A “city in a skyscraper” is a self-contained vertical urban environment that combines residential, commercial, and public spaces within a single high-rise structure. This concept envisions a city’s essential functions and amenities vertically stacked, creating a self-sustaining ecosystem within a single building.
The benefits of a city in a skyscraper are numerous. It promotes sustainability and reduces urban sprawl by concentrating development in a compact footprint. It enhances community living by fostering social interaction and providing convenient access to essential services. Additionally, it offers unparalleled views and transforms the urban skyline into a visually striking landmark.
The concept of a city in a skyscraper is not entirely new. In the early 20th century, architects and urban planners proposed similar ideas as a solution to the challenges of urbanization. However, due to technological limitations, these concepts remained largely theoretical. With advancements in construction techniques and sustainable design, the realization of vertical cities is becoming increasingly feasible.
1. Vertical Urbanism
Vertical urbanism is an approach to urban planning and design that emphasizes the use of high-rise buildings to create dense, compact, and sustainable cities. It is a key aspect of the “city in a skyscraper” concept, as it allows for the creation of self-contained vertical communities that minimize urban sprawl and promote efficient land use.
- Compact Footprint: Vertical urbanism reduces urban sprawl by concentrating development in a smaller footprint. This helps to preserve green spaces, reduce traffic congestion, and promote walkability.
- Mixed-Use Development: Vertical urbanism often involves mixed-use developments that combine residential, commercial, and public spaces within a single building. This creates a more diverse and vibrant urban environment, reducing the need for car travel.
- Efficient Infrastructure: Vertical urbanism can lead to more efficient infrastructure systems, such as water and energy distribution networks. By locating these systems within the building, it is possible to reduce energy consumption and improve sustainability.
- Community Building: Vertical urbanism can foster a sense of community by creating shared spaces and amenities within the building. This can help to reduce isolation and promote social interaction among residents.
Overall, vertical urbanism is a key aspect of the “city in a skyscraper” concept, as it allows for the creation of dense, compact, and sustainable urban environments that promote community living and reduce environmental impact.
2. Sustainability
In the context of a “city in a skyscraper,” sustainability encompasses a range of strategies and practices aimed at reducing environmental impact and promoting long-term viability. By integrating sustainable design principles into the planning and construction of high-rise buildings, architects and urban planners can create more environmentally friendly and livable urban environments.
- Energy Efficiency: Skyscrapers can be designed to maximize energy efficiency through the use of energy-efficient appliances, lighting systems, and building materials. Additionally, renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can be integrated into the building’s design to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Water Conservation: Water conservation measures can be implemented in skyscrapers to reduce water consumption and promote water sustainability. This can include the use of low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and drought-tolerant landscaping.
- Waste Management: Comprehensive waste management plans can be established to minimize waste and promote recycling and composting. This can help to reduce the environmental impact of the building and its occupants.
- Green Building Materials: The use of sustainable and recycled building materials can reduce the environmental impact of a skyscraper’s construction. These materials can include recycled steel, bamboo flooring, and low-VOC paints.
By incorporating these sustainable practices into the design and operation of skyscrapers, cities can create more environmentally friendly and livable urban environments that promote the well-being of both residents and the planet.
3. Community Living
Within the context of a “city in a skyscraper,” community living takes on a unique form, fostering a sense of belonging and social interaction among residents. By creating shared spaces and amenities within the building, architects and urban planners can promote community building and encourage a vibrant urban lifestyle.
- Shared Spaces and Amenities: Skyscrapers often incorporate communal spaces such as rooftop gardens, fitness centers, and lounges, providing opportunities for residents to socialize, relax, and build relationships.
- Community Events and Activities: Building management or resident associations can organize community events and activities, such as potlucks, movie nights, and fitness classes, to foster a sense of community and encourage interaction among residents.
- Vertical Neighborhoods: By combining residential, commercial, and public spaces within a single building, “cities in a skyscraper” create vertical neighborhoods where residents can live, work, and socialize without the need for extensive travel.
- Mixed-Income and Diversity: Skyscrapers can promote mixed-income and diverse communities by offering a range of housing options and amenities that cater to different income levels and lifestyles.
These facets of community living in a “city in a skyscraper” contribute to a more vibrant, connected, and sustainable urban environment, enhancing the overall quality of life for residents.
4. Compact Footprint
In the context of a “city in a skyscraper,” a compact footprint refers to the efficient use of land to create a dense, vertically oriented urban environment. This concept plays a crucial role in shaping the livability, sustainability, and overall character of a skyscraper city.
One of the key advantages of a compac
t footprint is reduced urban sprawl. By concentrating development within a smaller area, skyscrapers minimize the need for extensive horizontal expansion, preserving green spaces and agricultural land. This promotes a more sustainable and resource-efficient urban form.
Moreover, a compact footprint fosters walkability and reduces reliance on cars. With essential amenities and services located within or near the skyscraper, residents can easily access their daily needs without the inconvenience of long commutes. This promotes a healthier and more vibrant urban lifestyle while reducing traffic congestion and air pollution.
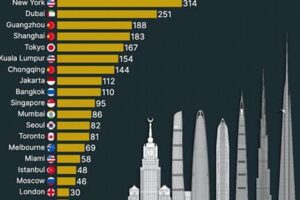
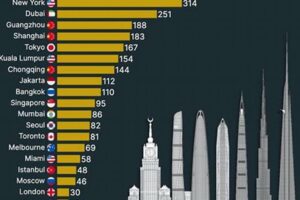
Real-life examples of successful skyscraper cities with compact footprints include Hong Kong, New York City, and Tokyo. These cities have embraced vertical urbanism to accommodate their dense populations while maintaining a high quality of life. They have achieved this through careful urban planning, mixed-use developments, and efficient public transportation systems that connect residents to their workplaces, recreational areas, and other essential destinations.
Understanding the connection between compact footprint and “city in a skyscraper” is crucial for architects, urban planners, and policymakers seeking to create livable, sustainable, and thriving urban environments. By embracing vertical urbanism and promoting compact development, cities can reduce their environmental impact, enhance community living, and foster a more vibrant and connected urban experience.
5. Architectural Marvel
An “architectural marvel,” in the context of a city in a skyscraper, refers to a building or structure that exhibits exceptional architectural design, innovation, and engineering prowess. These structures often push the boundaries of what is considered possible in the realm of architecture and become iconic landmarks that define a city’s skyline.
Architectural marvels play a significant role in shaping the identity and character of a city in a skyscraper. They serve as symbols of progress, ambition, and creativity, attracting tourists from around the world and contributing to the city’s cultural and economic vitality. Notable examples of architectural marvels in skyscraper cities include the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the Empire State Building in New York City, and the Shanghai Tower in Shanghai.
Understanding the connection between architectural marvels and cities in a skyscraper is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it highlights the importance of design excellence and innovation in shaping the built environment. By showcasing the possibilities of vertical urbanism, architectural marvels inspire future generations of architects and engineers to push the boundaries of design and construction.
Moreover, architectural marvels contribute to the economic prosperity of a city by attracting tourism and investment. They become destinations in their own right, generating revenue and creating employment opportunities. The iconic status of these structures also enhances the city’s global recognition and reputation.
In conclusion, the connection between architectural marvels and cities in a skyscraper is a testament to the power of human imagination and ingenuity. These structures not only reshape skylines but also serve as symbols of progress and economic vitality. By embracing architectural innovation and design excellence, cities can create unique and awe-inspiring urban environments that attract, inspire, and leave a lasting legacy for generations to come.
6. Urban Planning
Urban planning plays a pivotal role in shaping cities in a skyscraper. It involves the thoughtful and strategic management of land use, transportation, and infrastructure to create livable, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing urban environments. In the context of a city in a skyscraper, urban planning becomes even more critical due to the unique challenges and opportunities presented by vertical urbanism.
One of the key aspects of urban planning for a city in a skyscraper is ensuring efficient land use. By maximizing the use of vertical space, urban planners can create dense, compact developments that minimize urban sprawl and preserve green spaces. This approach promotes sustainability and reduces the environmental impact of the city.
Another important consideration in urban planning for a city in a skyscraper is transportation. The high density of residents and businesses in a skyscraper city requires a well-developed and integrated transportation system. This may include a combination of public transportation, such as subways and buses, as well as pedestrian-friendly infrastructure, such as sidewalks and bike lanes. Effective transportation planning helps reduce traffic congestion, improve air quality, and enhance the overall livability of the city.
Examples of successful urban planning for cities in a skyscraper can be found worldwide. Hong Kong, for instance, has implemented a comprehensive transportation system that includes an extensive network of public transportation, including the Mass Transit Railway (MTR), buses, and ferries. This system efficiently moves millions of people daily and helps reduce traffic congestion. Another example is Singapore, which has adopted a “compact city” approach, emphasizing high-density development and mixed-use zoning. This planning strategy has resulted in a vibrant and sustainable urban environment with a high quality of life.
Understanding the connection between urban planning and cities in a skyscraper is essential for architects, urban planners, and policymakers seeking to create livable, sustainable, and thriving urban environments. By embracing thoughtful planning and design, cities can harness the benefits of vertical urbanism while addressing the challenges associated with high-density development. This approach can lead to more sustainable, equitable, and prosperous cities in the future.
7. Technological Advancements
Technological advancements play a crucial role in shaping the development and functioning of cities in a skyscraper. These advancements enable architects, engineers, and urban planners to overcome the challenges of vertical urbanism and create sustainable, efficient, and livable high-rise environments.
- Sustainable Building Systems: Technological advancements have led to the development of innovative building systems that promote sustainability in cities in a skyscraper. These systems include energy-efficient lighting, heating, and cooling technologies, as well as water conservation measures. By incorporating these systems into high-rise buildings, cities can reduce their environmental impact and create more sustainable urban environments.
- Smart Building Management: Smart building management systems utilize sensors, data analytics, and automation to optimize building operations and enhance occupant comfort. These systems can monitor energy consumption, control lighting and temperature, and provide real-time data on building performance. By leveraging smart building management systems, cities in a skyscraper can improve energy efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and create more responsiv
e and adaptive living environments. - Advanced Construction Techniques: Technological advancements have revolutionized construction techniques, making it possible to build taller and more complex skyscrapers. These advancements include the use of lightweight materials, prefabrication, and modular construction methods. By employing these techniques, cities can reduce construction time, minimize waste, and improve the safety and quality of high-rise buildings.
- Vertical Transportation Systems: Efficient vertical transportation systems are essential for cities in a skyscraper. Technological advancements have led to the development of high-speed elevators, double-decker elevators, and skybridges. These systems enable residents and visitors to move quickly and conveniently between different levels of a skyscraper, reducing wait times and enhancing accessibility.
These technological advancements are not only transforming the design and construction of cities in a skyscraper but also shaping the way people live and work in these vertical environments. By embracing technological innovation, cities can create more sustainable, efficient, and livable high-rise communities that meet the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century.
8. Social Infrastructure
Social infrastructure is a crucial element that shapes the livability and well-being of communities within a “city in a skyscraper.” It refers to the physical and institutional structures that support the social, educational, healthcare, recreational, and cultural needs of a population. By providing these essential services and amenities, social infrastructure enhances the quality of life for residents and contributes to the overall success of a skyscraper city.
- Educational Facilities: Skyscraper cities often incorporate educational institutions within their high-rise structures, providing convenient access to learning and skill development. These facilities may include schools, universities, and training centers, catering to the educational needs of residents of all ages and backgrounds.
- Healthcare Services: Integrated healthcare facilities are vital components of social infrastructure in a city in a skyscraper. These facilities provide a range of medical services, including clinics, hospitals, and specialized healthcare centers. By bringing healthcare services closer to residents, skyscraper cities promote accessible and timely medical care.
- Community Spaces: Public spaces and community centers are essential for fostering social interaction and a sense of belonging among residents. These spaces may include parks, plazas, and community centers that provide opportunities for recreation, relaxation, and social gatherings. By creating vibrant community spaces, skyscraper cities encourage social cohesion and well-being.
- Cultural Amenities: A city in a skyscraper often serves as a cultural hub, offering a diverse range of cultural amenities. These amenities may include theaters, concert halls, museums, and art galleries. By providing access to cultural experiences, skyscraper cities enrich the lives of residents and contribute to a vibrant and dynamic urban environment.
The integration of social infrastructure into skyscraper cities creates a comprehensive and sustainable urban environment where residents have access to essential services, opportunities for personal growth, and a high quality of life. By carefully planning and investing in social infrastructure, cities can harness the potential of vertical urbanism to create thriving and inclusive communities.
9. Economic Hub
Within the context of a “city in a skyscraper,” the term “economic hub” refers to the concentration of economic activities, businesses, and financial institutions within a skyscraper or group of skyscrapers. This concentration creates a vibrant and dynamic urban environment that attracts businesses, investors, and skilled professionals from around the world.
The economic hub plays a crucial role in driving the city’s economy and creating employment opportunities for its residents. Skyscrapers, with their vast floor space and efficient vertical transportation systems, provide an ideal setting for businesses to operate and collaborate. The proximity of businesses and financial institutions fosters innovation, knowledge sharing, and the exchange of ideas, leading to economic growth and prosperity.
Real-life examples of skyscraper cities that serve as economic hubs include New York City, London, and Tokyo. In New York City, the concentration of financial institutions in the skyscrapers of the Wall Street area has established the city as a global financial center. Similarly, in London, the skyscrapers of the Canary Wharf financial district have transformed the city into a major hub for banking and international business. Tokyo, with its towering skyscrapers in the Shinjuku and Marunouchi districts, is a economic hub in Asia, housing numerous corporate headquarters and financial institutions.
Understanding the connection between “economic hub” and “city in a skyscraper” is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it highlights the importance of economic development and job creation in shaping the livability and sustainability of cities. Secondly, it emphasizes the role of vertical urbanism in accommodating the growing needs of businesses and populations in dense urban environments. By embracing vertical development and fostering economic activity within skyscrapers, cities can create vibrant and prosperous urban centers that attract talent, investment, and economic growth.
Frequently Asked Questions about “City in a Skyscraper”
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding the concept of a “city in a skyscraper,” providing concise and informative answers to enhance your understanding.
Question 1: How is a “city in a skyscraper” different from a traditional city?
A “city in a skyscraper” is a self-contained vertical urban environment that combines residential, commercial, and public spaces within a single high-rise structure. Unlike traditional cities spread horizontally across vast areas, a city in a skyscraper concentrates these functions and amenities vertically, creating a more compact and efficient urban form.
Question 2: What are the advantages of living in a “city in a skyscraper”?
Living in a city in a skyscraper offers several advantages, including convenient access to essential services and amenities within the building, reduced urban sprawl and environmental impact, and unparalleled views. The compact footprint promotes walkability and reduces reliance on cars, contributing to a more sustainable and healthy urban lifestyle.
Question 3: Are “cities in a skyscraper” environmentally sustainable?
The sustainability of a city in a skyscraper depends on various factors, including design, construction methods, and operational practices. By incorporating sustainable building materials, energy-efficient systems, and water conservation measures, architects and urban planners can create environmentally friendly skyscrapers that minimize their carbon footprint and promote long-term sustainability.
Question 4: How do “cities in a skyscraper” address the
challenges of high population density?
Cities in a skyscraper address the challenges of high population density through careful urban planning and design. By maximizing vertical space, these cities reduce urban sprawl and preserve green spaces. Mixed-use developments combine residential, commercial, and public functions within a single building, reducing the need for extensive travel and promoting community interaction.
Question 5: Are “cities in a skyscraper” affordable and accessible to all?
Affordability and accessibility in cities in a skyscraper vary depending on the specific project and location. Some cities in a skyscraper may offer a range of housing options, including affordable units, to promote inclusivity and diversity. Public transportation and pedestrian-friendly infrastructure can also enhance accessibility for residents and visitors alike.
Question 6: What is the future of “cities in a skyscraper”?
The future of cities in a skyscraper is promising, as advancements in architecture, engineering, and technology continue to push the boundaries of vertical urbanism. As cities worldwide grapple with population growth, environmental concerns, and limited land availability, the concept of a city in a skyscraper offers a sustainable and efficient solution for urban living. By embracing innovation and thoughtful planning, cities can harness the potential of vertical development to create thriving, livable, and sustainable urban environments for the future.
These FAQs provide a comprehensive overview of the key aspects and considerations surrounding the concept of a “city in a skyscraper.” By understanding these nuances, we can better appreciate the transformative potential of vertical urbanism and its role in shaping sustainable and livable cities of the future.
Next Article Section: Exploring the Impact of Vertical Urbanism on Urban Sustainability
Tips for Thriving in a “City in a Skyscraper”
Living in a vertical urban environment presents unique opportunities and challenges. Here are some tips to help you thrive in a “city in a skyscraper”:
Tip 1: Embrace Vertical LivingTake advantage of the compact and efficient nature of vertical living. Utilize vertical storage solutions, maximize natural light, and explore the building’s common areas to create a comfortable and functional living space.Tip 2: Foster a Sense of CommunityParticipate in building events, join social groups, and engage with your neighbors. Building a sense of community can enhance your living experience and create a supportive social network.Tip 3: Utilize Building AmenitiesMake the most of the amenities offered by your skyscraper, such as fitness centers, rooftop gardens, and business centers. These amenities can enrich your lifestyle and promote well-being.Tip 4: Plan for AccessibilityConsider the accessibility features of your building, such as elevators and stairs. Ensure you have a plan in place for any mobility challenges or emergencies.Tip 5: Embrace SustainabilitySupport sustainable practices within your skyscraper community. Participate in recycling programs, conserve energy, and reduce your carbon footprint.Tip 6: Explore Your SurroundingsVenture outside of your building and explore the surrounding neighborhood. Discover local amenities, cultural attractions, and green spaces to enhance your urban experience.Tip 7: Stay InformedKeep abreast of building announcements, safety regulations, and community events. Staying informed ensures your safety and involvement in your skyscraper community.Summary:By embracing these tips, you can maximize the benefits of living in a “city in a skyscraper” and create a thriving and fulfilling urban lifestyle. Remember to appreciate the unique aspects of vertical living, foster a sense of community, utilize building amenities, plan for accessibility, embrace sustainability, explore your surroundings, and stay informed.
Next Article Section: Exploring the Future of Vertical Urbanism
Conclusion
As cities worldwide continue to evolve, the concept of a “city in a skyscraper” offers a compelling and sustainable solution to the challenges of urbanization. By maximizing vertical space, promoting mixed-use development, and integrating smart technologies, cities can create livable, efficient, and environmentally friendly urban environments.
Vertical urbanism empowers architects, urban planners, and policymakers to rethink the traditional horizontal expansion of cities. It presents a path towards sustainable urban growth that preserves green spaces, reduces urban sprawl, and enhances community living. As we look to the future, embracing vertical urbanism will be crucial in creating thriving and sustainable cities that meet the needs of a growing global population.