Brick skyscrapers are high-rise buildings with exterior walls made primarily of brick. They were popular in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, particularly in the United States. One of the most famous examples is the Flatiron Building in New York City.
Brick skyscrapers offer several advantages over other types of construction. Bricks are durable, fire-resistant, and relatively inexpensive. They also provide good insulation, making them energy-efficient. However, brick skyscrapers are also heavy and can be difficult to construct. As a result, they have become less common in recent years.
Despite their decline in popularity, brick skyscrapers remain an important part of the architectural landscape of many cities. They are a testament to the skill and craftsmanship of the builders who constructed them and continue to be admired for their beauty and strength.
1. Durability
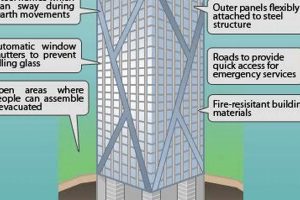
The exceptional durability of brick is a cornerstone of brick skyscrapers’ resilience. Its resistance to weathering and fire ensures the longevity of these structures, enabling them to withstand the test of time and harsh environmental conditions.
Brick’s low porosity makes it impervious to moisture, preventing water penetration and the resulting damage from freezing and thawing cycles. Additionally, its high fire resistance rating contributes to the overall fire safety of brick skyscrapers, minimizing the risk of catastrophic damage in the event of a fire.
The Flatiron Building in New York City, a renowned brick skyscraper, exemplifies the durability of this material. Constructed in 1902, it has weathered over a century of exposure to the elements, including extreme weather events, and remains a testament to the enduring qualities of brick construction.
The durability of brick skyscrapers is not only crucial for the longevity of individual buildings but also for the preservation of architectural heritage. These structures often serve as landmarks, embodying the history and character of cities. Their resilience ensures that future generations can continue to appreciate these architectural icons.
2. Strength
The strength of brick structures is a fundamental aspect of brick skyscrapers, contributing to their ability to withstand significant forces and maintain structural integrity.
- Exceptional Compressive Strength: Bricks are renowned for their high compressive strength, enabling them to bear the weight of multiple stories without buckling or collapsing. This inherent strength makes brick an ideal material for high-rise construction.
- Load-Bearing Walls: Brick skyscrapers often employ load-bearing walls, which means the exterior walls of the building carry the weight of the structure. These walls are constructed with thick, solid brick, providing exceptional stability and resistance to lateral forces, such as wind and seismic activity.
- Reinforced Brickwork: In modern brick skyscrapers, steel reinforcements are often incorporated into the brickwork to enhance its strength and ductility. This combination of brick and steel creates a composite structure that can withstand even greater loads and resist deformation.
- Seismic Resistance: Brick skyscrapers have demonstrated remarkable resistance to seismic activity. The inherent strength and mass of brickwork help to absorb and dissipate seismic energy, reducing the risk of structural damage during earthquakes.
The strength of brick structures is a critical factor in the design and construction of brick skyscrapers, ensuring their ability to withstand the demands of high-rise buildings and providing occupants with safe and stable living and working environments.
3. Fire Resistance
The fire resistance of brick is a crucial aspect of brick skyscrapers, contributing significantly to their safety and resilience in the event of a fire. Brick’s non-combustible nature ensures that it does not contribute to the spread of flames, providing valuable time for occupants to evacuate and firefighters to contain the blaze.
Historically, fires have posed a significant threat to high-rise buildings, with devastating consequences. Brick skyscrapers, however, have demonstrated remarkable fire resistance due to the inherent properties of brick. In the event of a fire, brick walls act as a barrier, preventing the spread of flames from one floor to another and compartmentalizing the fire within a limited area.
The fire resistance of brick skyscrapers has been proven in numerous real-life scenarios. For instance, during the Great Chicago Fire of 1871, buildings constructed with brick fared significantly better than those made of wood or other combustible materials. Similarly, in the 1911 Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire in New York City, the brick exterior walls of the building helped to contain the fire, preventing it from spreading to neighboring structures.
The fire resistance of brick skyscrapers is not only crucial for the safety of occupants but also for the preservation of the building itself. By preventing the spread of flames, brick construction helps to minimize structural damage, reducing repair costs and ensuring the longevity of the building.
4. Insulation
The insulating properties of brick walls are a significant advantage of brick skyscrapers, contributing to energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Brick’s low thermal conductivity and high thermal mass help to regulate indoor temperatures, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems.
In winter, brick walls absorb and store heat from the sun during the day, releasing it gradually at night. This thermal mass effect helps to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature, reducing the need for artificial heating. In summer, the thick brick walls help to keep the interior cool by blocking out heat from the sun.
The insulating properties of brick skyscrapers have been demonstrated in real-life scenarios. For instance, the Empire State Building in New York City, a renowned brick skyscraper, has been retrofitted with energy-efficient windows and lighting systems. However, the building’s original brick facade continues to contribute significantly to its overall energy efficiency.
The insulation provided by brick walls is not only beneficial for energy consumption but also for occupant comfort. Maintaining a stable indoor temperature reduces the risk of overheating or undercooling, creating a more comfortable and healthy living environment.
Understanding the connection between insulation and brick skyscrapers is crucial for architects and engineers designing energy-efficient and sustainable high-rise buildings. By incorporating brick’s insulating properties into building design, they can reduce energy consumption, lower operating costs, and enhance occupant well-being.
5. Aesthetics
The aesthetic appeal of brick facades is a defining characteristic of brick skyscrapers, contributing to their enduring popularity and architectural significance.
- Color and Texture: Bricks come in a wide range of colors and textures, allowing architects to create visually striking facades. The natural variations in brick surfaces add depth and character to the building’s exterior, making each brick skyscraper unique.
- Ornamentation: Brick facades can be ornamented with decorative details, such as arches, cornices, and moldings. These embellishments add visual interest and enhance the building’s overall aesthetic appeal.
- Patterns and Bonds: Bricks can be laid in various patterns and bonds, creating intricate and visually appealing textures. These patterns can range from simple running bonds to complex herringbone or basket weave patterns.
- Timeless Appeal: Brick facades have a timeless quality that transcends architectural trends. Their classic appearance ensures that brick skyscrapers remain visually appealing and relevant over decades, even centuries.
The aesthetic appeal of brick skyscrapers is not merely subjective but also has practical implications. A visually appealing building can enhance the surrounding environment, promote a sense of place, and contribute to the overall well-being of occupants and visitors.
6. Historical Significance
The historical significance of brick skyscrapers lies in their pivotal role in shaping the skylines of cities around the world. These towering structures, with their distinctive brick facades, have become iconic landmarks and symbols of urban progress and architectural innovation.
- Pioneers of Vertical Growth: Brick skyscrapers were among the first buildings to challenge the limitations of height in urban architecture. Their ability to withstand the weight and forces associated with high-rise construction paved the way for the development of even taller buildings, transforming cityscapes and creating new possibilities for urban living.
- Architectural Heritage: Many brick skyscrapers are considered architectural masterpieces, showcasing the skill and artistry of their designers and builders. Their intricate facades, decorative details, and innovative use of materials have earned them a place in the architectural heritage of cities, contributing to their cultural and historical identity.
- Historical Markers: Brick skyscrapers often serve as historical markers, reflecting the architectural styles and technological advancements of their time. By preserving these buildings, cities can connect with their past and showcase the evolution of urban design and construction.
- Economic and Social Impact: The construction of brick skyscrapers has had a significant economic and social impact on cities. These buildings have provided employment opportunities, stimulated economic growth, and attracted businesses and residents to urban centers. They have also played a role in shaping urban communities and creating new social dynamics.
The historical significance of brick skyscrapers extends beyond their architectural and aesthetic value. They represent the ingenuity and ambition of architects, engineers, and builders who pushed the boundaries of construction and design. These structures continue to inspire and captivate, serving as reminders of the rich history of urban development and the enduring legacy of brick as a building material.
7. Architectural Innovation
Brick skyscrapers emerged as a testament to architectural innovation, pushing the boundaries of engineering and design to create towering structures that redefined urban skylines. These buildings showcased a range of innovative construction techniques that not only enabled them to reach unprecedented heights but also contributed to their strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal.
- Skeleton Frame Construction:
Traditional load-bearing walls were replaced with a steel skeleton frame in brick skyscrapers. This innovative technique allowed for the construction of taller buildings by transferring the weight of the structure to the frame rather than the exterior walls. It also provided greater flexibility in interior design, allowing for open floor plans and large windows.
- Reinforced Concrete:
The introduction of reinforced concrete revolutionized brick skyscraper construction. Concrete, reinforced with steel rods, provided additional strength and rigidity to the structure, enabling the construction of even taller and more slender buildings. Reinforced concrete was used for both the structural frame and the exterior walls, creating a composite structure that was both strong and durable.
- Curtain Wall Facades:
Brick skyscrapers often featured curtain wall facades, a non-load-bearing exterior wall system that hangs from the building’s frame. This innovative technique allowed for the use of large glass panels, providing ample natural light and panoramic views while reducing the overall weight of the building. Curtain wall facades also enhanced the aesthetic appeal of brick skyscrapers, creating a sleek and modern appearance.
- Wind Bracing Systems:
To withstand lateral forces such as wind and seismic activity, brick skyscrapers employed innovative wind bracing systems. These systems, often consisting of diagonal steel beams or trusses, were integrated into the building’s structure to provide additional stability and prevent excessive sway.
The innovative construction techniques used in brick skyscrapers not only enabled the creation of taller and more visually striking buildings but also contributed to their enduring legacy. These structures continue to stand as testaments to the ingenuity and creativity of architects and engineers, shaping the skylines of cities around the world.
8. Cultural Heritage
Brick skyscrapers hold immense cultural heritage as they often become iconic landmarks, deeply embedded in a city’s architectural identity. Their unique designs, intricate details, and historical significance make them beloved symbols of urban heritage, attracting tourists and locals alike.
The cultural heritage of brick skyscrapers stems from their ability to embody a city’s history and architectural evolution. They serve as tangible reminders of past eras, showcasing the prevailing architectural styles, construction techniques, and
artistic sensibilities of their time. Preserving these buildings is crucial for maintaining a city’s cultural continuity and sense of place.
Recognizing the cultural heritage of brick skyscrapers has practical significance. It encourages preservation efforts, restoration projects, and adaptive reuse initiatives to maintain these iconic structures for future generations. By safeguarding their architectural integrity, cities can preserve their distinct character and foster a sense of civic pride among residents.
Furthermore, the cultural heritage of brick skyscrapers can serve as a catalyst for urban revitalization. By leveraging their historical and architectural significance, cities can attract tourism, promote cultural events, and stimulate economic development in surrounding areas. Adaptive reuse projects, which transform old skyscrapers into modern spaces, offer innovative ways to preserve heritage while meeting contemporary needs.
In conclusion, the cultural heritage of brick skyscrapers is an invaluable asset for cities. These iconic landmarks represent a city’s architectural legacy, foster a sense of place, and contribute to urban revitalization. Preserving and celebrating their cultural heritage ensures that brick skyscrapers continue to be cherished symbols of a city’s unique identity and architectural heritage.
9. Sustainability
The sustainability of brick skyscrapers stems from the inherent properties of brick as a building material. Brick is highly durable and can withstand the test of time, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. Its durability also contributes to the longevity of brick skyscrapers, minimizing the environmental impact associated with demolition and reconstruction.
In addition to its durability, brick is also a recyclable material. Unlike many other building materials, brick can be crushed and reused as aggregate in new construction projects. This closed-loop recycling process reduces the demand for raw materials and minimizes the amount of construction waste sent to landfills.
The sustainability of brick skyscrapers is not merely theoretical but has been demonstrated in real-life projects. One notable example is the Bullitt Center in Seattle, Washington. Completed in 2013, the Bullitt Center is a six-story commercial building constructed with sustainable materials and design principles. The building’s exterior is clad in locally sourced brick, contributing to its overall sustainability and durability.
Understanding the connection between sustainability and brick skyscrapers is crucial for architects, engineers, and policymakers. By incorporating sustainable building practices into the design and construction of brick skyscrapers, they can minimize the environmental impact of these structures throughout their lifecycle, from material extraction to end-of-life disposal.
In conclusion, the sustainability of brick skyscrapers is a key consideration for creating environmentally responsible and future-proof buildings. By leveraging the durability and recyclability of brick, architects and engineers can design and construct skyscrapers that meet the needs of today without compromising the well-being of future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions about Brick Skyscrapers
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions surrounding brick skyscrapers, providing concise and informative answers to enhance understanding of these architectural marvels.
Question 1: Are brick skyscrapers still being built today?
Yes, brick skyscrapers continue to be constructed in modern architecture. While other materials like glass and steel are prevalent, brick remains a popular choice for its durability, aesthetic appeal, and sustainable qualities.
Question 2: How do brick skyscrapers compare to skyscrapers made of other materials?
Brick skyscrapers offer several advantages. Bricks are highly durable, fire-resistant, and provide good insulation, contributing to energy efficiency. They also have a timeless aesthetic appeal and can be ornamented to create visually striking facades.
Question 3: Are brick skyscrapers safe in the event of a fire?
Yes, brick skyscrapers are generally considered safe in the event of a fire due to the non-combustible nature of brick. Brick walls act as a barrier, preventing the spread of flames and providing valuable time for occupants to evacuate.
Question 4: How do brick skyscrapers contribute to sustainability?
Brick skyscrapers can contribute to sustainability in several ways. Bricks are durable and can withstand the test of time, reducing the need for frequent repairs and replacements. Additionally, brick is a recyclable material that can be crushed and reused as aggregate in new construction projects, minimizing waste.
Question 5: What are some famous examples of brick skyscrapers?
Notable examples of brick skyscrapers include the Flatiron Building in New York City, the Reliance Building in Chicago, and the Bullitt Center in Seattle, Washington. These buildings showcase the architectural versatility of brick and have become iconic landmarks in their respective cities.
Question 6: How are brick skyscrapers maintained?
Brick skyscrapers require regular maintenance to preserve their structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. This includes cleaning the exterior facade, repairing any cracks or damage, and inspecting the building’s structural components to ensure safety.
Understanding these aspects of brick skyscrapers provides valuable insights into their continued relevance in modern architecture. By leveraging the unique properties of brick, architects and engineers can create sustainable, durable, and visually stunning high-rise structures that contribute to the urban landscape.
Moving forward, the discussion will explore the historical significance of brick skyscrapers, highlighting their role in shaping urban skylines and architectural styles.
Tips for Designing and Constructing Brick Skyscrapers
Brick skyscrapers present unique opportunities and challenges for architects and engineers. Here are several tips to consider when designing and constructing these architectural marvels:
Tip 1: Leverage the Durability of Brick
Capitalize on the exceptional durability of brick to create structures that can withstand the test of time. Brick’s resistance to weathering and fire ensures the longevity of the building, reducing maintenance costs and increasing its lifespan.
Tip 2: Optimize Structural Stability
Ensure the structural stability of brick skyscrapers by employing robust construction techniques. Utilize load-bearing walls, reinforced brickwork, and wind bracing systems to distribute weight effectively and resist lateral forces, such as high winds and seismic activity.
Tip 3: Enhance Fire Resistance
Prioritize fire safety by incorporating brick’s inherent fire resistance into the building’s design. Brick’s non-combustible nature creates a protective barrier, preventing the spread of flames and safeguarding occupants during a fire.
Tip 4: Achieve Energy Efficiency
Maximize energy efficiency by utilizing brick’s insulating properties. The thermal mass of brick walls helps regulate indoor temperatures, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems. This contributes to a more sustainable and cost-effective building.
Tip 5: Explore Aesthetic Possibilities
Embrace the aes
thetic versatility of brick to create visually striking facades. Explore various colors, textures, and patterns to add character and depth to the building’s exterior. Consider incorporating decorative elements, such as arches, cornices, and moldings, to enhance the architectural appeal.
Tip 6: Respect Historical Context
When designing brick skyscrapers in historic districts, consider the architectural heritage of the surrounding area. Respect the prevailing architectural styles and materials to maintain a harmonious urban fabric and preserve the city’s cultural identity.
Tip 7: Integrate Sustainable Practices
Promote sustainability by incorporating environmentally friendly practices into the construction and operation of brick skyscrapers. Utilize recycled or locally sourced materials, implement rainwater harvesting systems, and employ energy-efficient lighting and appliances to minimize the environmental footprint.
By following these tips, architects and engineers can harness the unique properties of brick to design and construct brick skyscrapers that are not only visually stunning but also durable, safe, energy-efficient, and sustainable.
Conclusion
Our exploration of brick skyscrapers has unveiled their enduring significance as architectural marvels. These towering structures, crafted from durable and versatile brick, have shaped urban skylines and showcased innovative construction techniques throughout history. Their strength, fire resistance, insulating properties, and aesthetic appeal continue to make them a preferred choice for high-rise buildings.
As we look to the future, brick skyscrapers will undoubtedly continue to play a vital role in urban architecture. Their sustainable qualities, coupled with their timeless beauty and ability to adapt to changing design trends, ensure their ongoing relevance. By embracing the unique properties of brick and incorporating innovative technologies, architects and engineers can create brick skyscrapers that meet the demands of modern society while preserving the rich architectural heritage of these iconic structures.