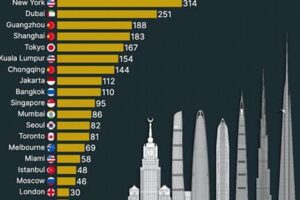
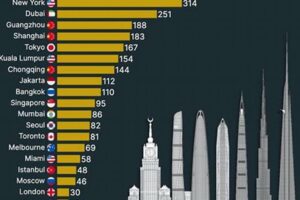
A “city of skyscrapers” is a metropolitan area characterized by an abundance of high-rise buildings, typically exceeding 50 stories in height. These structures are architectural marvels that push the boundaries of engineering and design, transforming skylines and redefining urban landscapes. New York City, often regarded as the quintessential “city of skyscrapers,” exemplifies this concept with its iconic skyscrapers, including the Empire State Building, One World Trade Center, and the Chrysler Building. Other notable examples include Hong Kong, Shanghai, Dubai, and Tokyo.
Skyscrapers offer several advantages. They maximize land use in densely populated urban areas, providing ample space for businesses, residential units, and public amenities. Their height allows for breathtaking panoramic views, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of a city. Moreover, skyscrapers can incorporate sustainable design features, such as energy-efficient systems and green spaces, contributing to environmental preservation. Historically, the construction of skyscrapers has been driven by economic growth, technological advancements, and architectural innovation.
The following article will delve into the fascinating world of “cities of skyscrapers,” exploring their architectural significance, economic impact, and social implications. We will examine notable examples from around the globe, highlighting their unique design features and contributions to the urban fabric. Furthermore, we will discuss the challenges and opportunities associated with the construction and management of these towering structures, considering their environmental impact, safety regulations, and the well-being of occupants.
1. Verticality
In the context of “cities of skyscrapers,” verticality plays a pivotal role in maximizing land use and enabling upward growth. The ability of skyscrapers to rise high into the sky allows cities to accommodate a greater population and diverse urban functions within a limited geographical footprint. This vertical expansion is particularly crucial in densely populated urban areas, where land is scarce and expensive.
Skyscrapers serve as a solution to the challenge of accommodating a growing population without sprawling outwards into surrounding. By building upwards, cities can preserve valuable green spaces, agricultural land, and natural ecosystems. Moreover, vertical development promotes compact and efficient urban planning, reducing the need for excessive transportation infrastructure and fostering walkability and connectivity.
Real-life examples abound, showcasing the transformative impact of skyscraper-driven verticality on urban landscapes. In Hong Kong, one of the most densely populated cities globally, skyscrapers have played a vital role in accommodating its 7.5 million residents within a relatively small land area. Similarly, in New York City, iconic skyscrapers like the Empire State Building and One World Trade Center have enabled the city to grow vertically, accommodating millions of people and businesses while preserving its vibrant street life and cultural heritage.
Understanding the significance of verticality in “cities of skyscrapers” is essential for urban planners and policymakers seeking to create sustainable and livable urban environments. By embracing vertical development, cities can optimize land use, reduce urban sprawl, and foster vibrant, connected communities.
2. Density
In the context of “city of skyscrapers”, density plays a central role in accommodating a large population within a relatively small footprint, fostering vibrant urban communities. Skyscrapers enable cities to maximize land use and create compact, walkable neighborhoods where residents and visitors can easily access amenities, services, and cultural attractions.
- High Population Density: Skyscrapers allow cities to house a large number of people in a limited geographical area, creating a critical mass of individuals and businesses that supports a diverse range of urban activities. This density fosters a sense of community and vibrancy, with a constant buzz of activity and a wide array of cultural offerings.
- Walkability and Connectivity: The high density of skyscrapers promotes walkability and connectivity, reducing reliance on cars and creating a more sustainable and livable urban environment. Residents and visitors can easily walk or cycle to work, shops, restaurants, and entertainment venues, fostering a sense of place and community.
- Mixed-Use Developments: Skyscrapers often incorporate mixed-use developments that combine residential, commercial, and retail spaces within a single building or complex. This integration promotes a live-work-play lifestyle, where people can live, work, and enjoy leisure activities within close proximity, reducing commuting times and enhancing convenience.
- Social and Cultural Vibrancy: The density of skyscrapers fosters social and cultural vibrancy by bringing together people from diverse backgrounds and walks of life. This diversity creates a rich tapestry of cultural experiences, with a wide range of restaurants, theaters, museums, and other cultural institutions catering to the varied interests of residents and visitors alike.
In conclusion, the density achieved through skyscrapers is a defining characteristic of “cities of skyscrapers,” enabling them to accommodate a large population, foster vibrant urban communities, and promote sustainable and livable urban environments.
3. Engineering Marvels
In the context of “city of skyscrapers,” engineering marvels play a pivotal role in pushing the boundaries of structural engineering and showcasing innovative designs and materials. Skyscrapers are not merely vertical structures but testaments to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of architectural excellence.
The construction of skyscrapers requires groundbreaking engineering solutions to overcome the challenges of height, weight, and wind resistance. Engineers and architects collaborate to create innovative structural systems that ensure the stability and safety of these towering structures. For instance, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the tallest building in the world, utilizes a buttressed core structural system that distributes the weight of the building evenly, allowing it to withstand strong winds and seismic forces.
The pursuit of innovative designs in skyscrapers extends beyond structural considerations. Architects and designers explore novel ways to create visually striking and aesthetically pleasing buildings that become iconic landmarks. The One World Trade Center in New York City, for
example, features a unique triangular footprint and a spire that evokes a sense of resilience and renewal. The Shanghai Tower in China showcases a spiraling form that reduces wind resistance and creates a dynamic architectural statement.
The engineering marvels of skyscrapers are not just feats of architectural prowess; they have practical significance as well. These structures house businesses, offices, residential units, and public spaces, contributing to the economic vitality and social fabric of cities. The innovative designs and materials used in skyscrapers also contribute to sustainability efforts, incorporating energy-efficient systems, green spaces, and rainwater harvesting technologies.
Understanding the connection between engineering marvels and “city of skyscrapers” is essential for appreciating the complexity and significance of these architectural wonders. Skyscrapers are not just tall buildings; they are symbols of human ambition, engineering ingenuity, and the continuous evolution of urban landscapes.
4. Economic Hubs
Skyscrapers, as prominent features of modern cities, serve as economic powerhouses and play a pivotal role in driving urban growth and prosperity. They house corporate headquarters, financial institutions, and businesses of various sizes, creating a vibrant and interconnected economic ecosystem.
- Corporate Headquarters: Skyscrapers provide a prestigious and central location for multinational corporations and industry leaders to establish their headquarters. This concentration of corporate giants fosters collaboration, innovation, and economic growth within the city. For instance, the presence of Fortune 500 companies like Google, Amazon, and Apple in New York City’s skyscrapers has significantly contributed to the city’s economic vitality and global influence.
- Financial Centers: Skyscrapers are often hubs for financial activities, housing banks, investment firms, and insurance companies. The proximity of these institutions facilitates networking, deal-making, and the flow of capital, creating a dynamic and competitive financial ecosystem. London’s Canary Wharf, with its cluster of skyscrapers, is a prime example of a thriving financial center that drives economic growth both within the city and beyond.
- Business Hubs: Skyscrapers accommodate a diverse mix of businesses, ranging from small startups to large enterprises. The vertical integration of office spaces, retail outlets, and other amenities within skyscrapers creates a convenient and efficient environment for businesses to operate and thrive. The Shinjuku area in Tokyo, known for its towering skyscrapers, is a bustling business hub that attracts companies from various industries, contributing to the city’s economic success.
- Job Creation: The construction, maintenance, and operation of skyscrapers generate significant employment opportunities in various sectors, including architecture, engineering, construction, real estate, and hospitality. The presence of corporate headquarters and businesses within skyscrapers creates a demand for skilled professionals, further driving economic growth and prosperity.
In conclusion, the connection between “Economic Hubs: They house corporate headquarters, financial institutions, and businesses, driving economic growth.” and “city of skyscrapers” is undeniable. Skyscrapers serve as vertical cities within cities, fostering a dynamic and interconnected economic ecosystem that drives urban growth, attracts investment, and creates employment opportunities. Their presence in modern cities is a testament to their importance as economic powerhouses and their ability to shape the economic landscape.
5. Cultural Landmarks
In the context of “city of skyscrapers,” cultural landmarks play a pivotal role in shaping the identity, attracting tourism, and enhancing the civic pride of cities. Iconic skyscrapers transcend their functional purpose, becoming symbols of urban achievement and cultural heritage.
The connection between cultural landmarks and “city of skyscrapers” is multifaceted. First, skyscrapers, with their towering presence and unique architectural designs, often become instantly recognizable symbols of the cities they inhabit. The Empire State Building in New York City, the Eiffel Tower in Paris, and the Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur are just a few examples of skyscrapers that have become synonymous with their respective cities. These landmarks attract tourists from around the world, eager to witness these architectural marvels and experience the vibrant urban culture they represent.
Moreover, cultural landmarks foster a sense of civic pride among residents. Skyscrapers embody the ambition, innovation, and architectural prowess of a city. They serve as a source of inspiration and a point of reference for local communities. For instance, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the tallest building in the world, has become a symbol of the city’s rapid growth and economic success. It is a source of immense pride for Dubai’s residents and a major tourist attraction.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between cultural landmarks and “city of skyscrapers” lies in the potential for urban development and tourism. Cities can leverage their iconic skyscrapers to promote tourism, attract investment, and enhance their global image. By investing in the design and construction of architecturally significant skyscrapers, cities can create landmarks that will become symbols of their cultural identity and drive economic growth.
In conclusion, the connection between “Cultural Landmarks: Iconic skyscrapers become symbols of cities, attracting tourists and enhancing civic pride.” and “city of skyscrapers” is undeniable. Skyscrapers are not merely tall buildings; they are cultural icons that shape the identity of cities, attract tourism, and foster a sense of civic pride. Understanding this connection is essential for urban planners, architects, and policymakers seeking to create vibrant, attractive, and culturally rich cities.
6. Sustainable Design
In the context of “city of skyscrapers,” sustainable design plays a pivotal role in mitigating the environmental impact of these towering structures and creating more livable and sustainable urban environments. Modern skyscrapers incorporate green features that promote energy efficiency and environmental responsibility, contributing to the overall sustainability of cities.
The connection between sustainable design and “city of skyscrapers” is multifaceted. Firstly, skyscrapers, due to their size and energy consumption, have the potential to significantly impact the environment. By incorporating green features, such as energy-efficient lighting systems, low-flow water fixtures, and double-glazed windows, skyscrapers can reduce their energy consumption and carbon emissions. For example, the Bank of America Tower in New York City is designed to be one of the most energy-efficient skyscrapers in the world, utilizing natural ventilation and rainwater collection systems to minimize its environmental impact.
Moreover, sustainable design in skyscrapers promo
tes occupant well-being and productivity. Green features, such as access to natural light and views, improved indoor air quality, and rooftop gardens, can enhance the physical and mental health of building occupants. The One Barangaroo building in Sydney, Australia, is a prime example of a skyscraper that prioritizes occupant well-being through its innovative design, which incorporates natural ventilation, abundant natural light, and access to green spaces.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between sustainable design and “city of skyscrapers” lies in the potential for urban sustainability and resilience. By embracing sustainable design principles, cities can reduce their overall carbon footprint, mitigate the effects of climate change, and create healthier and more livable urban environments. Additionally, sustainable skyscrapers can attract environmentally conscious tenants, businesses, and investors, boosting the city’s economic competitiveness.
In conclusion, the connection between “Sustainable Design: Modern skyscrapers incorporate green features, promoting energy efficiency and environmental responsibility.” and “city of skyscrapers” is undeniable. Sustainable design is not merely a trend but a necessity for creating sustainable and livable cities of the future. By embracing green building practices, skyscrapers can reduce their environmental impact, enhance occupant well-being, and contribute to the overall sustainability of cities.
7. Urban Renewal
In the context of “city of skyscrapers,” urban renewal is closely tied to the transformative power of skyscrapers in revitalizing downtrodden areas and fostering economic growth. Skyscrapers, with their vertical expansion and mixed-use capabilities, play a pivotal role in urban renewal projects, breathing new life into neglected neighborhoods and transforming them into thriving urban centers.
One of the key ways in which skyscrapers contribute to urban renewal is by attracting investment and economic activity. The construction of skyscrapers often serves as a catalyst for broader development in an area, attracting businesses, residents, and tourists. For example, the redevelopment of the Hudson Yards area in New York City, anchored by the construction of several skyscrapers, has transformed a once-neglected industrial area into a vibrant mixed-use neighborhood with residential towers, retail spaces, and cultural attractions.
Furthermore, skyscrapers can provide much-needed housing options in densely populated urban areas. By building upwards, cities can alleviate pressure on land resources and create new residential units without sprawling outwards. This is particularly important in cities facing a housing shortage or affordability crisis. For instance, the construction of skyscrapers in the Canary Wharf area of London has significantly increased the supply of housing in the city, providing more options for residents and contributing to the overall economic vitality of the area.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between urban renewal and “city of skyscrapers” lies in its potential to guide urban planning and development strategies. By leveraging the transformative power of skyscrapers, cities can revitalize neglected areas, attract investment, create jobs, and improve the overall quality of life for residents. This understanding can help policymakers and urban planners make informed decisions about the use of skyscrapers as a tool for urban renewal and sustainable city development.
In conclusion, the connection between “Urban Renewal: Skyscrapers can revitalize downtrodden areas, transforming them into thriving urban centers.” and “city of skyscrapers” is undeniable. Skyscrapers are not merely tall buildings; they are powerful tools for urban renewal, with the potential to transform neglected areas into vibrant and economically prosperous urban centers. Understanding this connection is essential for creating sustainable and thriving cities of the future.
FAQs on “City of Skyscrapers”
This section addresses commonly asked questions and misconceptions surrounding the concept of “city of skyscrapers.” It provides concise and informative answers to enhance understanding and clarify key aspects of this topic.
Question 1: What defines a “city of skyscrapers”?
A “city of skyscrapers” is a metropolitan area characterized by an abundance of high-rise buildings, typically exceeding 50 stories in height. These structures dominate the urban skyline and contribute to the city’s architectural identity and economic vitality.
Question 2: What are the key advantages of skyscrapers?
Skyscrapers offer several advantages, including maximizing land use, providing ample space for businesses, residential units, and public amenities. Their height allows for breathtaking panoramic views, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of a city. Additionally, skyscrapers can incorporate sustainable design features, contributing to environmental preservation.
Question 3: How do skyscrapers contribute to urban renewal?
Skyscrapers play a pivotal role in urban renewal projects by attracting investment and economic activity. They can revitalize downtrodden areas, creating new residential units and commercial spaces. By building upwards, cities can alleviate pressure on land resources and promote sustainable development.
Question 4: What are the environmental implications of constructing skyscrapers?
The construction of skyscrapers can have environmental implications, including the consumption of resources and the generation of waste. However, modern skyscrapers increasingly incorporate green design features to minimize their environmental impact. These features include energy-efficient systems, water conservation measures, and the use of sustainable materials.
Question 5: How do skyscrapers impact the quality of life in urban areas?
Skyscrapers can positively impact the quality of life in urban areas by providing access to various amenities and services within close proximity. They can also contribute to a vibrant urban culture by housing cultural and entertainment venues. However, it is important to consider factors such as population density and accessibility when planning and constructing skyscrapers to ensure a positive impact on livability.
Question 6: What are some notable examples of “cities of skyscrapers”?
Notable examples of “cities of skyscrapers” include New York City, Hong Kong, Shanghai, Dubai, and Tokyo. These cities are renowned for their iconic skylines, architectural landmarks, and the economic power they wield as global financial and business hubs.
These FAQs provide a deeper understanding of the concept of “city of skyscrapers,” addressing key aspects such as their definition, advantages, and impact on urban development and livability. By clarifying common questions and misconceptions, this section enhances the overall comprehension of this topic.
Tips for Thriving in a City of Skyscrapers
In a city of skyscrapers, where vertical living is the norm, it is essential to adapt and thrive in this unique environment. Here are some tips to help you make the most of your experience:
Tip 1: Embrace Vertical Living
Skyscrapers offer a unique perspective on urban living. Embrace the verticality by taking advantage of rooftop gardens, observation decks, and other common areas that provide stunning city views.Tip 2: Utilize Public Transportation
In densely populated cities of skyscrapers, public t
ransportation is often the most efficient way to get around. Familiarize yourself with the public transportation system and utilize it to save time and reduce stress.Tip 3: Explore Your Neighborhood
While skyscrapers dominate the skyline, don’t forget to explore the street level. Many cities of skyscrapers have vibrant street life with charming cafes, independent shops, and hidden gems.Tip 4: Seek Green Spaces
Even in a city of skyscrapers, green spaces are essential for well-being. Seek out parks, gardens, and other outdoor areas to connect with nature and escape the urban hustle.Tip 5: Maximize Natural Light
In high-rise buildings, natural light can be limited. Make the most of the available light by positioning your desk or living space near windows and utilizing sheer curtains or blinds.Tip 6: Create a Sense of Community
In a city of skyscrapers, it can be easy to feel isolated. Make an effort to connect with your neighbors, join community groups, and participate in local events to foster a sense of belonging.Tip 7: Utilize Building Amenities
Many skyscrapers offer amenities such as fitness centers, pools, and social spaces. Take advantage of these amenities to enhance your lifestyle and well-being.Tip 8: Embrace the Views
One of the best things about living in a city of skyscrapers is the breathtaking views. Make time to enjoy the panoramic vistas from your apartment, office, or a nearby observation deck.
By following these tips, you can not only survive but thrive in a city of skyscrapers. Embrace the unique opportunities and challenges that come with vertical living, and enjoy the vibrant and dynamic lifestyle that these cities have to offer.
Conclusion
Cities of skyscrapers represent architectural marvels that have reshaped urban landscapes worldwide. They stand as testaments to human ingenuity, engineering prowess, and economic vitality. These vertical cities offer numerous advantages, including efficient land use, breathtaking views, and sustainable design features.
Skyscrapers not only shape skylines but also drive economic growth by housing corporate headquarters, financial institutions, and diverse businesses. They serve as cultural landmarks, attracting tourists and enhancing civic pride. Furthermore, modern skyscrapers embrace sustainable practices, minimizing their environmental impact while promoting occupant well-being.
Understanding the significance of cities of skyscrapers is crucial for urban planners, policymakers, and architects seeking to create sustainable, livable, and thriving urban environments. As cities continue to grow vertically, it is essential to embrace innovative approaches that leverage the benefits of skyscrapers while addressing the challenges they present.
The future of cities of skyscrapers holds endless possibilities. As technology advances and architectural boundaries are pushed, we can expect to see even more innovative and sustainable skyscrapers that will continue to shape the urban experience in the years to come.