aspects.
Proceed to the conclusion to summarize the key takeaways and explore further insights related to skyscrapers.
Conclusion
Our exploration of the “list of skyscrapers” has revealed the multifaceted nature of these architectural marvels. Skyscrapers are not merely tall buildings but symbols of human ambition, ingenuity, and the quest to redefine urban landscapes. Their designs showcase a rich tapestry of architectural styles, reflecting the cultural and historical contexts in which they were built.
The engineering feats involved in constructing skyscrapers are a testament to human innovation. These structures withstand immense forces and provide safe and habitable spaces for millions worldwide. Moreover, modern skyscrapers incorporate sustainable features, demonstrating our commitment to environmental responsibility and well-being.
Skyscrapers have transcended their functional purpose to become iconic symbols of cities. They shape skylines, attract investment, and serve as catalysts for urban development. Understanding the significance of skyscrapers is essential for appreciating their impact on our built environment, cultural heritage, and aspirations for the future.
As we continue to push the boundaries of architectural innovation, the “list of skyscrapers” will undoubtedly evolve, reflecting the ever-changing needs and aspirations of our societies. These towering structures will continue to inspire, challenge, and captivate us, serving as enduring testaments to human ingenuity and the indomitable spirit of progress.