Skyscraper, exceptionally tall high-rise structure with numerous stories. Skyscrapers are designed to house large numbers of people who work, live, or shop within them. The world’s first skyscraper, the Home Insurance Building in Chicago, was completed in 1885 and had 10 stories.
Skyscrapers offer several advantages over traditional low-rise buildings. They can accommodate more people and businesses in a smaller area, making them more efficient and space-saving. Skyscrapers are also more energy-efficient, as they can be designed to take advantage of natural light and ventilation. In addition, skyscrapers can be iconic landmarks that define a city’s skyline.
The construction of skyscrapers has been made possible by advances in engineering and technology. The development of new materials, such as steel and concrete, has allowed buildings to be built taller and stronger. In addition, the invention of the elevator has made it possible to access the upper floors of skyscrapers quickly and easily.
1. Height
The height of skyscrapers is one of their defining characteristics. Reaching hundreds of meters into the sky, they tower over other buildings and dominate the skyline. This height offers several advantages:
- Increased floor space: Taller buildings can accommodate more floor space, allowing for a greater number of occupants and businesses.
- Improved views: Upper floors offer panoramic views of the surrounding city and landscape, which can be a valuable amenity for tenants.
- Reduced land use: Skyscrapers can concentrate a large number of people and businesses in a relatively small area, reducing the need for urban sprawl.
- Iconic landmarks: Skyscrapers can become iconic landmarks that define a city’s skyline and identity.
However, the height of skyscrapers also presents challenges. These include:
- Structural engineering: Taller buildings require innovative engineering solutions to ensure structural stability and safety.
- Wind resistance: Skyscrapers must be designed to withstand high winds and other weather conditions.
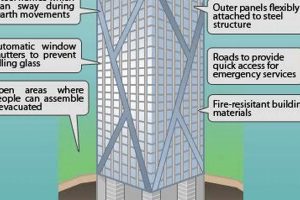
- Fire safety: Evacuating tall buildings in the event of a fire can be challenging, and fire safety systems must be carefully designed and maintained.
- Transportation: Elevators and other transportation systems must be efficient and reliable to move people and goods throughout tall buildings.
Overall, the height of skyscrapers offers both advantages and challenges. Engineers and architects must carefully consider these factors when designing and constructing skyscrapers to ensure their safety, functionality, and impact on the urban environment.
2. Density
Skyscrapers are designed to maximize space utilization, allowing for a high density of occupants and businesses within a relatively small footprint. This space efficiency offers several advantages, including:
- Reduced land use: Skyscrapers can concentrate a large number of people and businesses in a compact area, reducing the need for urban sprawl and preserving valuable land resources.
- Increased accessibility: By accommodating a large number of people in a centralized location, skyscrapers improve accessibility to services, amenities, and transportation hubs.
- Enhanced community building: Densely populated skyscrapers can foster a sense of community and encourage interaction among residents and workers.
- Economic benefits: Space efficiency can lead to cost savings in construction, maintenance, and operation, making skyscrapers a more economical option for businesses and developers.
The density of skyscrapers also presents some challenges, such as increased traffic congestion, demand for infrastructure, and potential overcrowding. However, careful planning and design can mitigate these challenges and ensure that skyscrapers remain sustainable and livable.
3. Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency is a key consideration in the design of skyscrapers, as these buildings can consume significant amounts of energy. By incorporating sustainable design strategies, architects and engineers can reduce the energy consumption of skyscrapers while improving the comfort and well-being of occupants.
One important aspect of energy efficiency in skyscrapers is the use of natural light and ventilation. By maximizing the use of daylight, skyscrapers can reduce their reliance on artificial lighting, leading to energy savings. Additionally, natural ventilation can reduce the need for mechanical cooling systems, further reducing energy consumption.
Several real-life examples demonstrate the effectiveness of energy-efficient design in skyscrapers. The Burj Khalifa in Dubai, for instance, incorporates a double-skin faade that allows for natural ventilation while reducing heat gain. The Shanghai Tower in China uses a rainwater harvesting system and solar panels to reduce its energy consumption. These buildings serve as models for sustainable skyscraper design, showcasing the practical benefits of energy efficiency.
In conclusion, energy efficiency is a crucial aspect of skyscraper design, helping to reduce energy consumption, lower operating costs, and promote sustainability. By incorporating strategies such as natural light and ventilation, architects and engineers can create skyscrapers that are both environmentally friendly and comfortable for occupants.
4. Engineering
Engineering plays a crucial role in the construction of skyscrapers, as innovative solutions are necessary to ensure their structural stability and safety. The unique challenges posed by skyscrapers, such as their immense height and weight, require engineers to develop cutting-edge techniques and materials.
One of the key engineering considerations for skyscrapers is wind resistance. As skyscrapers rise higher into the sky, they become more susceptible to wind forces. Engineers must design skyscrapers to withstand strong winds without compromising their structural integrity. This often involves the use of advanced wind engineering techniques, such as wind tunnel testing and computational fluid dynamics modeling.
Another engineering challenge in skyscraper construction is seismic activity. In earthquake-prone areas, skyscrapers must be designed to withstand the forces o
f an earthquake without collapsing. Engineers use various techniques to enhance the seismic resistance of skyscrapers, such as base isolation systems and tuned mass dampers.
The construction of skyscrapers also requires innovative solutions for fire safety. Skyscrapers are inherently difficult to evacuate in the event of a fire due to their height and the large number of occupants. Engineers must design fire safety systems that can quickly and efficiently detect and suppress fires, as well as provide safe evacuation routes for occupants.
In conclusion, engineering is a critical component of skyscraper construction, as innovative solutions are required to ensure their structural stability, wind resistance, seismic resistance, and fire safety. By pushing the boundaries of engineering knowledge and technology, engineers make it possible to construct skyscrapers that are both safe and habitable.
5. Technology
Skyscrapers, with their towering heights and complex designs, rely heavily on technology to ensure their functionality and safety. Among the most critical technologies are elevators, fire safety systems, and other building systems that play a vital role in the daily operation and maintenance of these high-rise structures.
Elevators, for instance, are indispensable for transporting people and goods efficiently within skyscrapers. Without elevators, it would be impractical or even impossible to access the upper floors of these buildings, limiting their usability and value. Advanced elevator systems, equipped with features such as high-speed operation and destination dispatching, are essential for managing the heavy traffic flow in skyscrapers, ensuring efficient movement of occupants.
Fire safety systems are equally crucial for the safety of occupants in skyscrapers. These systems include smoke detectors, fire sprinklers, and fire alarms, which work together to detect, suppress, and alert occupants of a fire. In the event of a fire, these systems provide valuable time for evacuation and minimize the risk of injury or loss of life.
Other building systems, such as heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), electrical systems, and plumbing, are also essential for the comfort and well-being of occupants in skyscrapers. These systems ensure that the indoor environment is maintained at a comfortable temperature, with adequate air quality and lighting, and that there is a reliable supply of water and electricity throughout the building.
The integration of these technologies into skyscrapers is a testament to the ingenuity and engineering prowess of architects and engineers. By harnessing the power of technology, they have made it possible to construct and operate skyscrapers that are not only awe-inspiring but also safe, efficient, and comfortable for their occupants.
6. Urban planning
Skyscrapers are not just isolated structures; they are integral components of the urban fabric, and their construction and presence have a profound impact on urban planning and the development of cities. As cities grow and densify, skyscrapers offer a solution to accommodate more people and businesses within a limited land area. By concentrating high-density development in vertical spaces, skyscrapers help optimize land use and preserve valuable open spaces.
The construction of skyscrapers also influences the transportation infrastructure and urban mobility patterns. They often become focal points for public transportation systems, with subway stations and bus stops located nearby. This integration encourages the use of public transportation and reduces traffic congestion. Additionally, skyscrapers can incorporate mixed-use developments that combine residential, commercial, and retail spaces, creating vibrant and walkable neighborhoods.
However, the construction of skyscrapers also presents challenges that urban planners must carefully consider. The influx of people and businesses into skyscraper-dense areas can strain infrastructure and services, such as water supply, energy consumption, and waste management. Therefore, urban planning must consider the long-term sustainability and livability of skyscraper-dominated neighborhoods.
In conclusion, skyscrapers are not merely architectural marvels; they are catalysts for urban transformation and economic growth. However, their integration into cities requires careful planning and management to ensure they contribute positively to the overall urban environment and the well-being of city dwellers.
7. Cultural significance
Skyscrapers have become iconic symbols of cities around the world, shaping their identity and skyline. They are architectural marvels that attract tourists and locals alike, serving as landmarks that define a city’s character and history. The cultural significance of skyscrapers lies in their ability to embody the aspirations, values, and achievements of a city and its people.
One prime example is the Empire State Building in New York City. With its Art Deco design and towering height, the Empire State Building has become synonymous with the city’s skyline and is recognized globally as a symbol of American ambition and prosperity. Similarly, the Eiffel Tower in Paris is an iconic landmark that represents the city’s rich cultural heritage and architectural prowess.
Beyond their aesthetic value, skyscrapers also hold cultural significance as symbols of economic and technological advancement. They reflect a city’s ability to innovate, push boundaries, and achieve new heights of construction and engineering. The Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, are a testament to the country’s rapid economic growth and modernization.
Understanding the cultural significance of skyscrapers is important for appreciating their value beyond their functional purpose. They are not just buildings but symbols of a city’s identity, aspirations, and achievements. Preserving and celebrating these iconic landmarks ensures that future generations can continue to connect with the history and culture of their city.
Frequently Asked Questions about Skyscrapers
Skyscrapers have become ubiquitous in major cities worldwide, shaping skylines and serving as symbols of economic and cultural achievements. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about these architectural marvels:
Question 1: What is the tallest skyscraper in the world?
Answer: As of 2023, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, holds the title of the tallest skyscraper in the world, standing at an impressive height of 828 meters (2,717 feet).
Question 2: How do skyscrapers withstand strong winds and earthquakes?
Answer: Skyscrapers employ various engineering techniques to ensure stability and safety in the face of strong winds and earthquakes. These techniques include the use of wind-resistant structural designs, shock absorbers, and tuned mass dampers to minimize vibrations.
Question 3: Are skyscrapers energy-efficient?
Answer: Modern skyscrapers incorporate sustainable design features to enhance energy efficiency. They utilize energy-efficient lighting systems, double-pan
ed windows for insulation, and rainwater harvesting systems to reduce their environmental impact.
Question 4: How are people evacuated from skyscrapers in case of emergencies?
Answer: Skyscrapers have comprehensive fire safety systems and evacuation plans in place. These include fire sprinklers, smoke detectors, and pressurized staircases that provide safe and efficient means of escape during emergencies.
Question 5: What are some of the challenges associated with constructing skyscrapers?
Answer: Constructing skyscrapers involves significant engineering challenges, such as ensuring structural stability at great heights, managing wind loads, and implementing effective fire safety measures.
Question 6: How do skyscrapers contribute to urban development?
Answer: Skyscrapers play a vital role in urban development by maximizing land use, reducing urban sprawl, and creating mixed-use spaces that foster economic growth and community building.
In summary, skyscrapers are marvels of modern engineering and architectural ingenuity, pushing the boundaries of design and construction. Their presence in cities worldwide shapes skylines, symbolizes economic prosperity, and contributes to sustainable urban development.
Transition to the next article section: Skyscrapers have become iconic landmarks and symbols of progress. Explore their cultural significance and the ways they reflect the aspirations and achievements of cities and societies.
Skyscraper Design and Construction Tips
Designing and constructing skyscrapers require meticulous planning, innovative engineering, and adherence to strict safety standards. Here are some essential tips to consider:
Tip 1: Prioritize Structural StabilitySkyscrapers must withstand various forces, including wind loads and seismic activity. Employ robust structural systems, such as diagrid or tube-in-tube designs, to ensure stability and minimize sway.Tip 2: Optimize Wind ResistanceConduct wind tunnel tests to analyze wind patterns and design the building’s shape and cladding accordingly. Utilize wind baffles or vortex shedding devices to reduce wind-induced vibrations.Tip 3: Implement Fire Safety MeasuresIncorporate comprehensive fire safety systems, including sprinklers, smoke detectors, and pressurized staircases. Compartmentalize the building to prevent fire spread and provide safe evacuation routes.Tip 4: Enhance Energy EfficiencyIncorporate sustainable design strategies, such as double-glazed windows, energy-efficient lighting, and rainwater harvesting systems. Optimize building orientation to maximize natural light and ventilation, reducing energy consumption.Tip 5: Address Transportation and AccessPlan for efficient vertical transportation systems, such as elevators and escalators, to manage the flow of occupants. Consider integrating the building with public transportation hubs to promote accessibility and reduce traffic congestion.Tip 6: Ensure Occupant ComfortDesign the building with ample natural light, comfortable indoor temperatures, and good air quality. Incorporate amenities such as green spaces, fitness centers, and retail outlets to enhance occupant well-being.Tip 7: Consider Urban ContextRespect the surrounding urban fabric and architectural style. Design the skyscraper to complement the existing cityscape and contribute positively to the neighborhood’s character.
By following these tips, architects and engineers can create skyscrapers that are not only structurally sound and safe but also sustainable, comfortable, and iconic additions to the urban landscape.
Transition to the article’s conclusion: Skyscrapers represent the pinnacle of architectural and engineering achievements. Their design and construction require meticulous attention to detail, innovation, and adherence to the highest safety standards.
Conclusion
Skyscrapers have indelibly transformed the urban landscape, becoming symbols of progress, innovation, and architectural prowess. Their construction requires meticulous planning, cutting-edge engineering, and unwavering adherence to safety standards.
As we look towards the future of skyscrapers, sustainability and occupant well-being will continue to be at the forefront of design considerations. Architects and engineers will strive to create skyscrapers that not only reach for the sky but also minimize their environmental impact and enhance the lives of those who inhabit them.
Skyscrapers stand as testaments to human ingenuity and ambition. Their enduring legacy will continue to inspire and captivate generations to come, shaping the skylines of cities worldwide and serving as icons of architectural achievement.