A skyscraper with no windows is a hypothetical high-rise building that lacks any conventional windows or other transparent openings in its exterior walls, a unique architectural concept that challenges traditional design norms.
While no such structures currently exist, the idea of a windowless skyscraper has been explored in architectural discourse and science fiction, with proponents suggesting potential benefits such as enhanced energy efficiency, reduced noise pollution, and increased structural integrity. However, the absence of windows also raises concerns regarding natural light deprivation, ventilation, and emergency egress.
In the realm of architectural theory, windowless skyscrapers have been proposed as a means to optimize building performance and sustainability. By eliminating windows, architects could potentially create structures with superior insulation, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling. Furthermore, the lack of openings would minimize noise transmission from the outside environment, providing a quieter and more peaceful indoor atmosphere.
1. Energy efficiency
In the context of skyscrapers, windows are a major source of heat loss and gain. During winter, heat escapes through windows, leading to increased energy consumption for heating. Conversely, in summer, sunlight entering through windows can cause overheating, requiring more energy for cooling. By eliminating windows, skyscrapers can significantly reduce their energy consumption for heating and cooling, resulting in lower operating costs and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reduced heat loss: Without windows, there are no gaps in the building envelope for heat to escape, making the building more energy-efficient.
- Reduced solar heat gain: Eliminating windows prevents sunlight from directly entering the building, reducing the need for air conditioning.
- Improved insulation: Windowless walls can be constructed with thicker and more effective insulation materials, further reducing heat transfer.
- hermtique: The absence of windows eliminates air leakage, which can account for a significant portion of energy loss in conventional buildings.
Overall, eliminating windows in skyscrapers can lead to substantial energy savings, making them more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
2. Noise reduction
Skyscrapers, by their very nature, are often located in densely populated urban areas, where noise pollution from traffic, construction, and other human activities can be significant. The absence of windows in a skyscraper can provide a significant advantage in reducing noise levels within the building.
- Acoustic insulation: Without windows, there are no gaps in the building envelope for sound to enter. The walls, roof, and floor of the building can be constructed with sound-absorbing materials, creating a quieter indoor environment.
- Reduced traffic noise: Windows facing busy streets or highways can allow traffic noise to penetrate the building. Eliminating windows can significantly reduce noise levels, creating a more peaceful and relaxing indoor atmosphere.
- Improved concentration and productivity: Noise pollution can be distracting and impair concentration. By reducing noise levels, windowless skyscrapers can improve the cognitive performance and productivity of occupants.
- Enhanced sleep quality: Excessive noise can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to fatigue. The absence of windows in a skyscraper can help to create a quieter and more conducive environment for sleep.
Overall, the absence of windows in a skyscraper can provide substantial noise reduction benefits, creating a more comfortable and productive indoor environment for occupants.
3. Structural integrity
In the design of skyscrapers, structural integrity is paramount to ensure the safety and stability of the building. The absence of windows in a skyscraper can have significant implications for its structural integrity, offering both advantages and potential challenges.
- Enhanced lateral stability: Windows can create weak points in the building’s structure, particularly in resisting lateral forces such as wind and seismic loads. By eliminating windows, the building’s exterior walls become more continuous and better able to withstand lateral forces.
- Reduced stress concentrations: Windows introduce stress concentrations around their openings, which can increase the risk of structural failure. The absence of windows eliminates these stress concentrations, making the building’s structure more uniform and less susceptible to failure.
- Improved load distribution: Without windows, the building’s exterior walls can be designed to carry more of the load, reducing the reliance on internal columns and beams. This can lead to a more efficient and robust structural system.
- Simplified construction: The absence of windows simplifies the construction process, as there is no need to frame and install windows, which can reduce construction time and costs.
Overall, the elimination of windows in a skyscraper can enhance its structural integrity by increasing lateral stability, reducing stress concentrations, improving load distribution, and simplifying construction. However, careful consideration must be given to the potential challenges, such as the need for alternative means of natural light and ventilation.
4. Artificial lighting
In a skyscraper with no windows, the absence of natural light necessitates the exclusive use of artificial lighting systems to illuminate interior spaces. This reliance on artificial lighting has several implications for the design, operation, and occupant experience of the building.
Design considerations: The lack of natural light requires careful planning and design of the artificial lighting system to ensure adequate illumination levels and visual comfort for occupants. Architects and lighting designers must consider factors such as light distribution, glare control, and energy efficiency when selecting and positioning lighting fixtures.
Operational costs: Artificial lighting systems consume
a significant amount of energy, which can contribute to the operating costs of a skyscraper. The choice of energy-efficient lighting technologies and control systems can help to minimize energy consumption and reduce operating expenses.
Occupant experience: The quality of artificial lighting can have a significant impact on the well-being and productivity of occupants. Factors such as light intensity, color temperature, and flicker can affect mood, alertness, and visual performance. Human-centric lighting design approaches aim to create lighting environments that support the circadian rhythm and enhance occupant comfort.
Overall, the exclusive reliance on artificial lighting in a skyscraper with no windows presents both design challenges and opportunities. Careful planning, energy-efficient technologies, and human-centric lighting design are essential to create interior spaces that are well-lit, comfortable, and conducive to occupant well-being and productivity.
5. Ventilation
In a skyscraper with no windows, the absence of natural ventilation necessitates the installation of mechanical ventilation systems to maintain acceptable indoor air quality. These systems are designed to circulate and exchange the air within the building, removing stale air and introducing fresh air from the outside.
Proper ventilation is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps to remove pollutants and contaminants from the air, such as carbon dioxide, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter. These pollutants can accumulate in enclosed spaces and pose health risks to occupants. Secondly, ventilation provides fresh air, which is essential for human health and well-being. Fresh air contains oxygen, which is necessary for cellular respiration, and it helps to remove odors and create a more comfortable indoor environment.
The design and operation of mechanical ventilation systems in a skyscraper with no windows require careful consideration. The system must be capable of providing adequate ventilation rates to maintain acceptable air quality throughout the building, even in areas with high occupancy or high levels of pollutants. Energy efficiency is also an important factor, as mechanical ventilation systems can consume a significant amount of energy.
Overall, mechanical ventilation systems play a critical role in maintaining indoor air quality in skyscrapers with no windows. Proper design, installation, and maintenance of these systems are essential to ensure the health and well-being of occupants.
6. Emergency egress
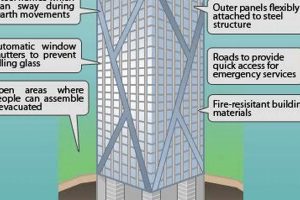
In a skyscraper with no windows, the lack of traditional escape routes poses unique challenges for emergency egress. Careful planning and innovative solutions are required to ensure the safe evacuation of occupants in the event of a fire or other emergency.
- Designated escape routes: In the absence of windows, alternative escape routes must be clearly designated and well-lit. These routes may include enclosed stairwells, fire escapes, or refuge areas.
- Emergency lighting and signage: Emergency lighting and signage are essential to guide occupants to the designated escape routes in low-visibility conditions, such as during a power outage or smoke-filled environment.
- Communication systems: Robust communication systems are crucial for providing timely evacuation instructions and updates to occupants. These systems may include public address systems, intercoms, or mobile phone applications.
- Evacuation drills: Regular evacuation drills are essential for familiarizing occupants with the designated escape routes and procedures. These drills help to ensure that occupants can evacuate the building quickly and safely in the event of an emergency.
By carefully planning emergency egress procedures and implementing appropriate safety measures, it is possible to mitigate the risks associated with the lack of windows in a skyscraper and ensure the safety of occupants in the event of an emergency.
7. Psychological impact
In skyscrapers with no windows, the absence of natural light and views can have a significant impact on the psychological well-being of occupants. Natural light has been shown to regulate the body’s circadian rhythm, which affects sleep-wake cycles, hormone production, and overall mood. Studies have demonstrated that people who work or live in environments with limited natural light may experience increased levels of stress, anxiety, and depression.
The lack of views can also contribute to a sense of isolation and detachment from the outside world. In traditional buildings with windows, occupants can connect with the outdoors and experience changing weather patterns, natural landscapes, and urban environments. This connection to the external environment can provide psychological benefits, such as reducing stress, improving mood, and fostering a sense of well-being.
In skyscrapers with no windows, it is essential to consider the psychological impact of the lack of natural light and views and implement design strategies to mitigate these effects. This may include providing access to outdoor spaces, such as balconies or rooftop gardens, incorporating skylights or light wells to introduce natural light into interior spaces, and using artificial lighting systems that mimic the qualities of natural light.
8. Architectural innovation
The concept of a skyscraper with no windows challenges conventional architectural design norms and opens up new avenues for innovation. By eliminating windows, architects can explore novel structural systems, energy-efficient building envelopes, and alternative approaches to natural light and ventilation.
- Structural innovation
Windowless skyscrapers necessitate innovative structural solutions to maintain stability and withstand lateral forces such as wind and seismic loads. This has led to the development of reinforced concrete cores, diagrid structures, and composite materials that provide both strength and aesthetic appeal. - Energy efficiency
The absence of windows reduces heat loss and gain, significantly improving the energy efficiency of windowless skyscrapers. This has prompted architects to explore advanced building envelope systems that incorporate high-performance insulation, airtight construction, and renewable energy sources. - Alternative natural light sources
To compensate for the lack of natural light, architects are experimenting with innovative ways to introduce natural light into interior spaces. This includes the use of skylights, light wells, and reflective surfaces to redirect and distribute daylight throughout the building. - Mechanical ventilation systems
In the absence of windows, mechanical ventilation systems are essential for maintaining indoor air quality. Architects a
re integrating advanced HVAC systems that provide efficient and effective ventilation, ensuring a healthy and comfortable indoor environment for occupants.
The exploration of new possibilities in windowless skyscraper design pushes the boundaries of architectural innovation. These innovative approaches not only address the challenges posed by the absence of windows but also create opportunities for sustainable, energy-efficient, and visually striking buildings that redefine the urban landscape.
FAQs on Skyscrapers with No Windows
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions surrounding the concept of skyscrapers with no windows, providing informative answers based on architectural and engineering principles.
Question 1: Are skyscrapers with no windows even feasible?
Yes, skyscrapers with no windows are feasible from an architectural and engineering standpoint. While no such structures currently exist, the concept has been explored in architectural discourse and science fiction, with proponents suggesting potential benefits in energy efficiency, noise reduction, and structural integrity.
Question 2: How can a skyscraper without windows maintain acceptable indoor air quality?
Skyscrapers with no windows require mechanical ventilation systems to maintain indoor air quality. These systems circulate and exchange the air within the building, removing stale air and introducing fresh air from the outside. Proper design and maintenance of these systems are crucial to ensure the health and well-being of occupants.
Question 3: How do occupants evacuate a skyscraper with no windows in an emergency?
In the absence of windows, alternative escape routes must be carefully planned and clearly designated. These routes may include enclosed stairwells, fire escapes, or refuge areas. Emergency lighting and signage are essential to guide occupants to safety, and regular evacuation drills are crucial for familiarizing occupants with the procedures.
Question 4: Wouldn’t the lack of natural light and views negatively impact occupants’ well-being?
The absence of natural light and views can indeed have an impact on occupants’ well-being. Architects consider these factors and explore innovative solutions, such as access to outdoor spaces, skylights, and artificial lighting systems that mimic the qualities of natural light, to mitigate these effects.
Question 5: Are windowless skyscrapers more energy-efficient than traditional skyscrapers?
Yes, eliminating windows can significantly improve energy efficiency. Windows are a major source of heat loss and gain, so their absence reduces the energy consumption for heating and cooling. Advanced building envelope systems with high-performance insulation and airtight construction further enhance energy efficiency.
Question 6: Do windowless skyscrapers offer any advantages in terms of structural integrity?
The absence of windows can potentially enhance structural integrity. Windows create weak points in the building’s structure, particularly in resisting lateral forces such as wind and seismic loads. By eliminating windows, the building’s exterior walls become more continuous and better able to withstand these forces.
Overall, while windowless skyscrapers present unique challenges, they also offer opportunities for innovative architectural and engineering solutions that prioritize sustainability, energy efficiency, and occupant well-being.
Transition to the next article section…
Tips for Designing and Constructing Skyscrapers with No Windows
Incorporating the concept of windowless skyscrapers requires careful planning and innovative approaches. Here are a few tips to consider for successful implementation:
Tip 1: Prioritize Energy Efficiency
The absence of windows presents an opportunity to significantly enhance energy efficiency. Utilize advanced building envelope systems featuring high-performance insulation and airtight construction to minimize heat loss and gain. Integrate renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, to reduce reliance on external energy sources.
Tip 2: Implement Mechanical Ventilation Systems
To maintain acceptable indoor air quality, install efficient mechanical ventilation systems. These systems should be designed to circulate and exchange the air within the building, removing stale air and introducing fresh air from the outside. Regular maintenance and monitoring are crucial to ensure optimal performance.
Tip 3: Plan for Emergency Egress
In the absence of windows, alternative escape routes must be carefully planned and clearly designated. Consider enclosed stairwells, fire escapes, and refuge areas as alternative means of egress. Provide emergency lighting and signage to guide occupants to safety, and conduct regular evacuation drills to familiarize occupants with the procedures.
Tip 4: Mitigate Psychological Impacts
The lack of natural light and views can potentially impact occupants’ well-being. Provide access to outdoor spaces, such as balconies or rooftop gardens, to connect occupants with the external environment. Incorporate skylights or light wells to introduce natural light into interior spaces, and explore artificial lighting systems that mimic the qualities of natural light to enhance occupant comfort.
Tip 5: Embrace Architectural Innovation
Windowless skyscrapers challenge conventional architectural design norms, presenting opportunities for innovation. Explore novel structural systems, such as reinforced concrete cores and diagrid structures, to maintain stability and withstand lateral forces. Experiment with alternative approaches to natural light and ventilation, pushing the boundaries of architectural design while prioritizing sustainability and occupant well-being.
Summary: By embracing these tips, architects and engineers can design and construct windowless skyscrapers that are energy-efficient, safe, and comfortable for occupants. These innovative structures can redefine the urban landscape and contribute to a more sustainable built environment.
Conclusion
The concept of skyscrapers with no windows presents a unique and challenging architectural proposition. While no such structures currently exist, their potential benefits in energy efficiency, noise reduction, and structural integrity have sparked considerable interest and discussion. The exploration of this concept requires careful consideration of alternative approaches to natural light, ventilation, emergency egress, and the psychological impact on occupants.
Successful implementation of windowless skyscrapers demands innovative solutions in architectural design, engineering, and building technologies. By embracing advanced building envelope systems, mechanical ventilation systems, and alternative means of egress, architects and engineers can create windowless skyscrapers that are safe, comfortable, and sustainable. Furthermore, incorporating skylights, light wells, and artificial lighting systems that mimic natural light can mitigate the potential negative effects on occupant well-being.
As we continue to push the boundaries of architectural design, windowless skyscrapers have the potential to redefine the urban landscape and contribute to a more sustainable built environment. They offer a unique opportunity to explore new possibilities in structural engineering, energy efficiency, and occupant comfort, while challenging conventional design norms and inspiring future innovations.